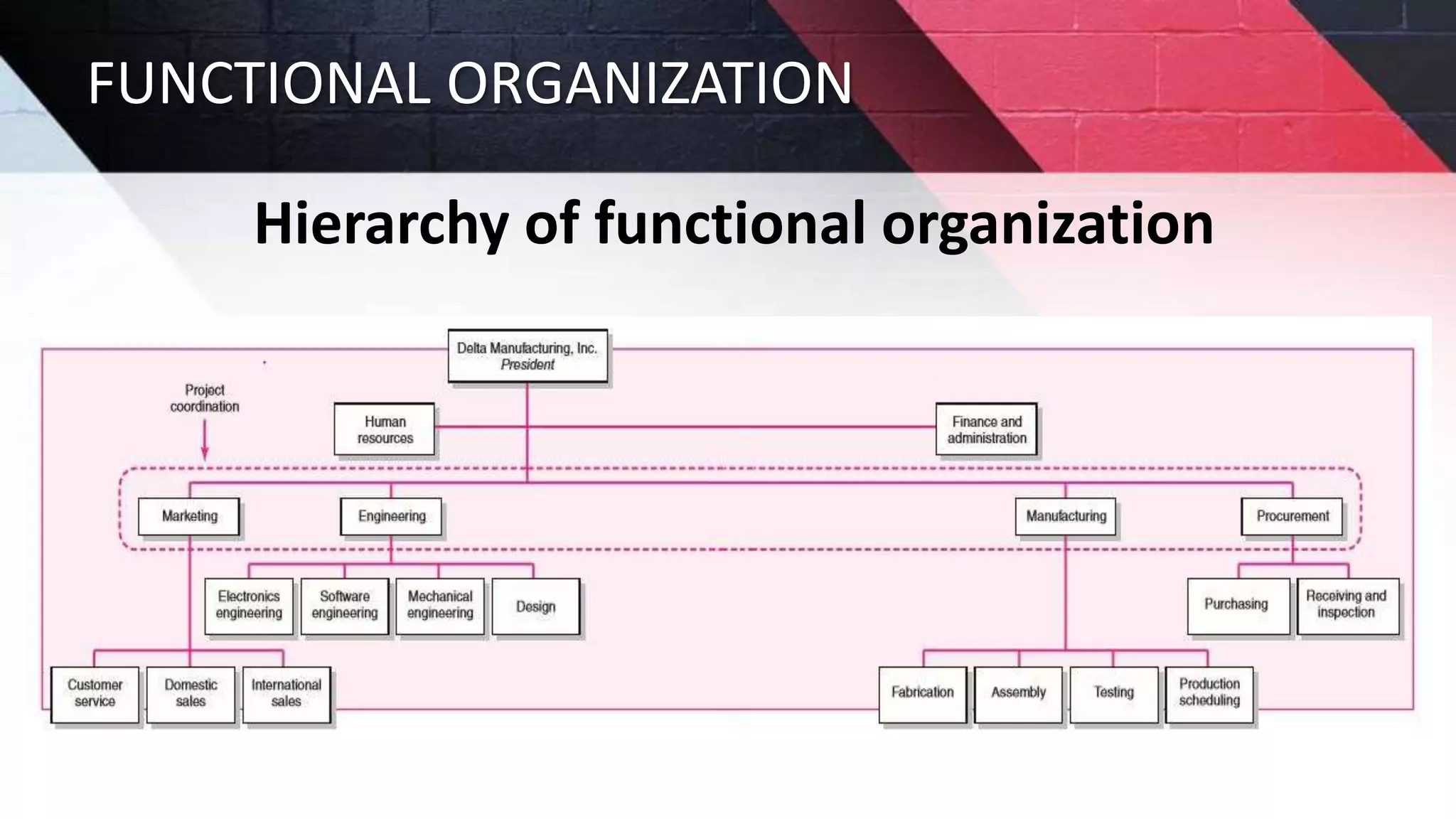
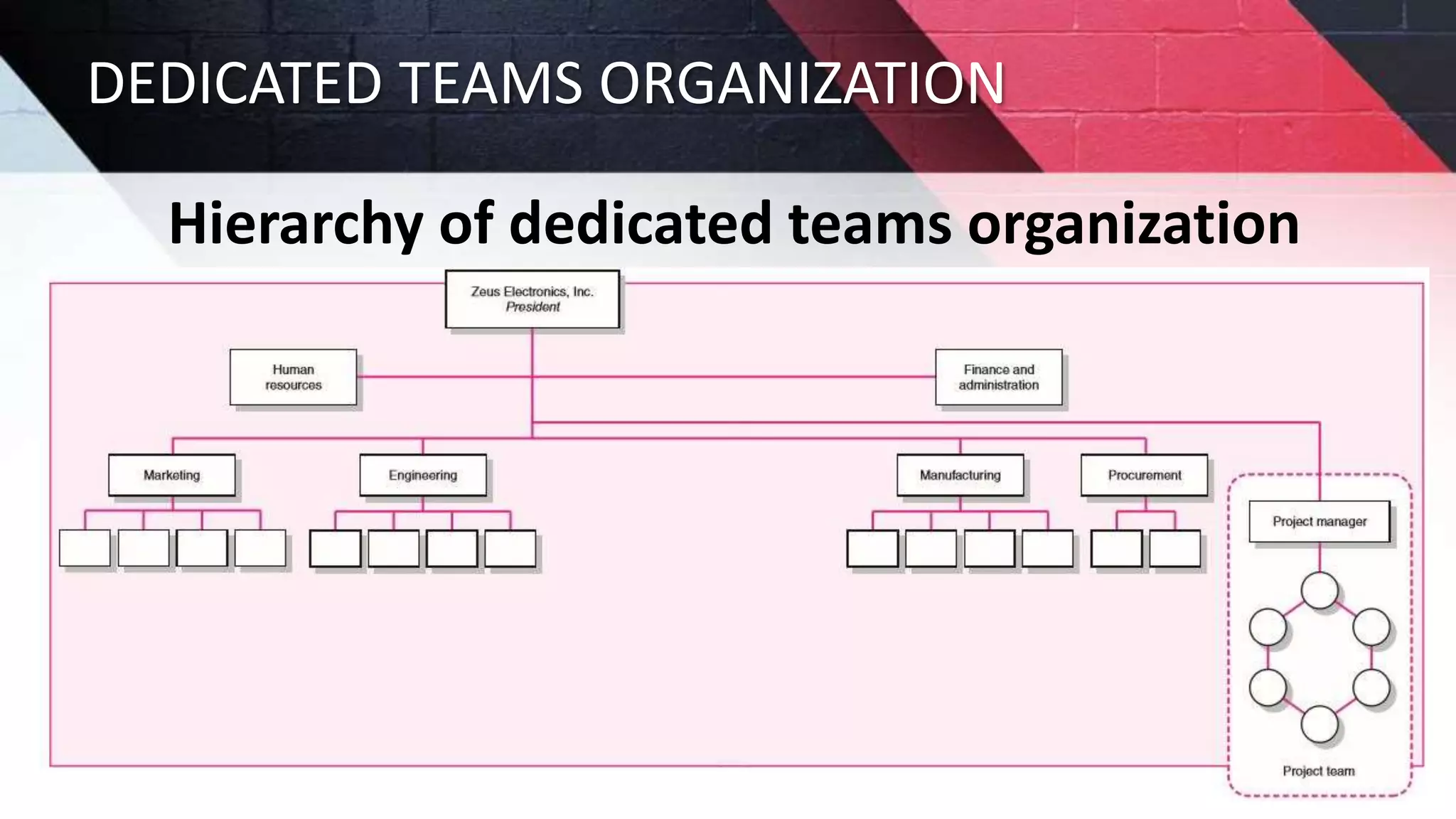
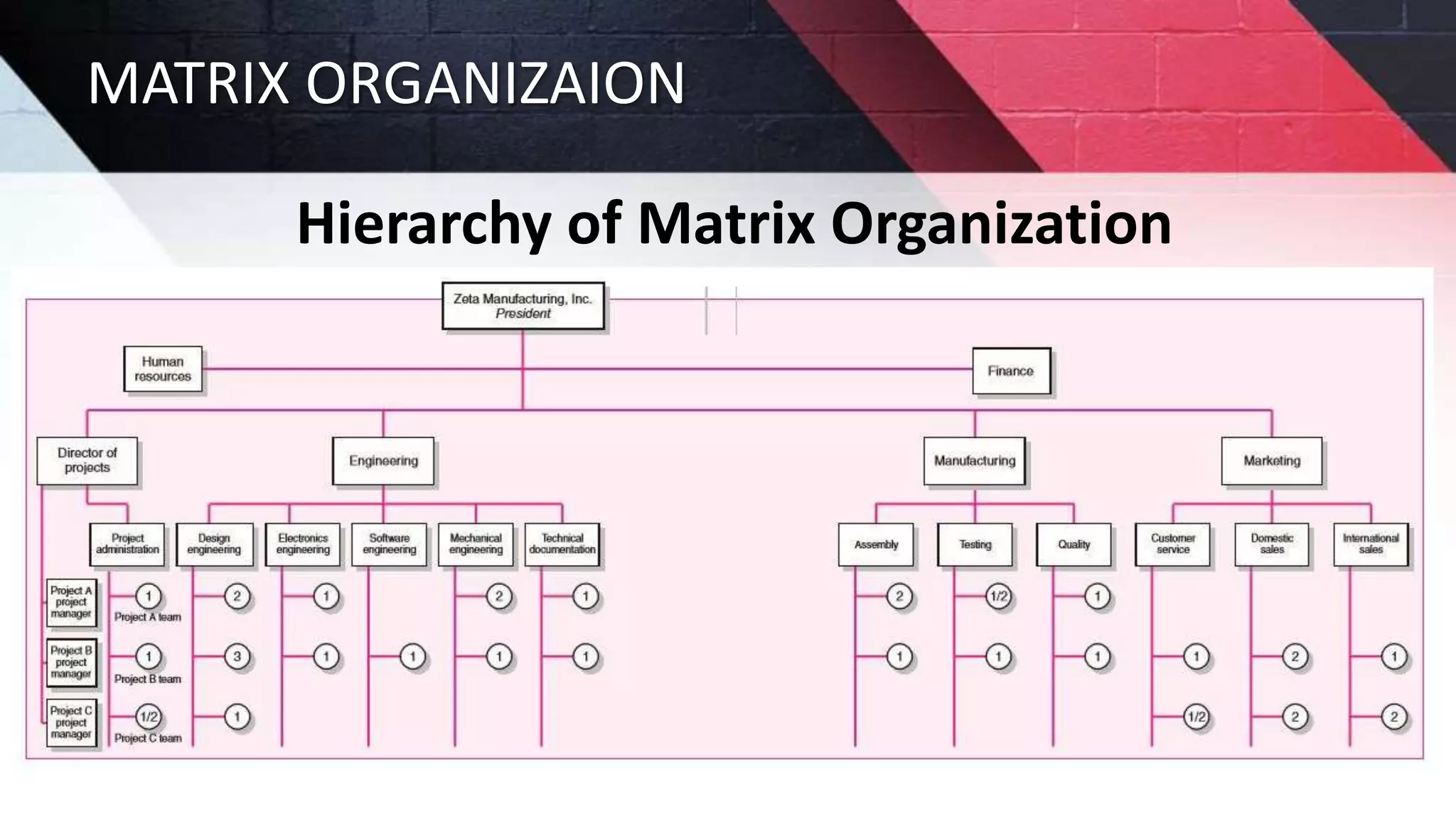
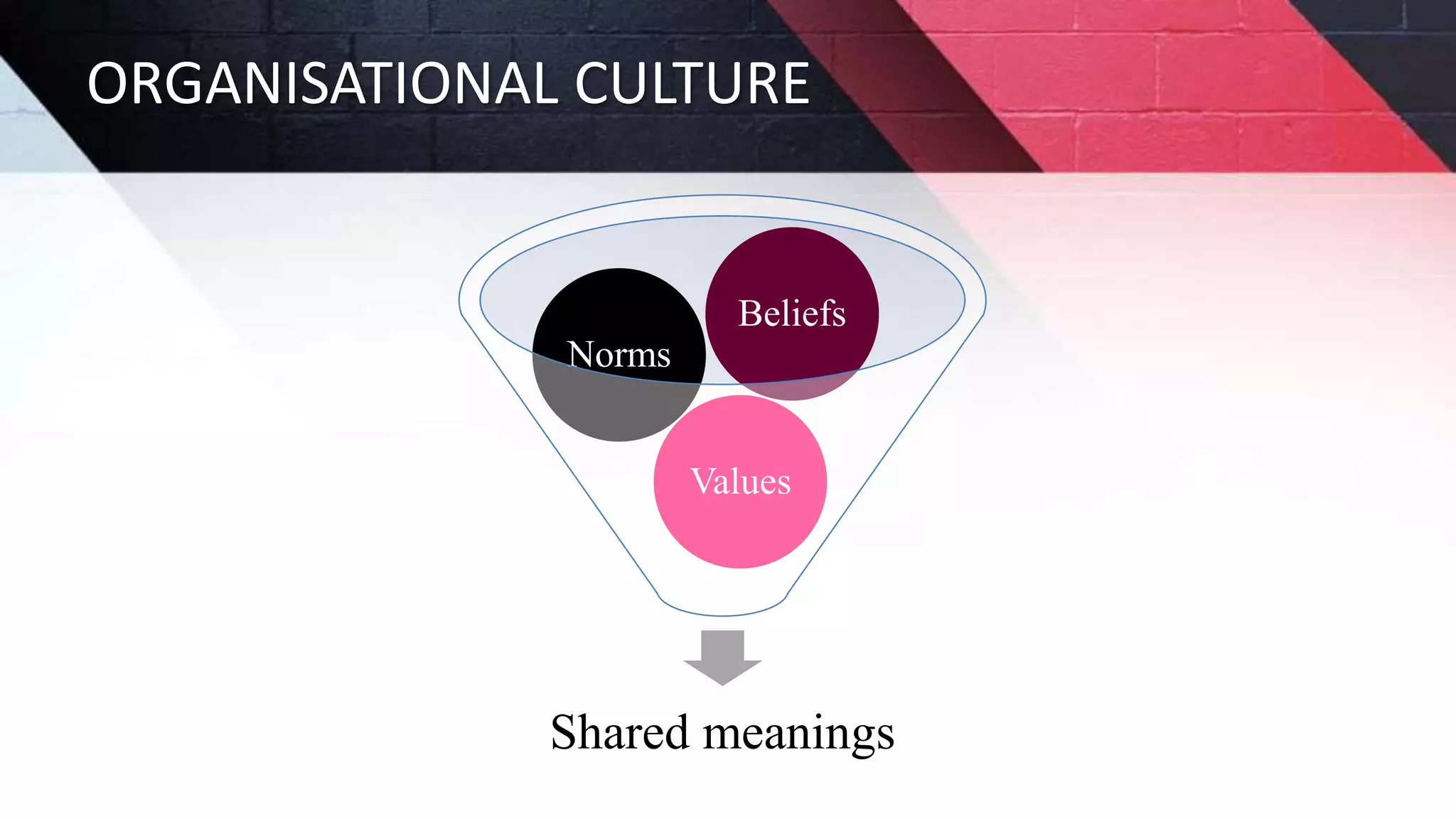
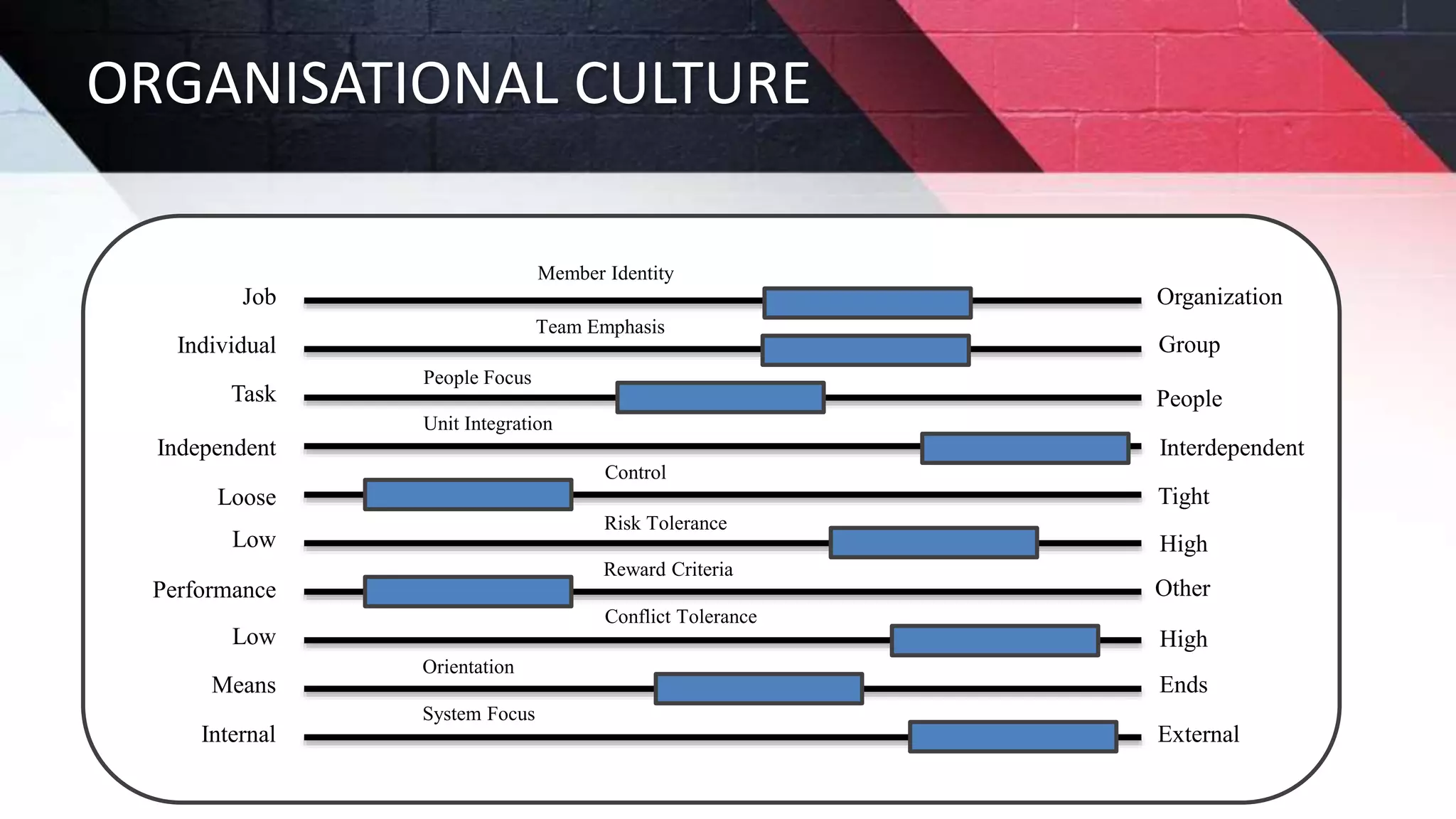
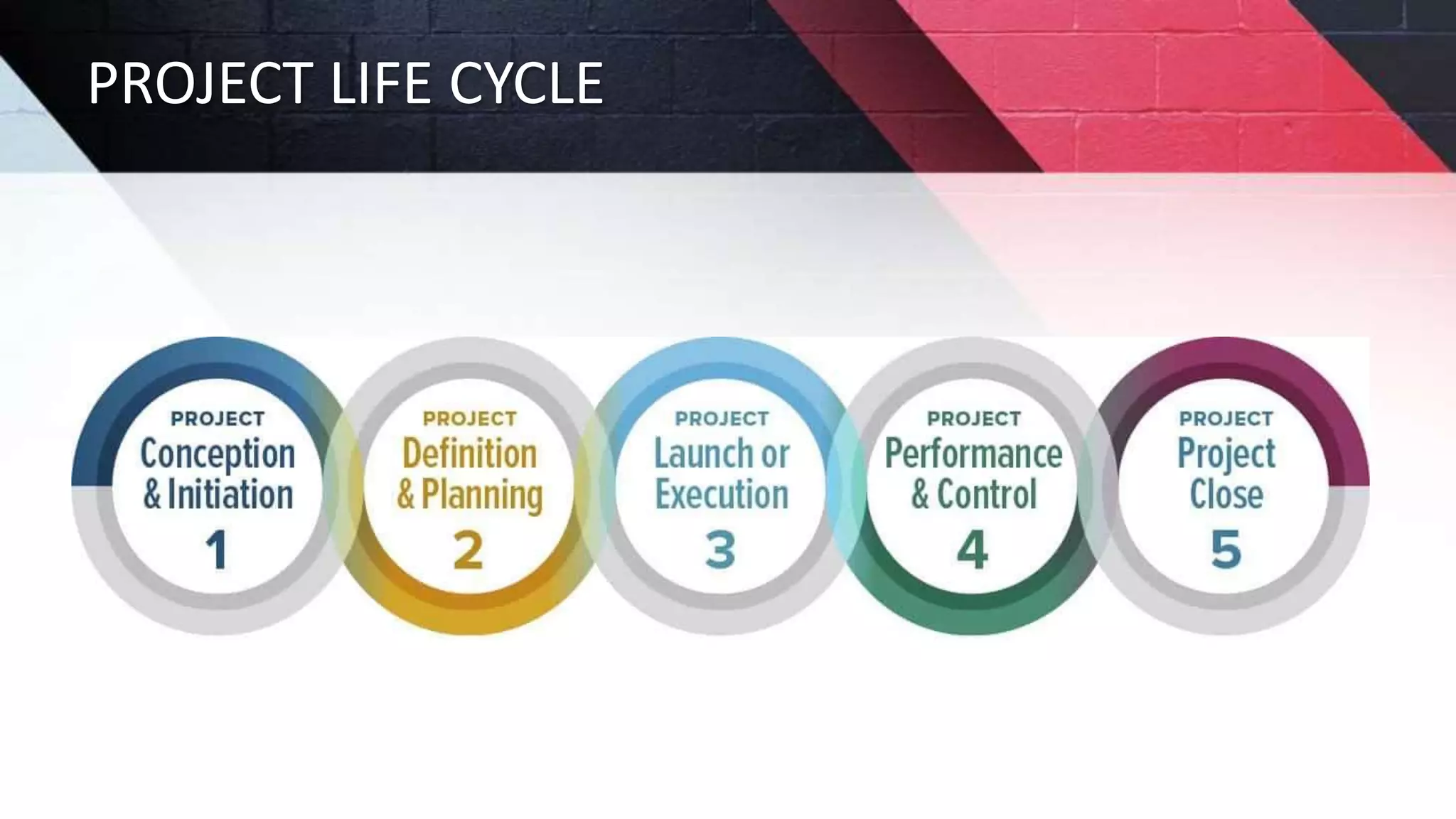
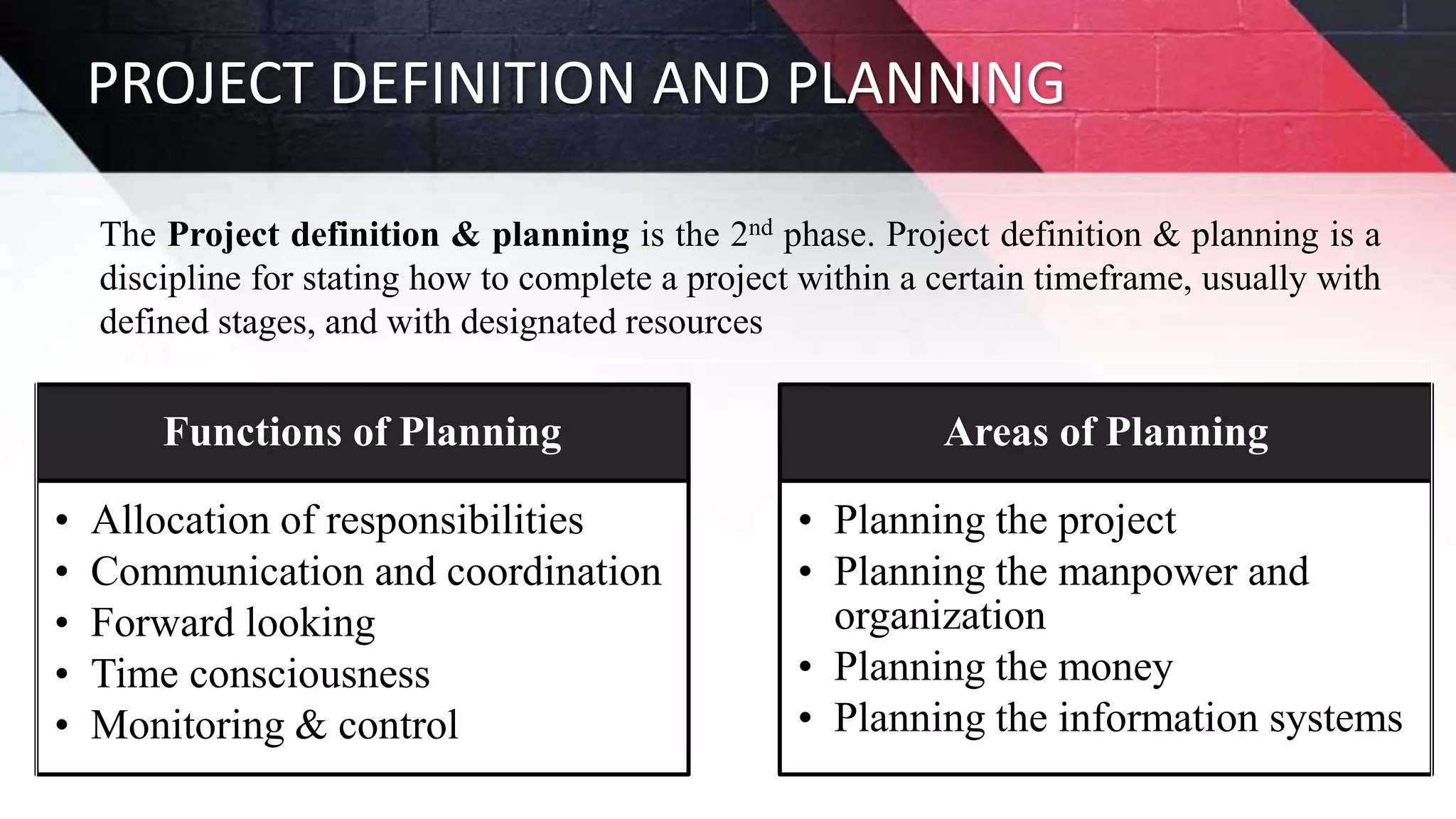
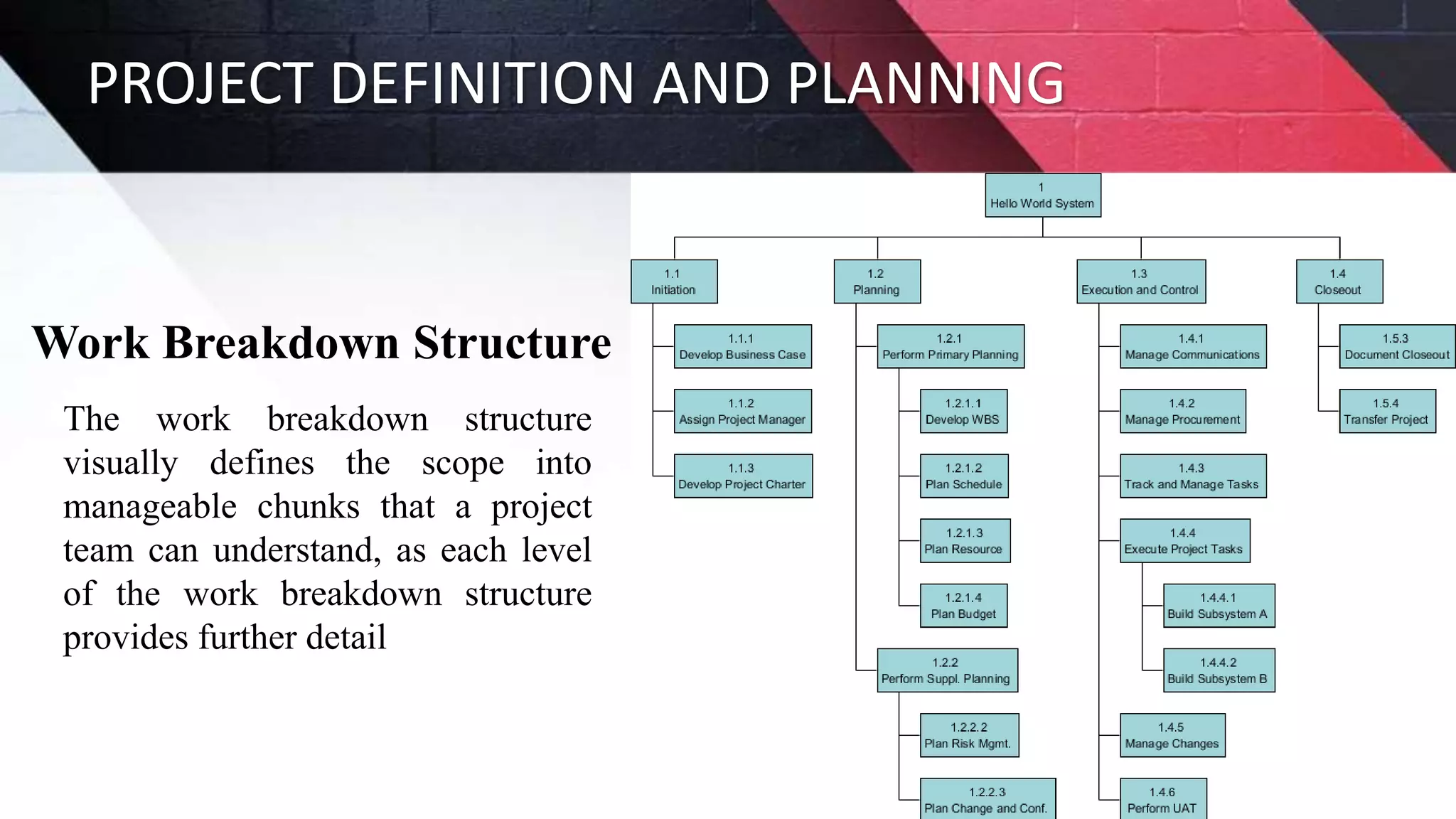
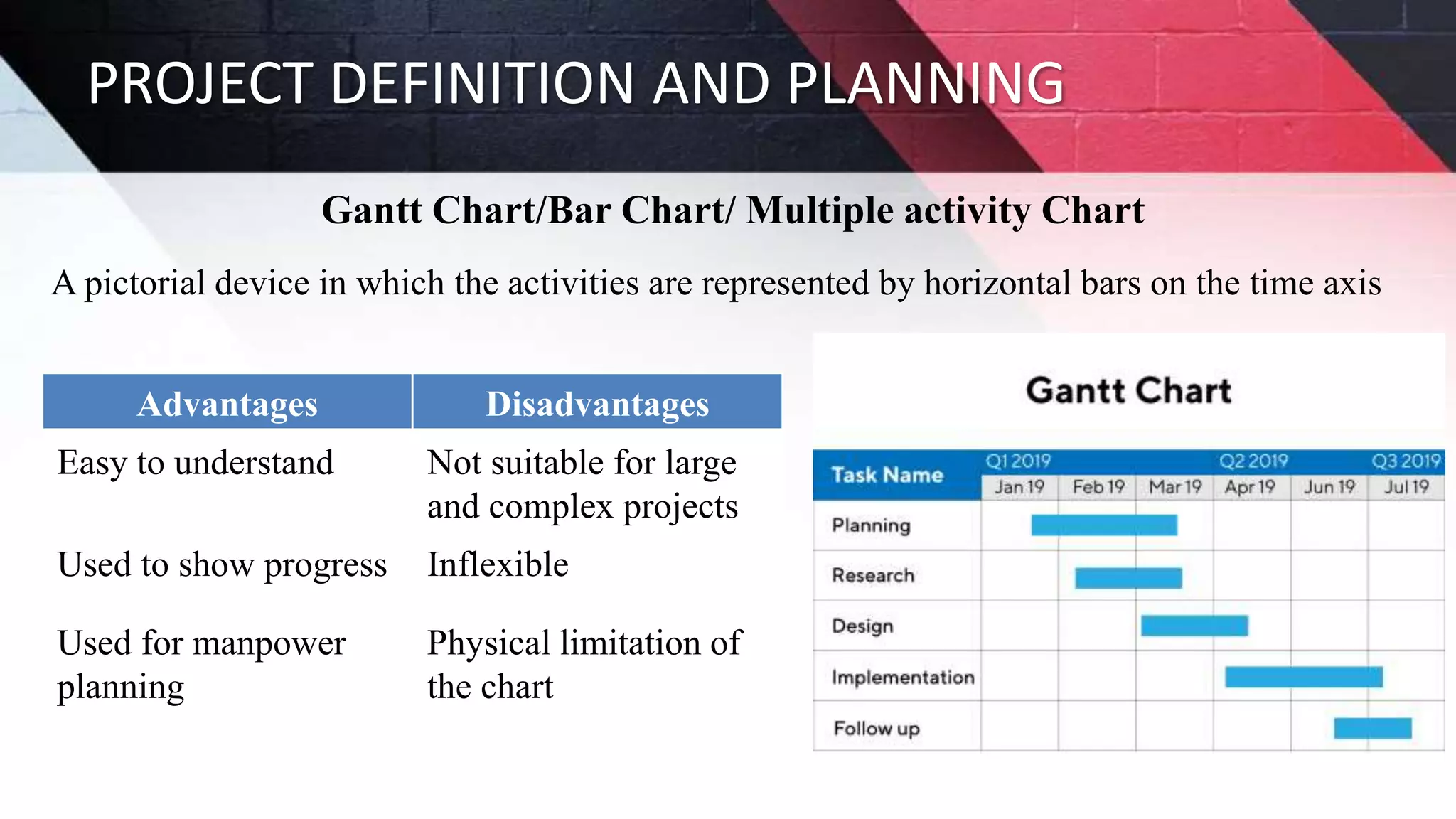
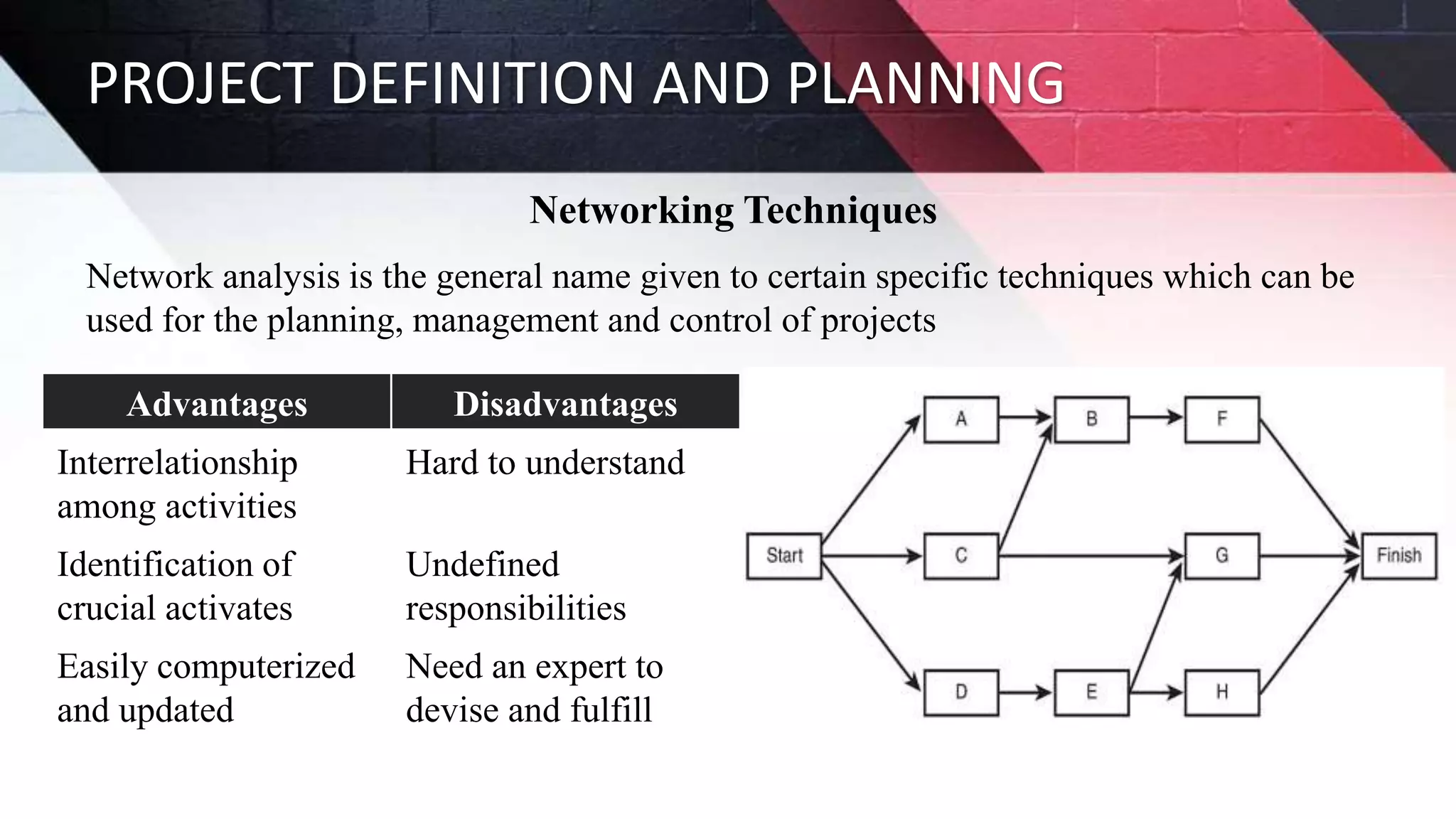
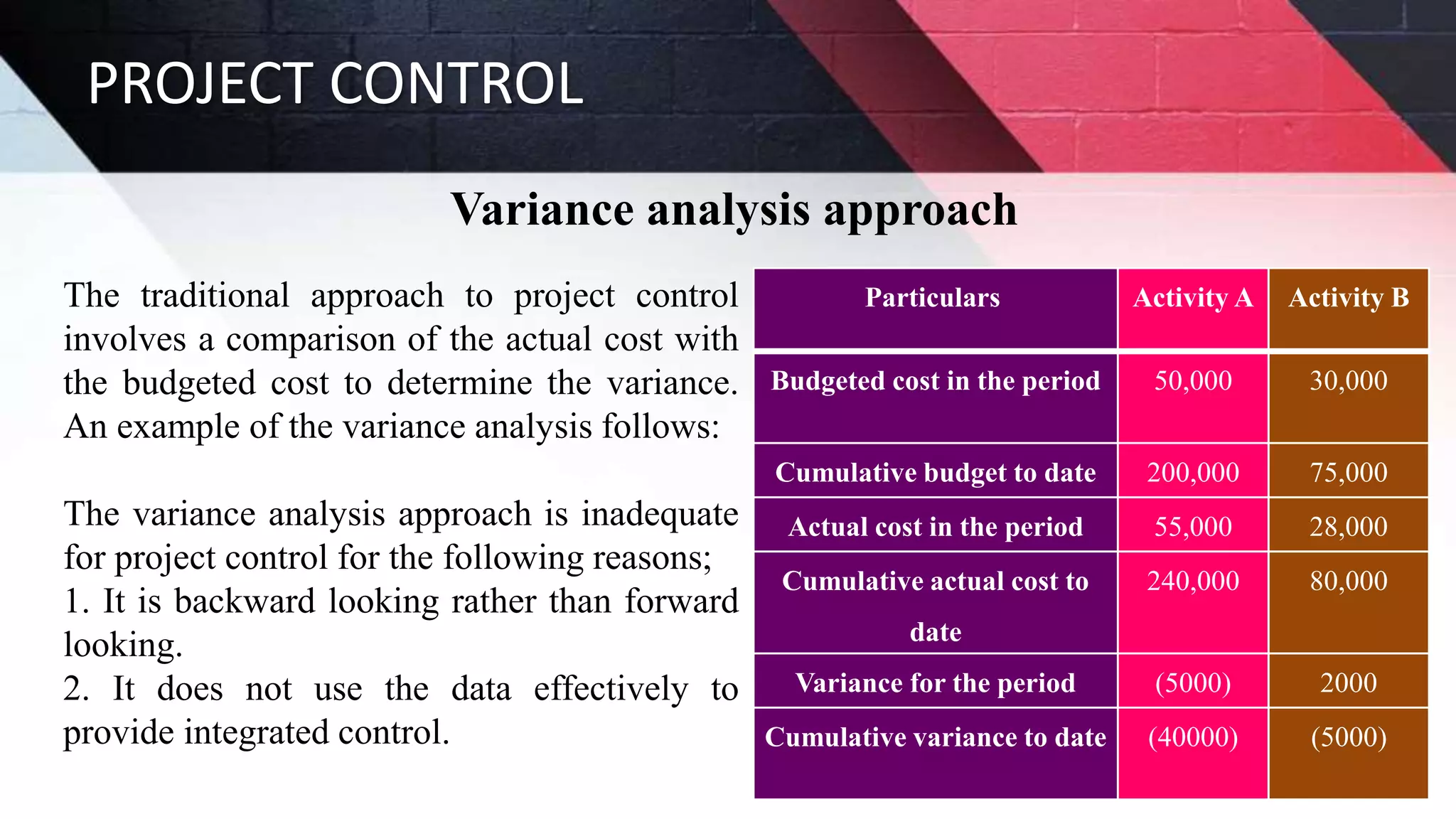
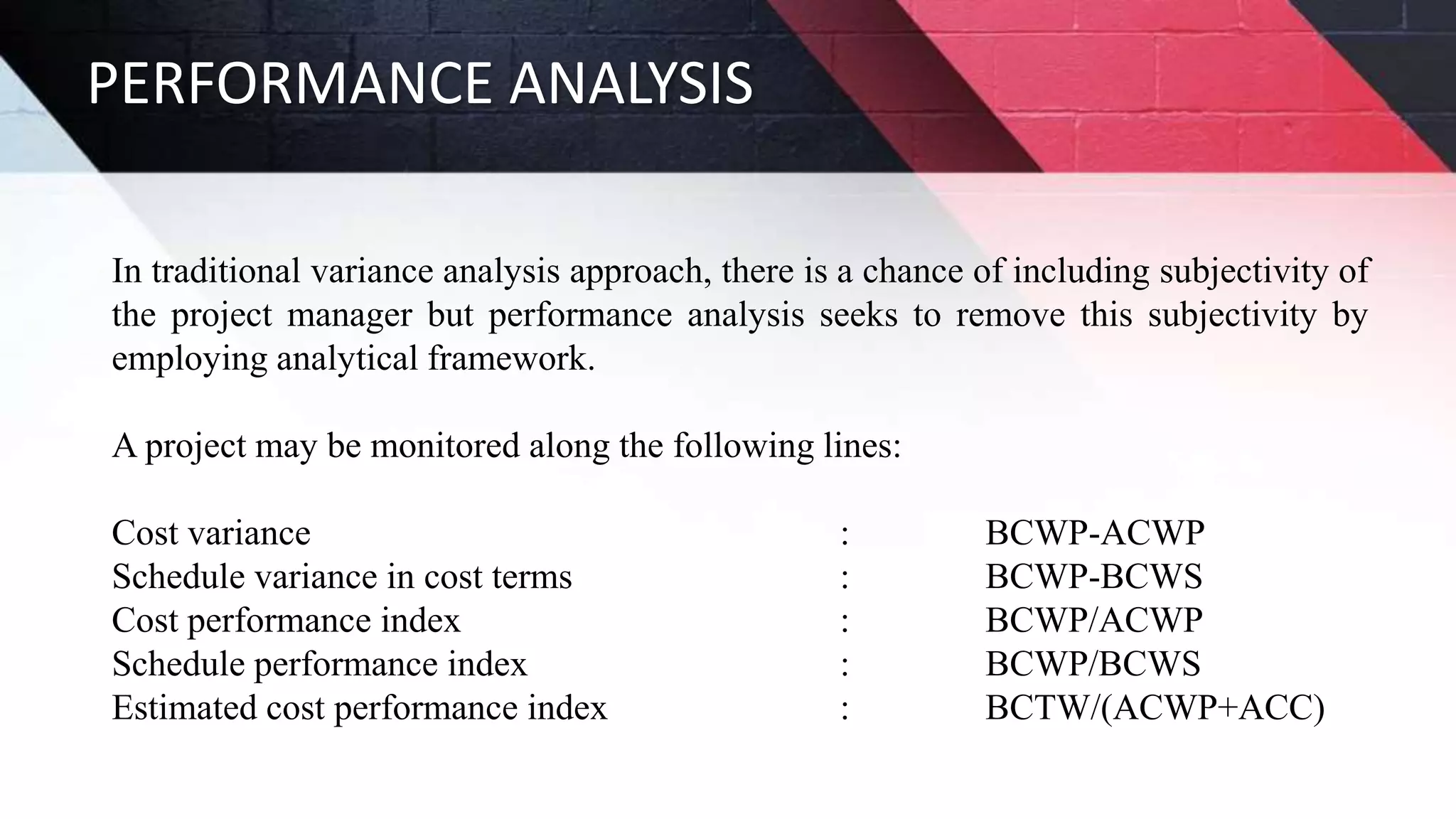
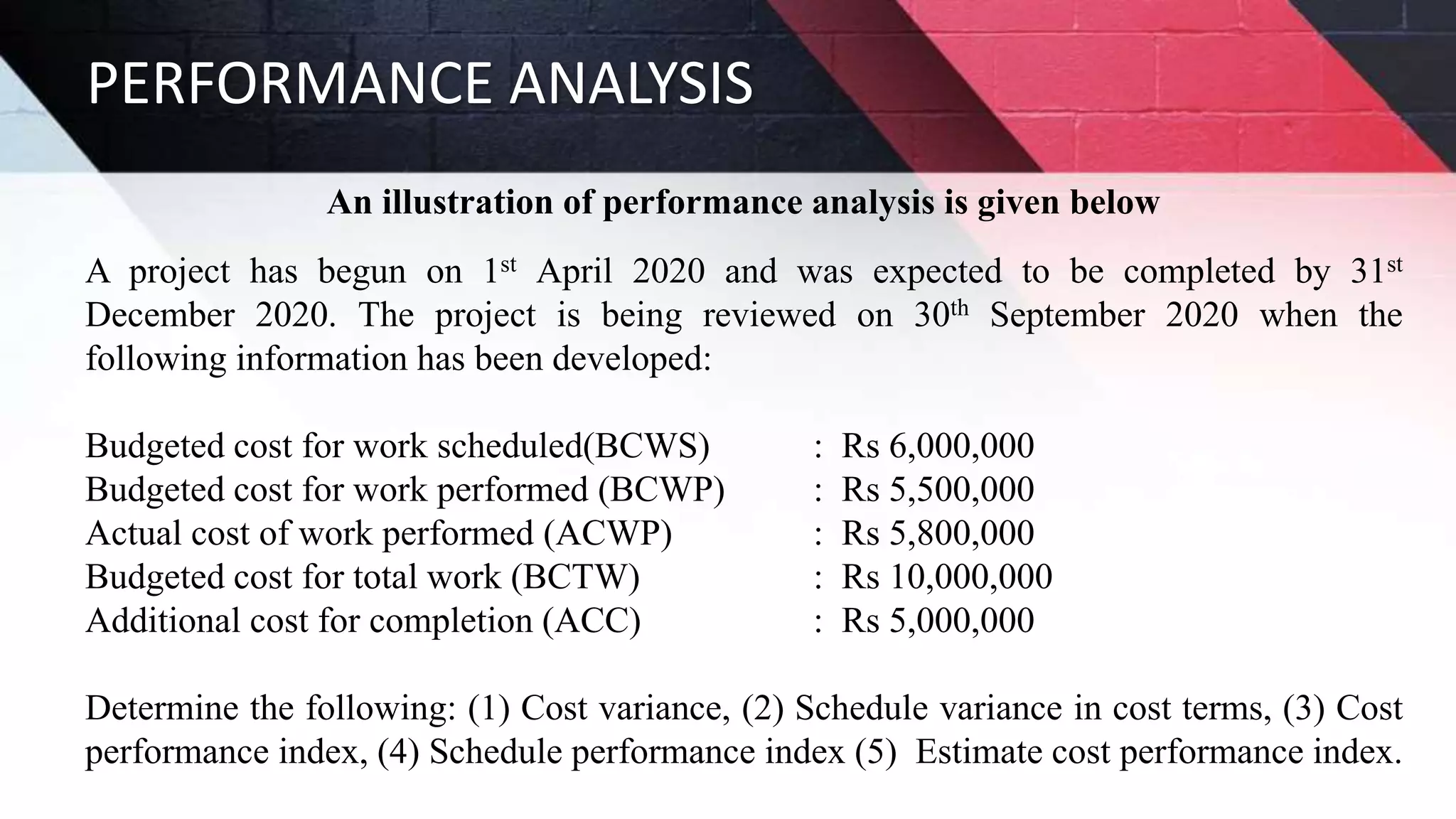
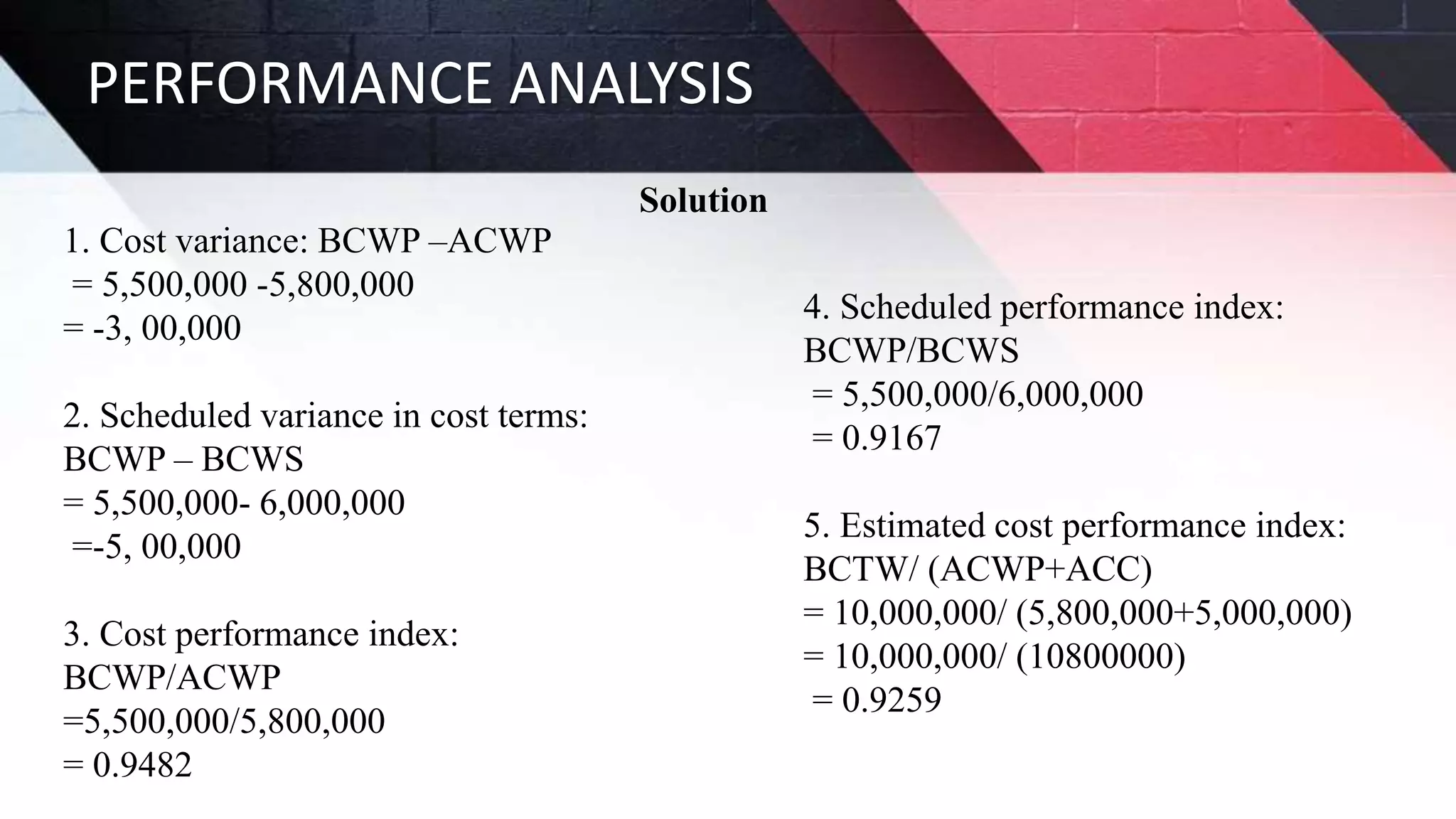
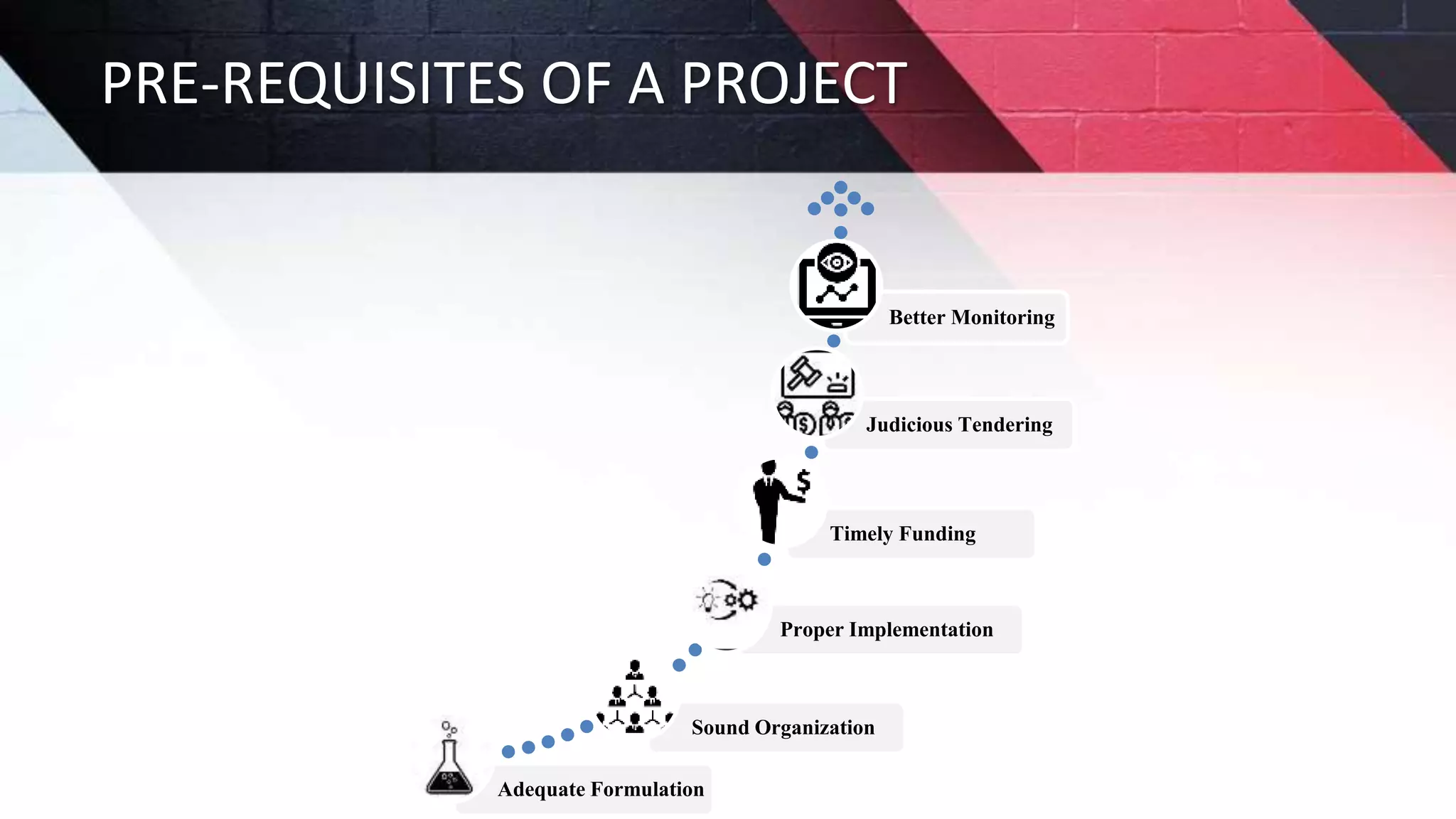
The document discusses key aspects of project management including different forms of project organization, the project life cycle, performance analysis tools, and human aspects. It describes three main forms of project organization: functional, dedicated teams, and matrix. The project life cycle includes initiation, planning, execution, control, and closing phases. Two performance analysis tools discussed are variance analysis and earned value management. Finally, it covers human aspects like authority, orientation, and motivation that impact project management.