The document discusses various applications of stacks including:
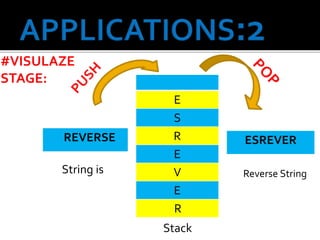
1) Reversing strings by pushing characters onto a stack and popping them off in reverse order.
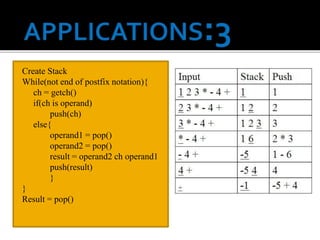
2) Calculator operations using postfix notation and a stack.
3) Recursive functions using a stack to store previous function calls and variables.
4) Determining if a word is a palindrome by pushing characters onto a stack and comparing to the popped off characters.
Code examples are provided for reversing strings, recursive summation, and determining palindromes using stacks.






![#SOURCE CODE:
void push(int *top, element
item)
{
/* add an item to the global
stack */
if (*top >=
MAX_STACK_SIZE-1) {
stack_full( );
return;
}
stack[++*top] = item;
}
Push
element pop(int *top)
{
/* return the top element
from the stack */
if (*top == -1)
return
stack_empty( );
/* returns and error key */
return stack[(*top)--];
}
Pop](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-copy-160404081828/85/Project-of-data-structure-8-320.jpg)


![#define MAX 20
int top = -1;
char stack[MAX];
char pop();
void push(char);
main()
{
char str[20];
int i;
printf(“Enter the string : ” );
gets(str);
for(i=0;i<strlen(str);i++)
push(str[i]);
for(i=0;i<strlen(str);i++)
str[i]=pop();
printf(“Reversed string is : “);
puts(str);
void push(char item){
if(top == (MAX-1))
{
printf(“Stack Overflown”);
return;
}
stack[++top] =item;
}/*End of push()*/
char pop(){
if(top == -1)
{
printf(“Stack Underflown”);
exit(1);
}
return stack[top–];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-copy-160404081828/85/Project-of-data-structure-12-320.jpg)









![Source code:
char stk[50];
int top=-1;
void push(char c){
top++;
stk[top]=c;
}
char pop(){
char c;
c=stk[top];
top–;
return c;
}
void main(){
char in[30],b[30];
int i;
printf(“nn ENTER UR STRINGt”);
gets(in);
for(i=0;in[i]!=‘’;i++){
push(in[i]);
}
i=0;
while(top!=-1){
b[i]=pop();
i++;
}
b[i]=‘’;
if(strcmp(in,b)==0){
printf (“n STRING is
PALLINDROME”);
}
else{
printf (“n STRING IS NOT
PALLNDROME”);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/project-copy-160404081828/85/Project-of-data-structure-23-320.jpg)
