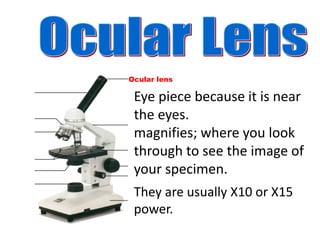
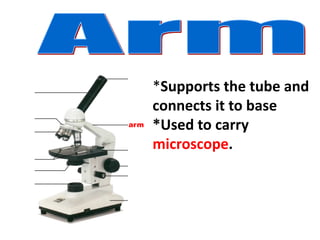
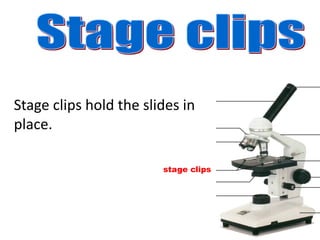
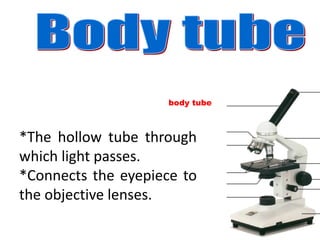
The microscope is an important tool for studying living things. It has different parts that allow the user to view very small specimens magnified. The key parts include the stage to hold samples, objective lenses of different powers to magnify the sample, and an eyepiece or ocular lens for the user to view the magnified image. The document provides details on the functions of each major part and how to properly use and store a microscope.