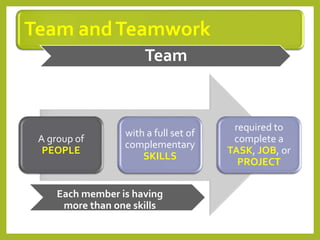
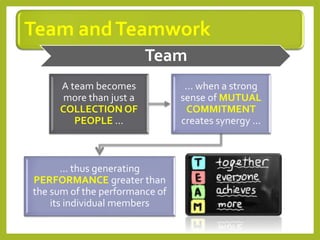
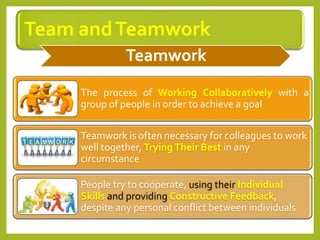
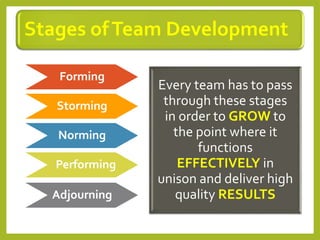
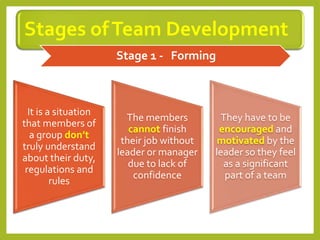
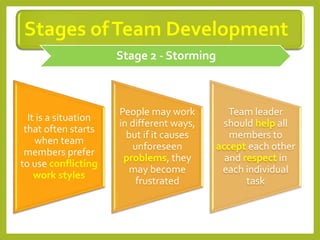
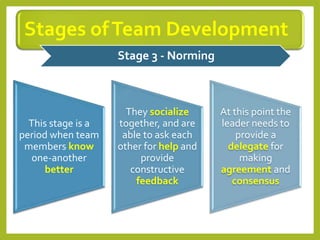
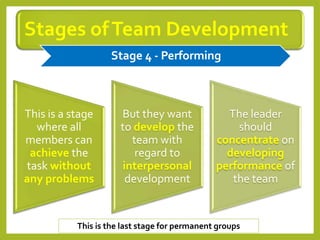
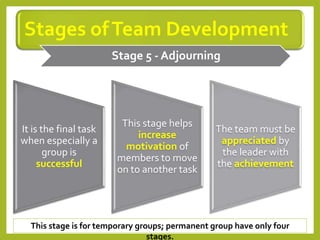
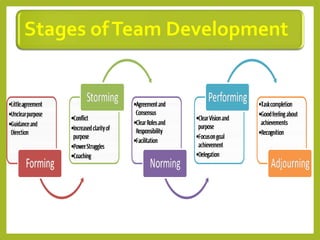
This document provides an overview of project team roles and responsibilities. It discusses the roles of the project manager, project team members, project sponsor, executive sponsor, steering committee members, and project client. The project manager is responsible for the overall project management and leads the project team. Project team members work on assigned tasks. The project sponsor and executive sponsor provide support and approve key decisions. The steering committee provides strategic guidance. The project client represents the needs of the organization for which the project is being conducted.