The document outlines a quality management plan for a construction project. It discusses:
- The roles and responsibilities for quality management, including a quality control manager who will oversee inspections and testing.
- A quality management process involving defining requirements, assurance, control, deliverables acceptance, and final acceptance.
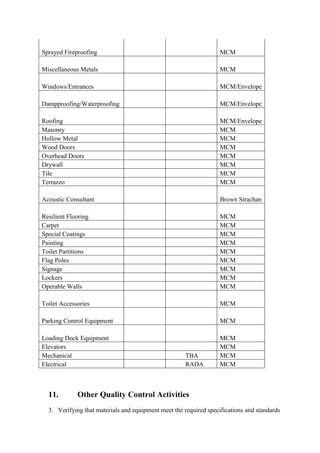
- Tools and techniques used for quality planning, assurance, and control such as audits, reviews, and checklists.
- Key quality assurance activities like reviewing plans, inspecting materials, and monitoring subcontractor work.
The quality control manager will implement the plan, documenting inspections and tests, to help ensure the project meets specifications.