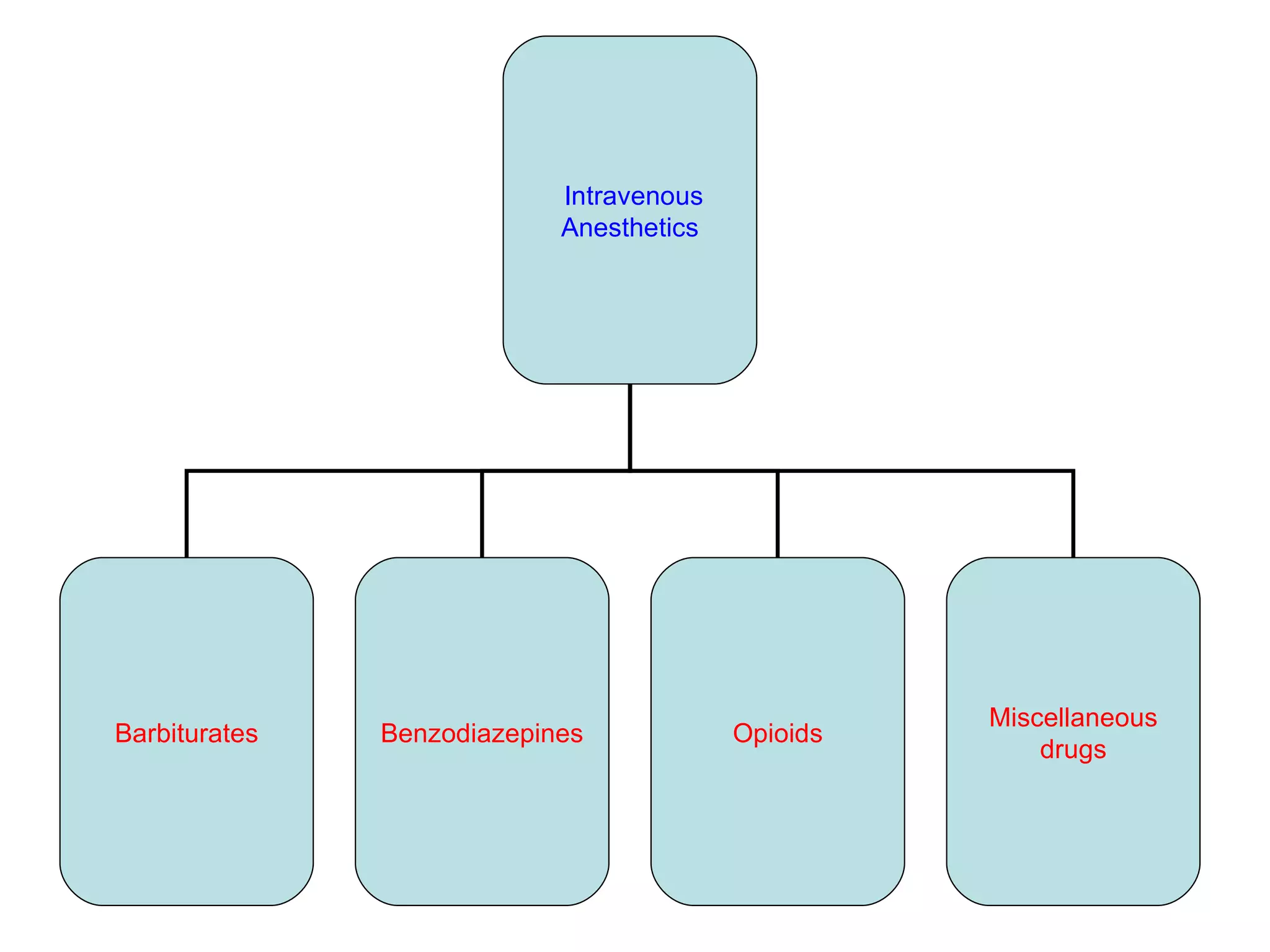
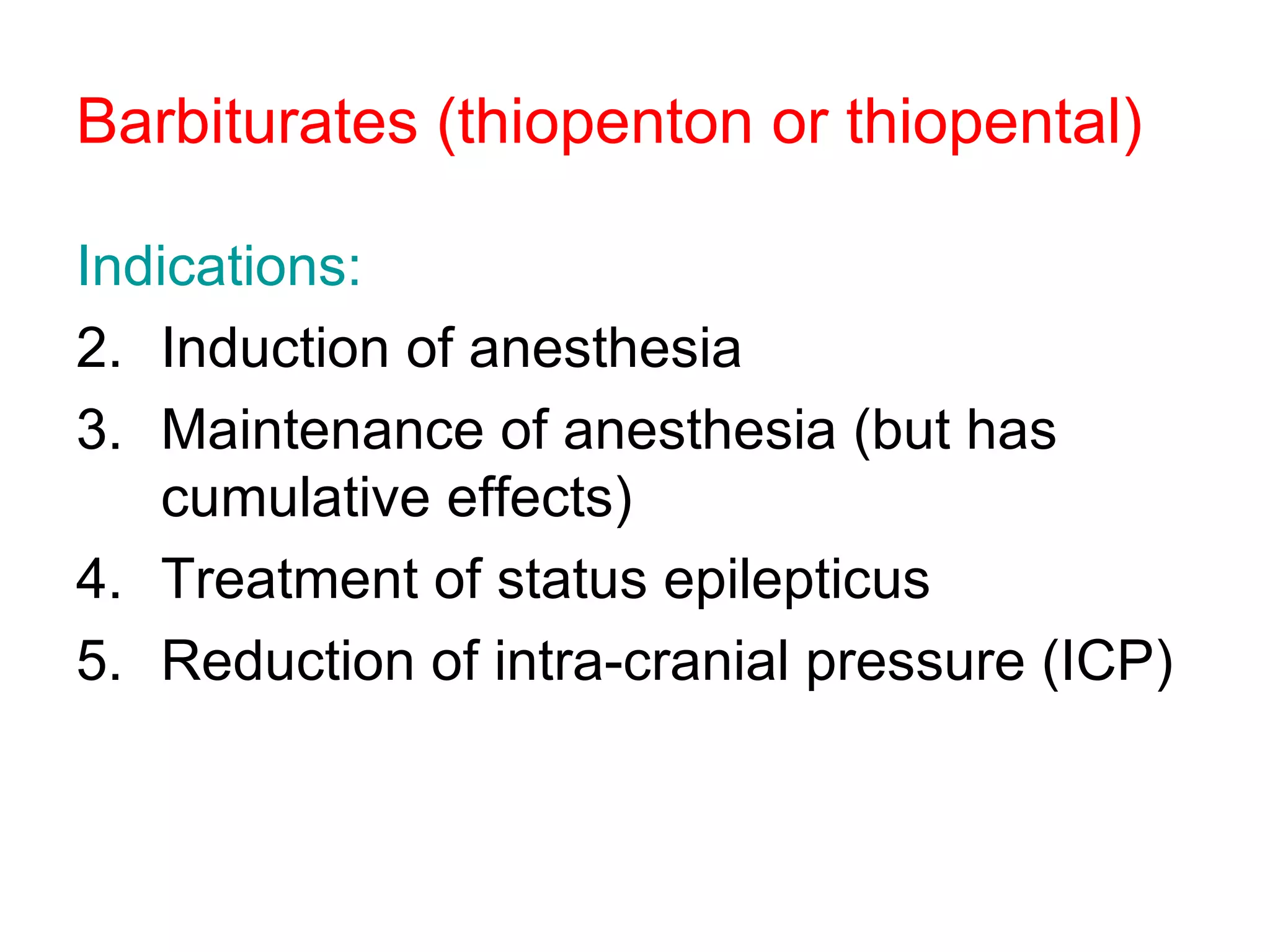
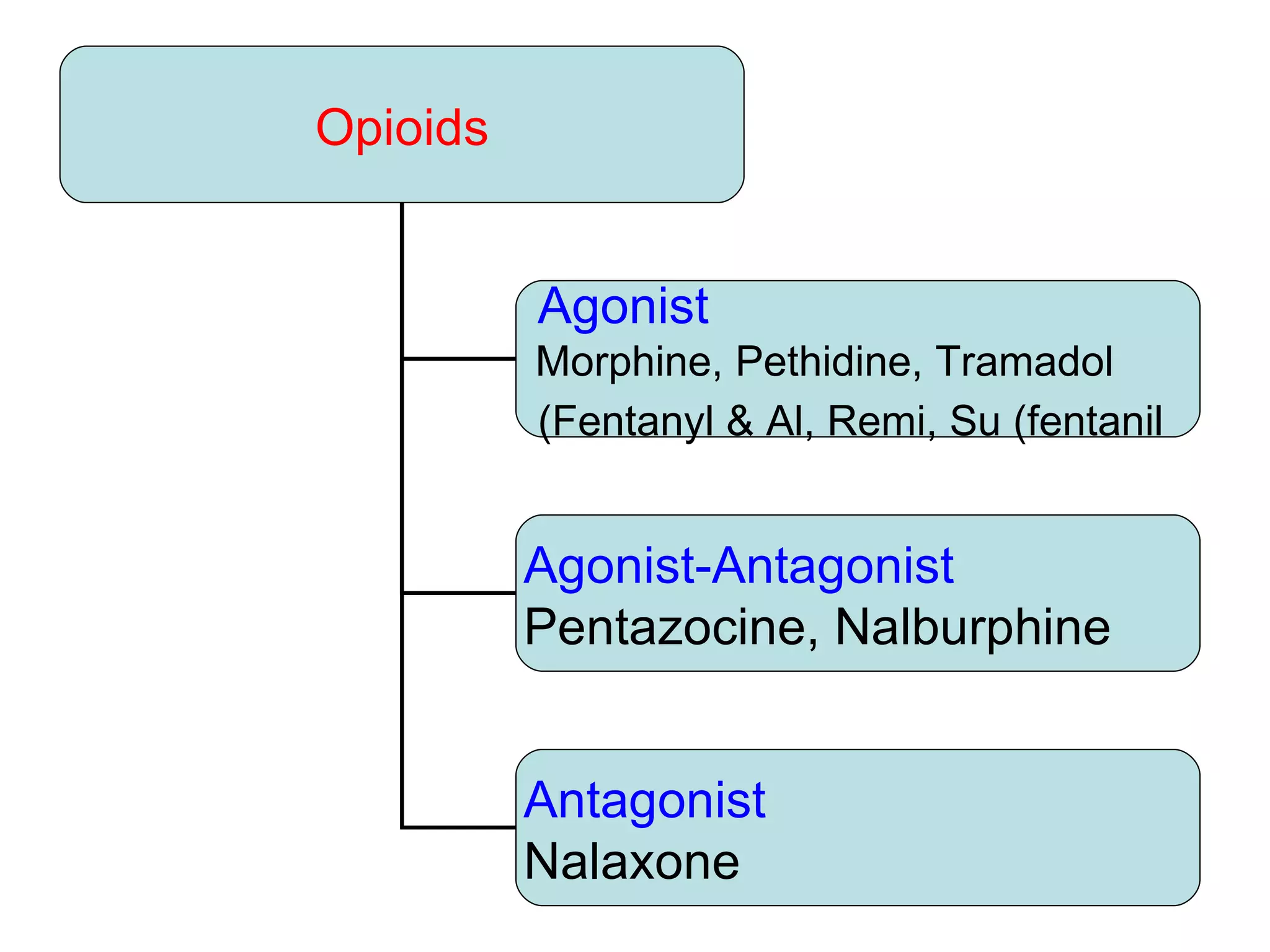
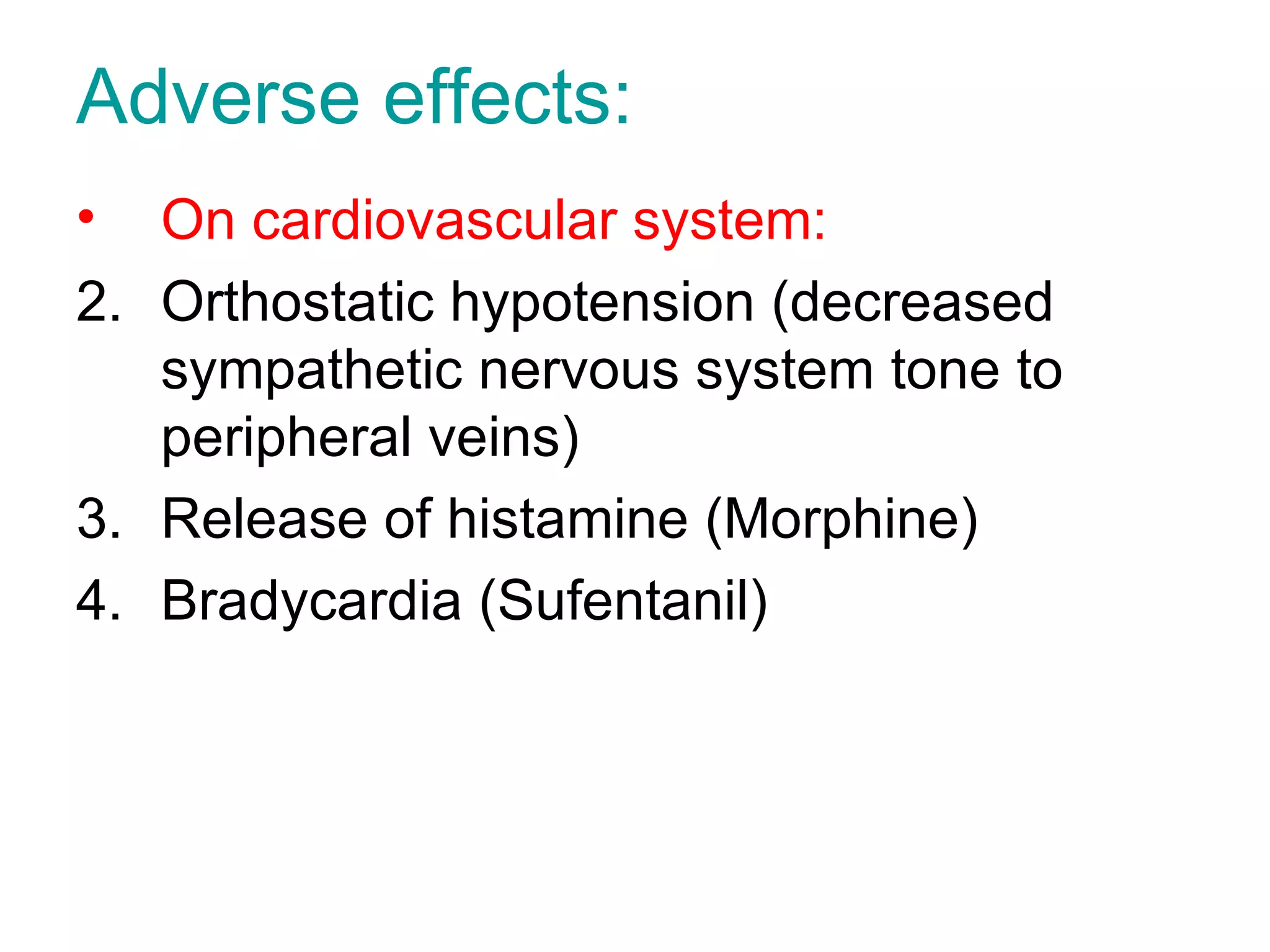
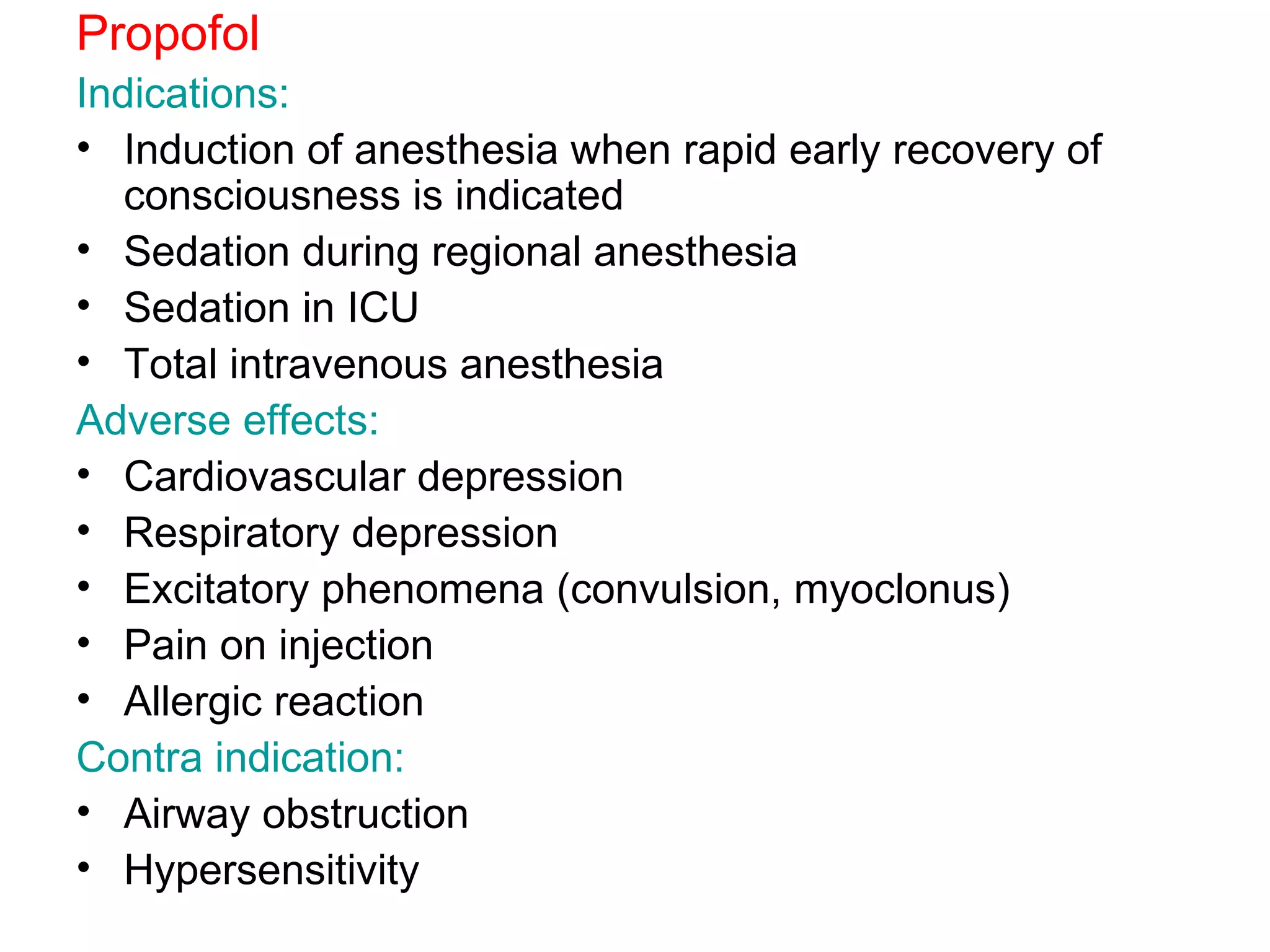
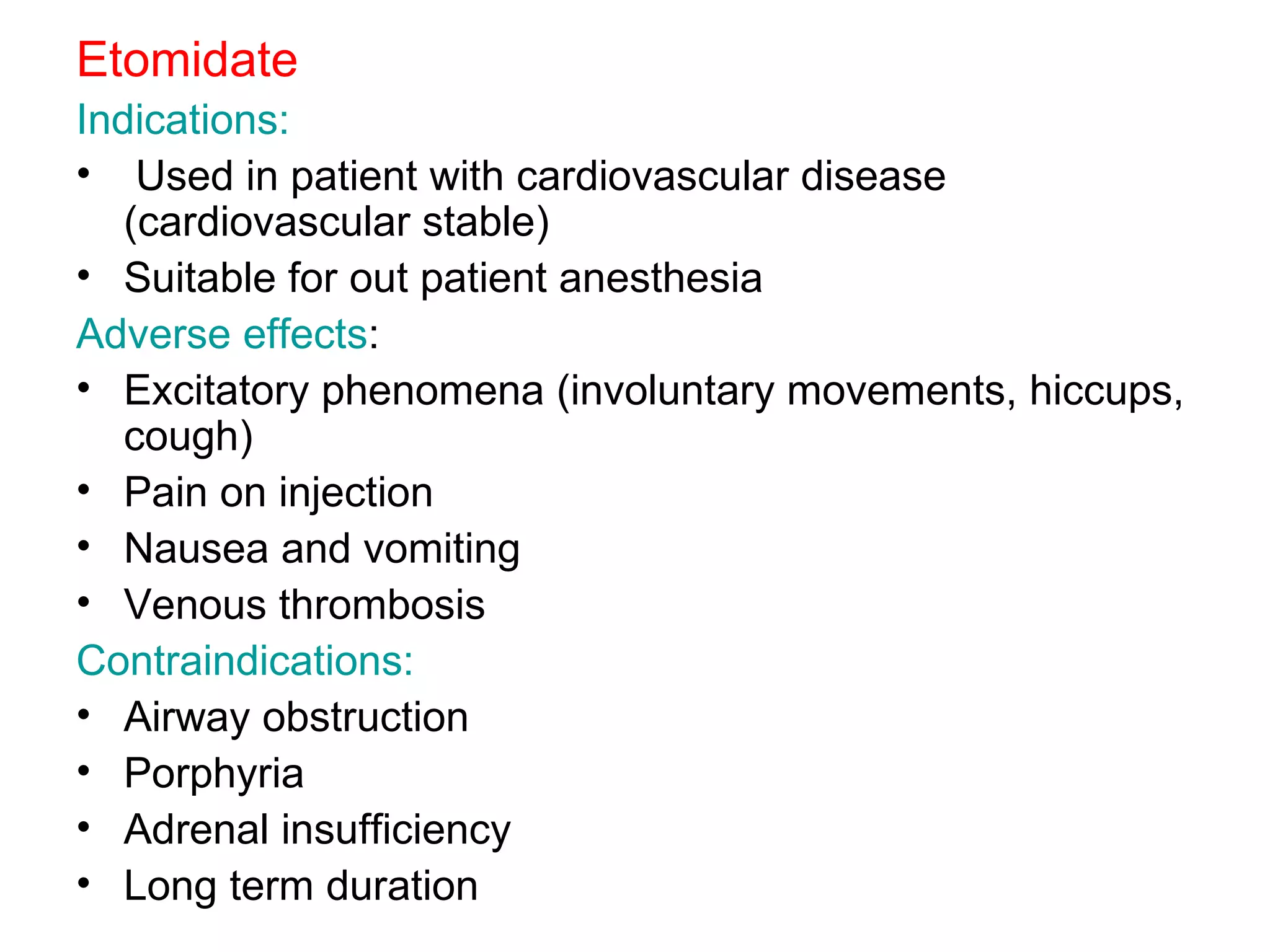
Intravenous anesthetic agents include barbiturates, benzodiazepines, opioids, and miscellaneous drugs. They are used for induction and maintenance of anesthesia, as well as sedation. Barbiturates like thiopental are used for induction but have cumulative effects. Benzodiazepines provide sedation and are used in regional anesthesia and intensive care. Opioids like fentanyl, alfentanil, and remifentanil provide analgesia before and after surgery. They can cause respiratory depression, nausea, and vomiting. Ketamine is used in shocked patients and where equipment is limited due to rapid onset and short duration.