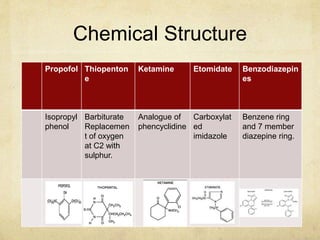
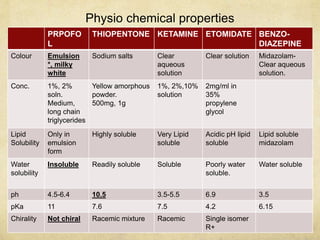
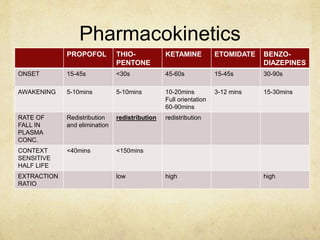
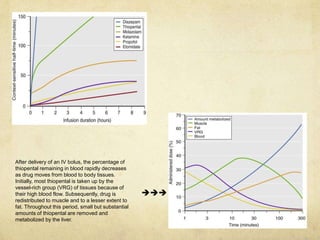
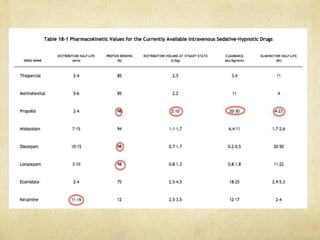
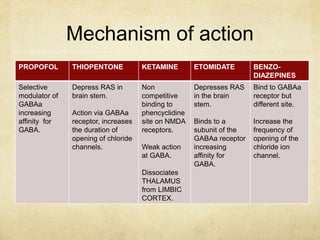
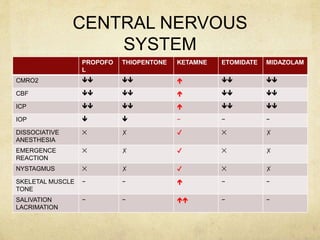
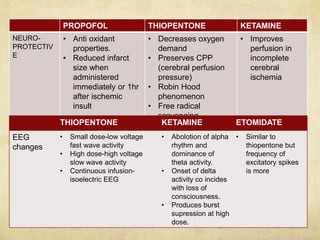
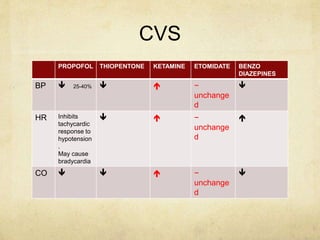
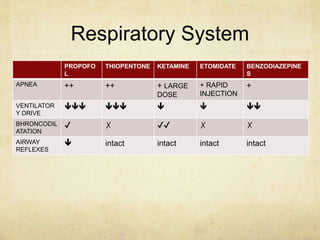
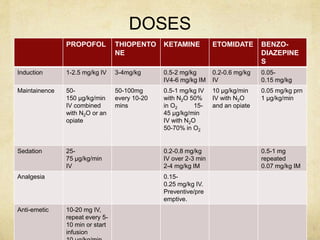
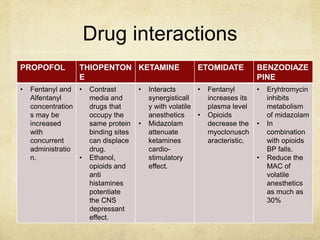
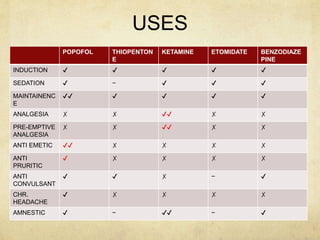
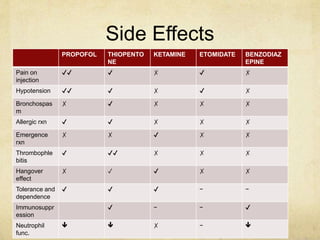
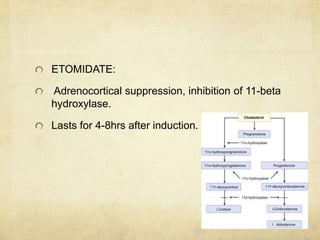
This document provides information on various intravenous anesthetic agents including propofol, thiopentone, ketamine, etomidate, benzodiazepines, and dexmedetomidine. It discusses their chemical structures, pharmacokinetic properties, mechanisms of action, metabolic pathways, uses, doses, and side effects. The agents have different onset and duration times, cardiovascular and respiratory effects, and indications for use in induction, sedation and analgesia. Dexmedetomidine is a highly selective alpha-2 agonist that provides sedation resembling natural sleep while maintaining respiratory drive and hemodynamic stability.