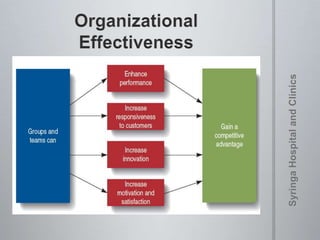
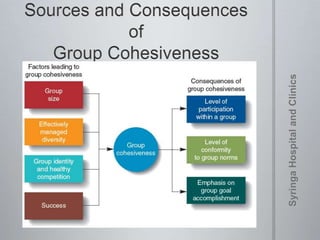
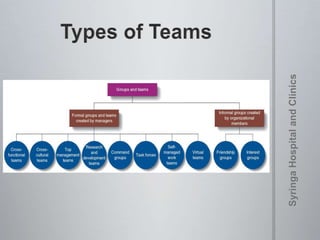
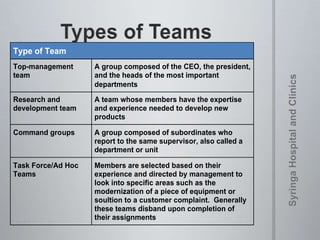
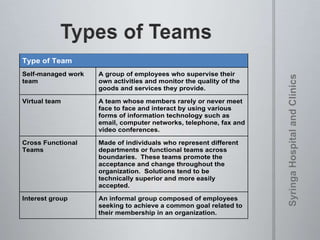
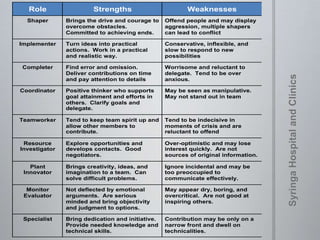
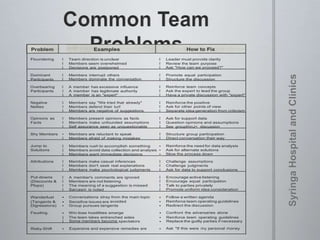
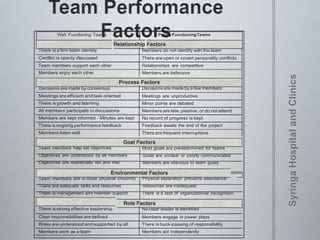
The document provides information on team dynamics and effective team management. It discusses the differences between groups and teams, stages of team development including forming, storming, norming and performing. It also covers topics like diversity in teams, team roles, challenges like social loafing and groupthink, and strategies for effective team leadership. The overall message is that teams require careful management to develop cohesion, establish roles and processes, and maximize performance.