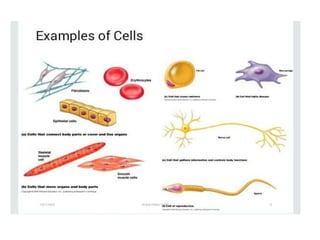
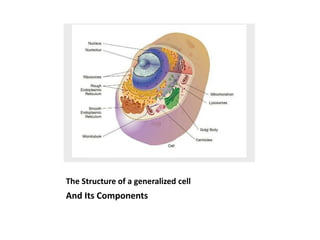
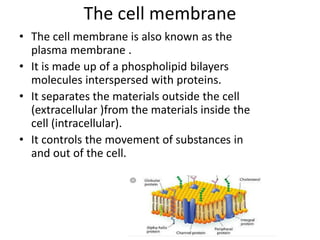
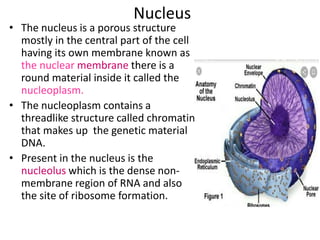
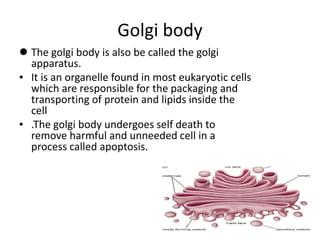
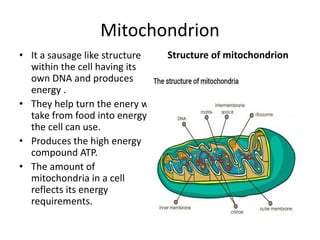
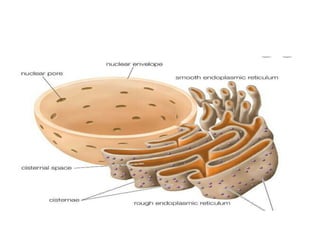
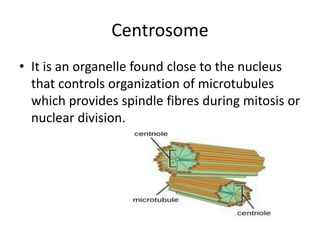
This document summarizes the structure of a generalized cell. It discusses that cells make up organisms and were first discovered by Robert Hooke. The structure of the cell refers to its components that perform essential life processes. A generalized animal cell consists of a cell membrane, nucleus, and cytoplasm. The cell membrane separates intra- and extracellular materials and controls movement of substances in and out of the cell. The nucleus contains genetic material DNA and nucleolus. The cytoplasm is a gel-like fluid containing organelles that perform specific functions. Organelles include ribosomes for protein synthesis, mitochondria for energy production, and the Golgi body for packaging and transporting proteins and lipids.