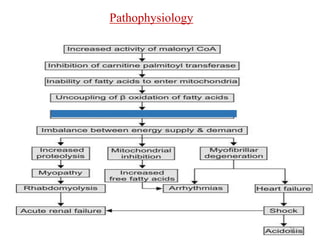
The document provides an extensive overview of propofol and ketamine, detailing their chemical properties, mechanisms of action, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, clinical uses, and side effects. Propofol is commonly used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia, while ketamine offers dissociative anesthesia with analgesic and amnesic properties. Key concerns associated with both agents include side effects from prolonged administration, such as propofol infusion syndrome and various complications related to ketamine's cardiovascular and central nervous system impacts.