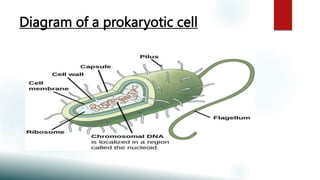
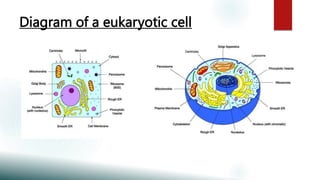
This document provides information about prokaryotes and eukaryotes. It discusses that prokaryotes lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes have a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. The key differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes are that prokaryotes lack a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles, have circular DNA, and are smaller, while eukaryotes have a nuclear membrane and membrane-bound organelles, have multiple rod-shaped chromosomes, and are generally larger and more complex.