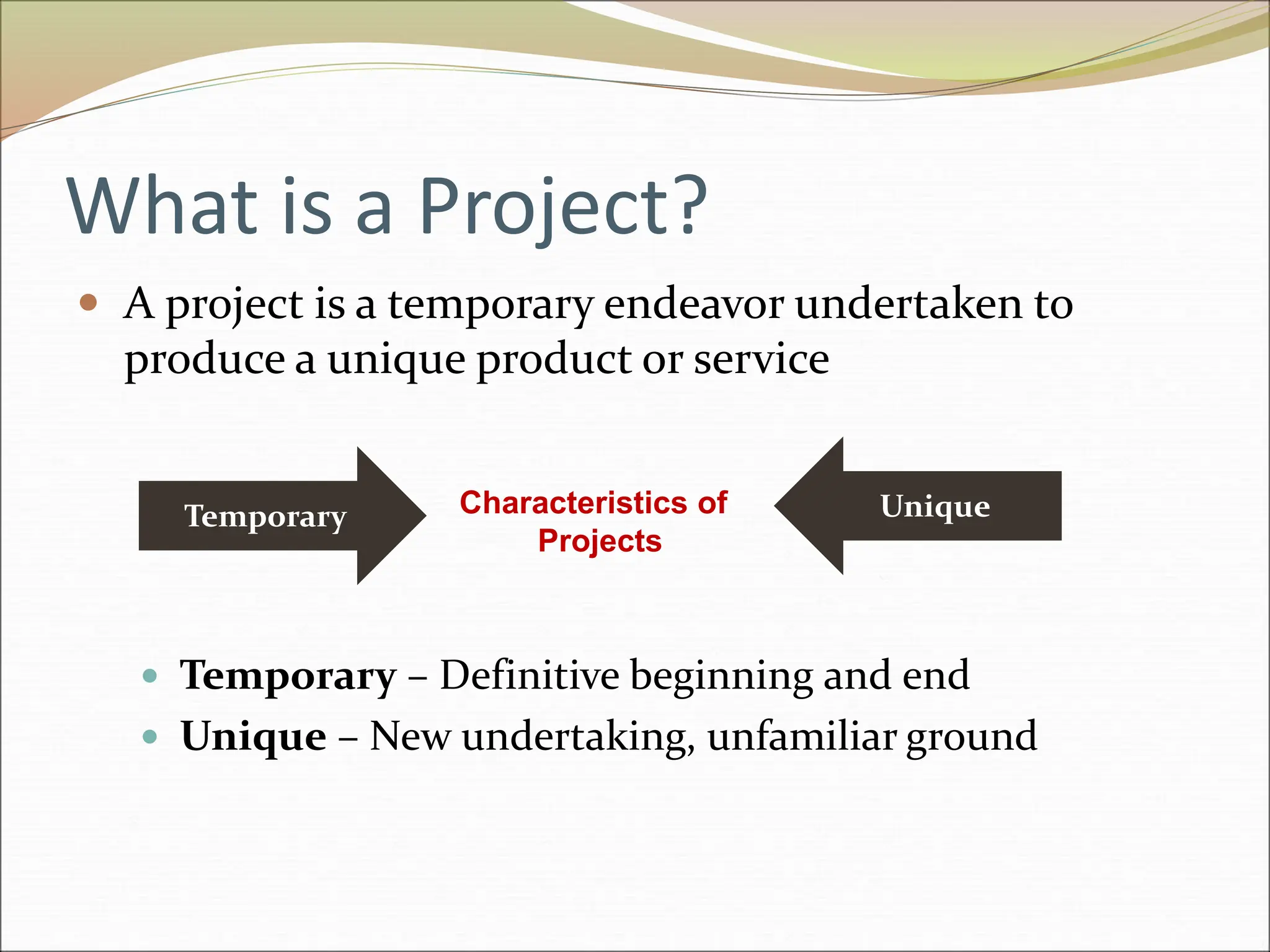
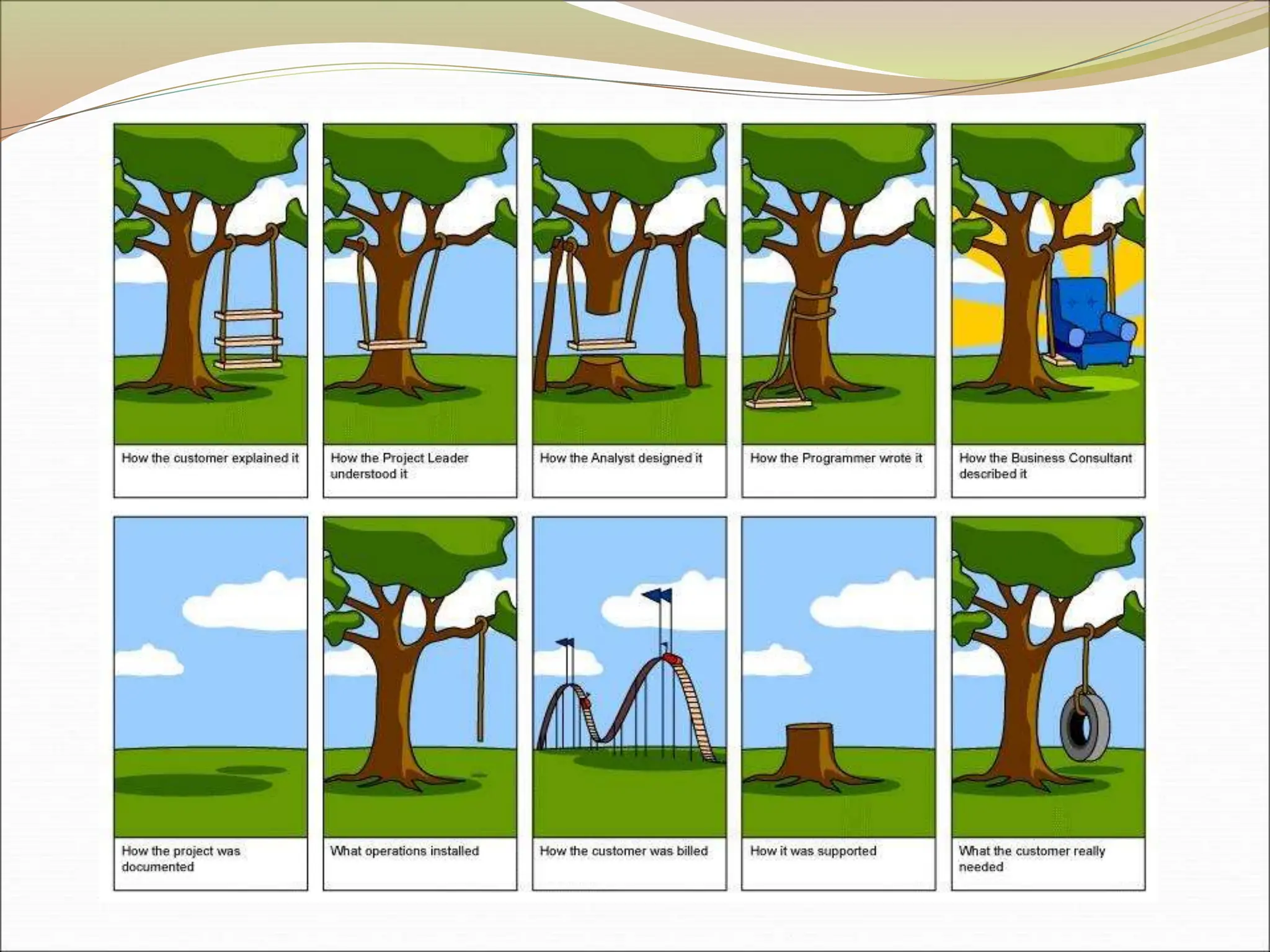
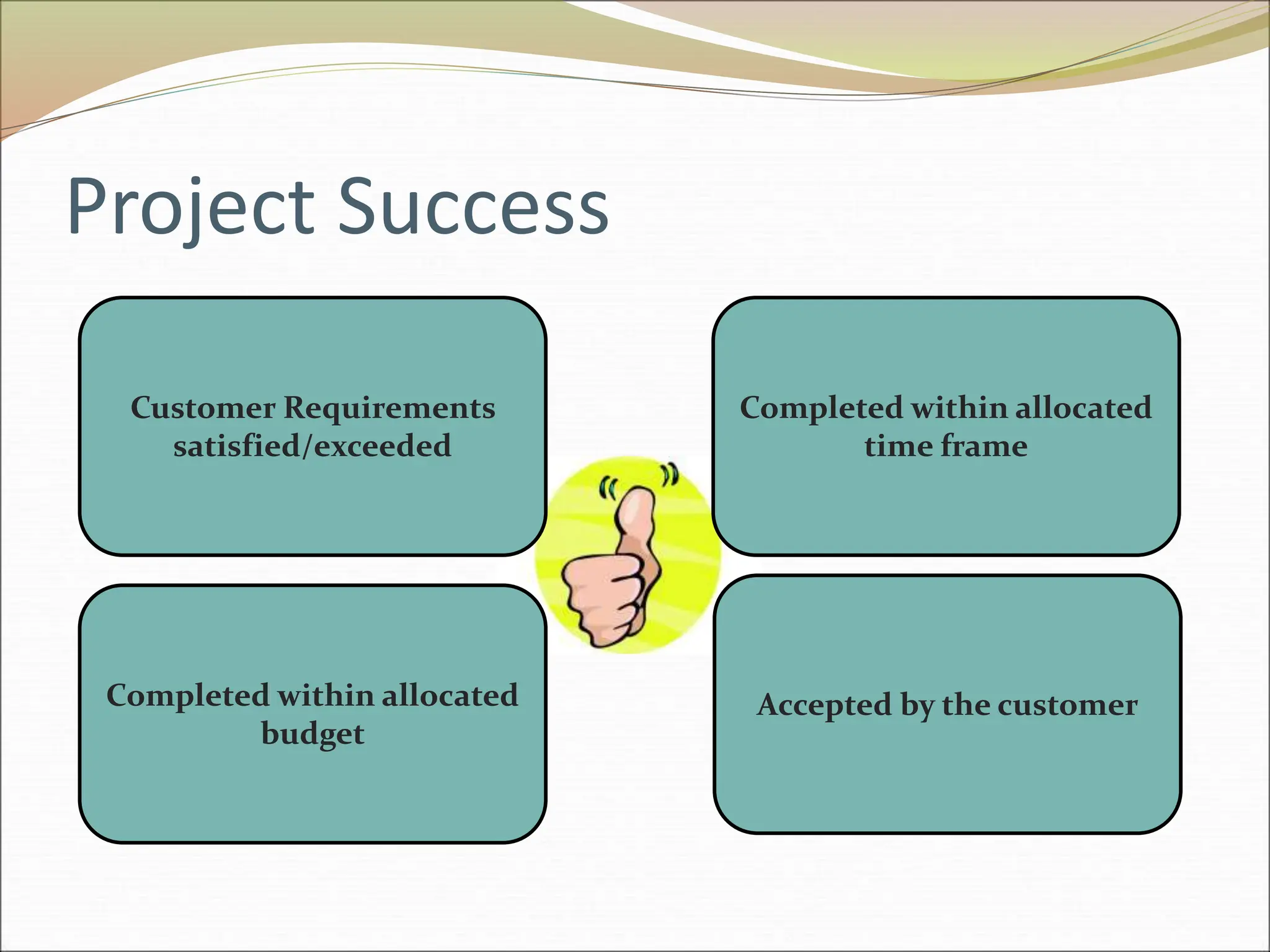
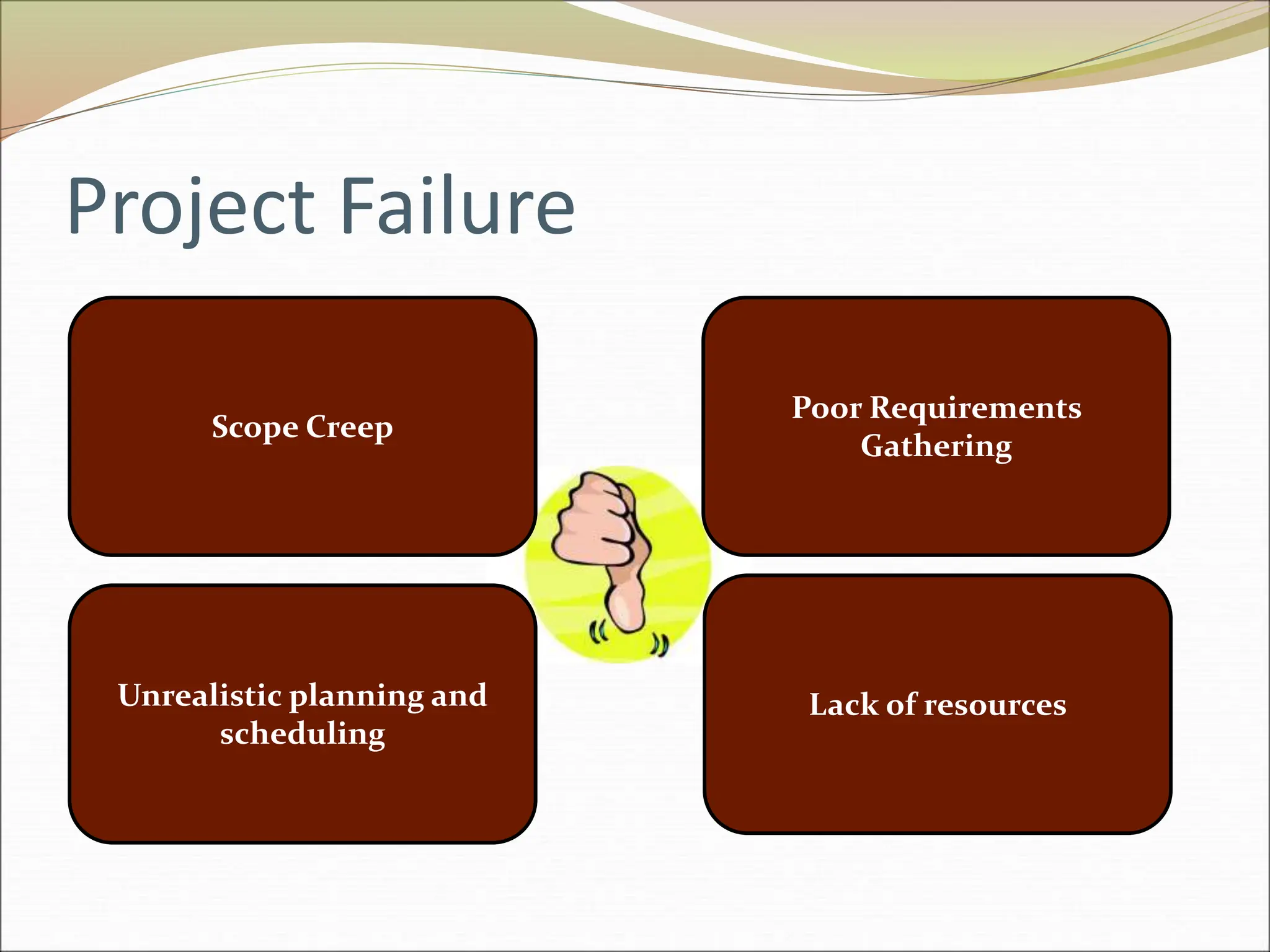
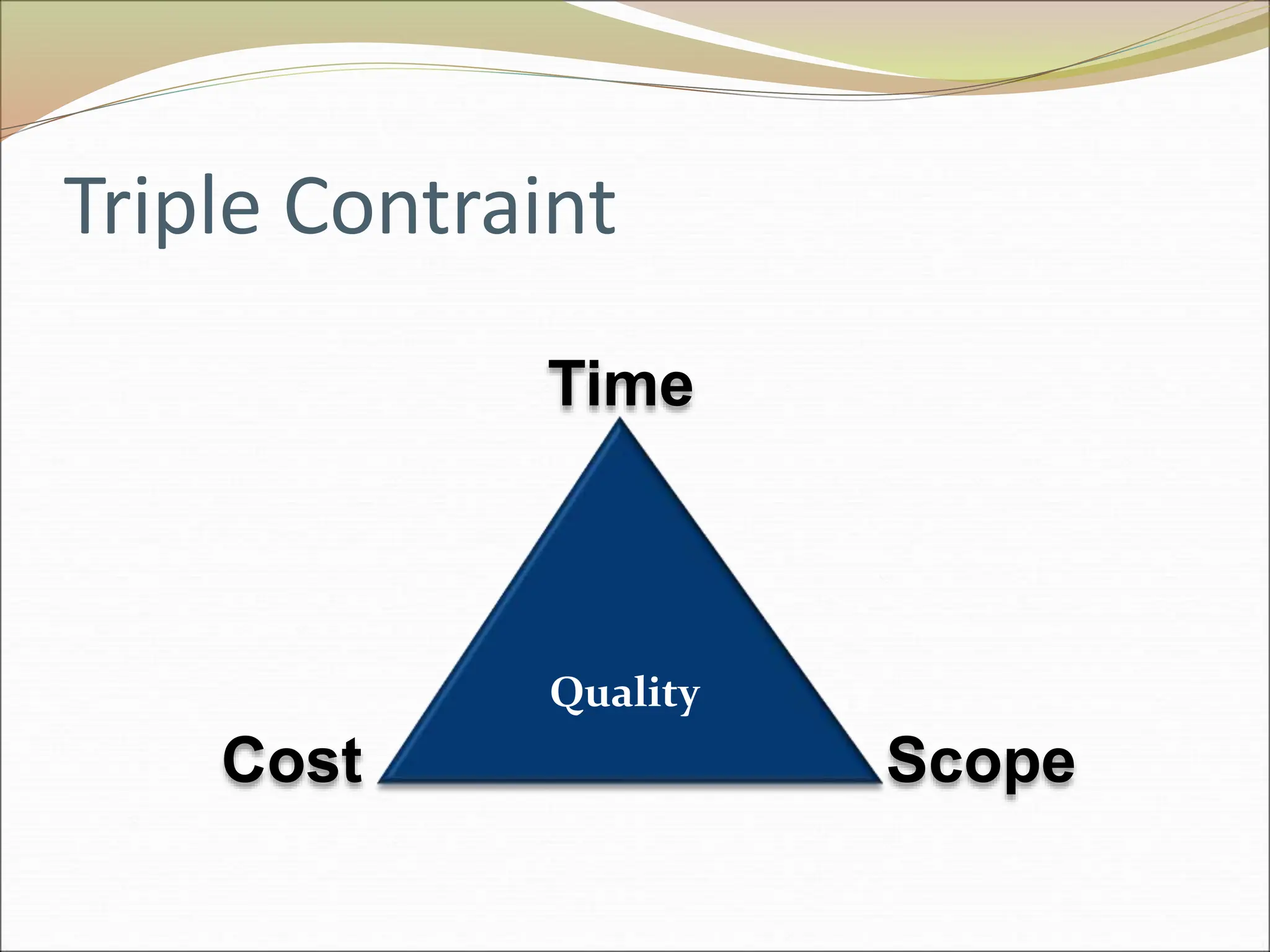
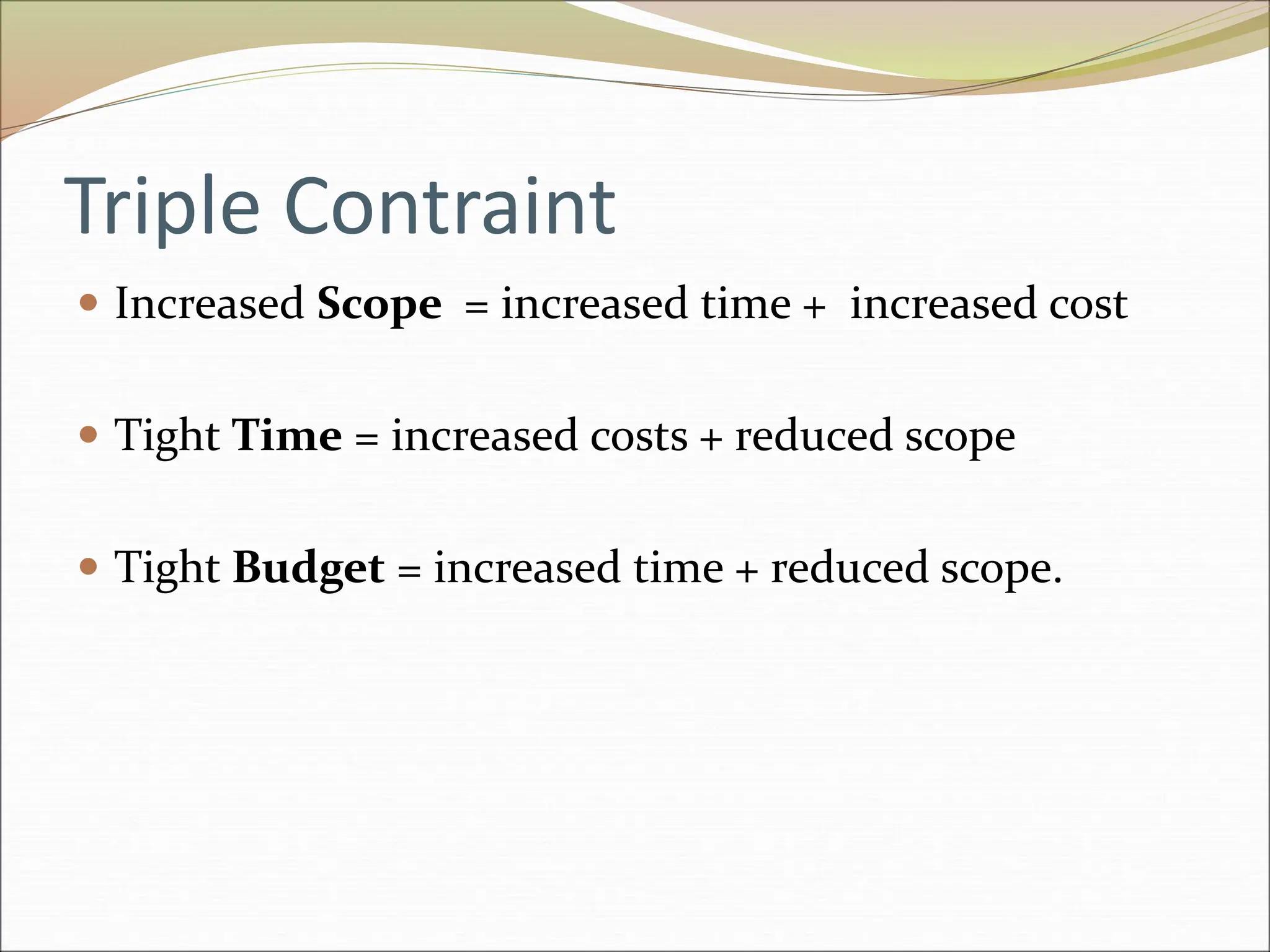
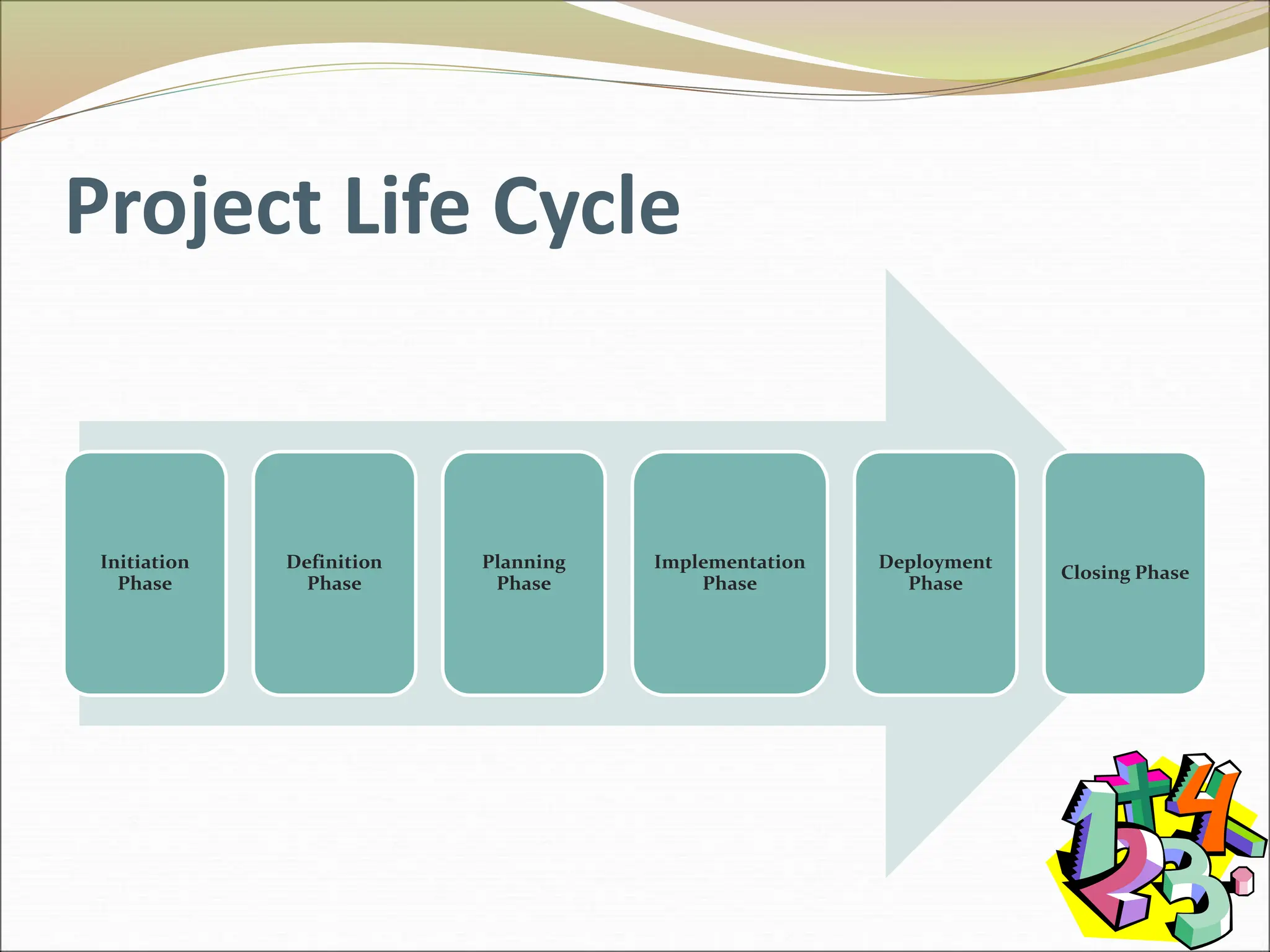
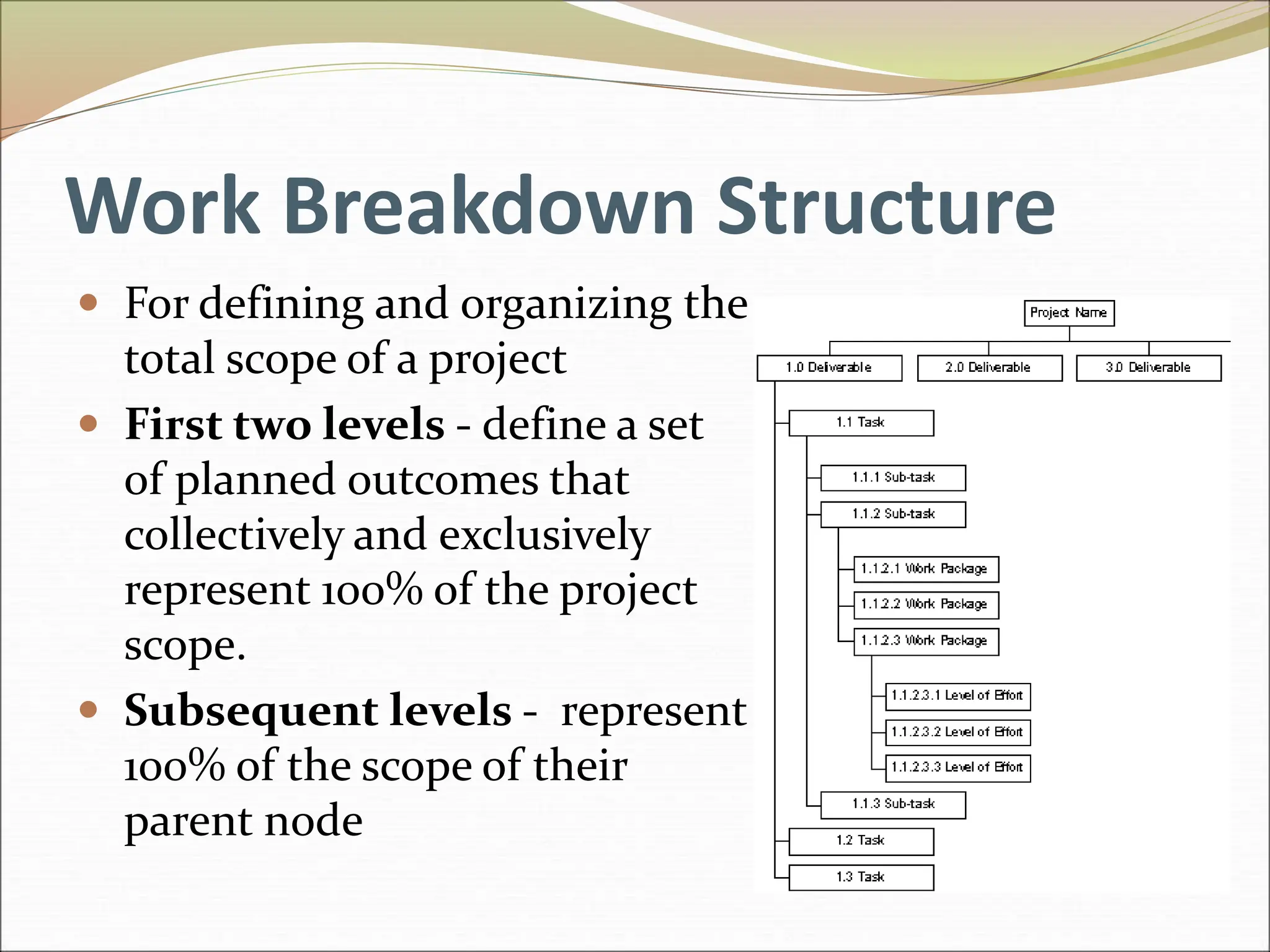
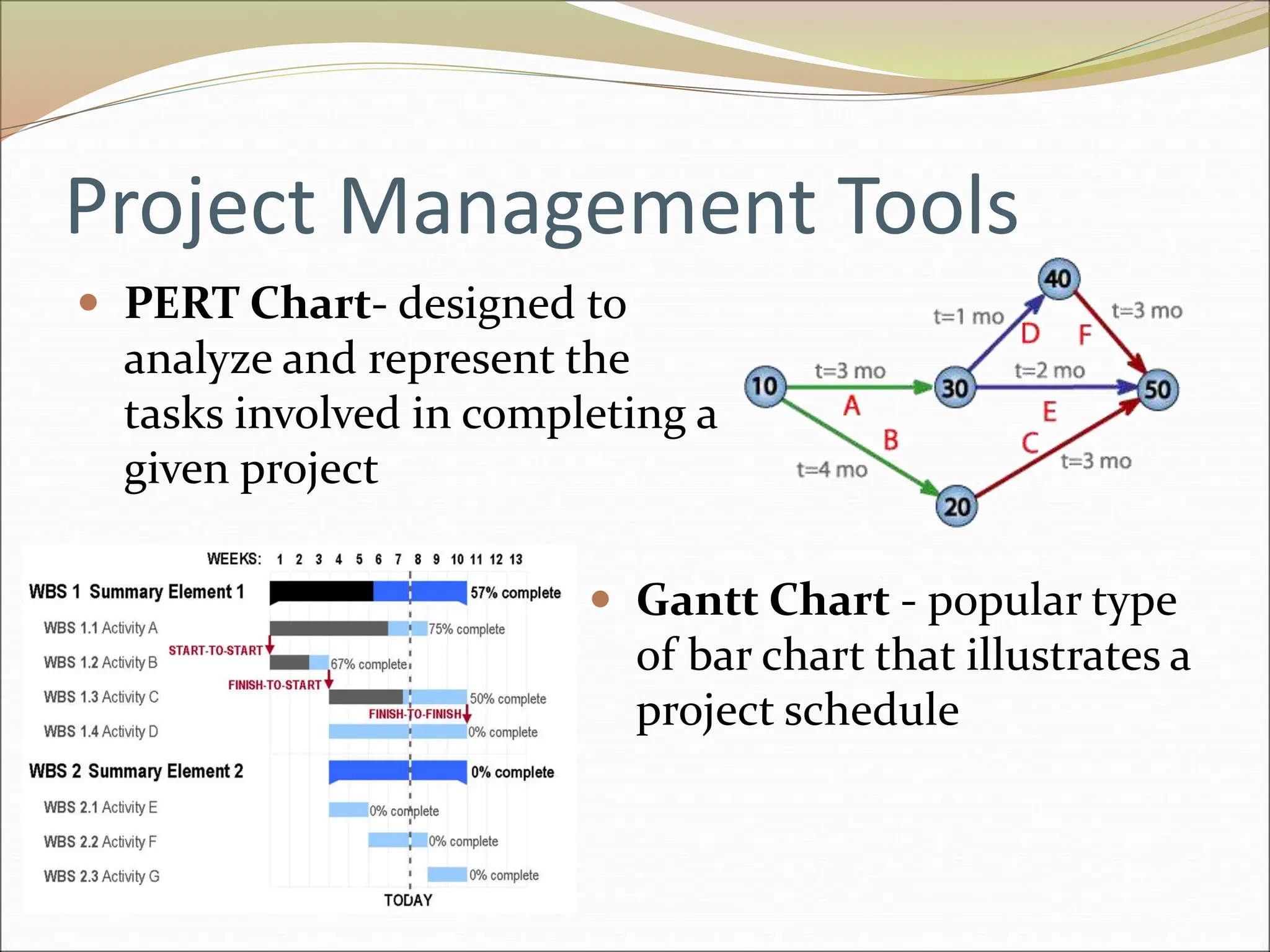
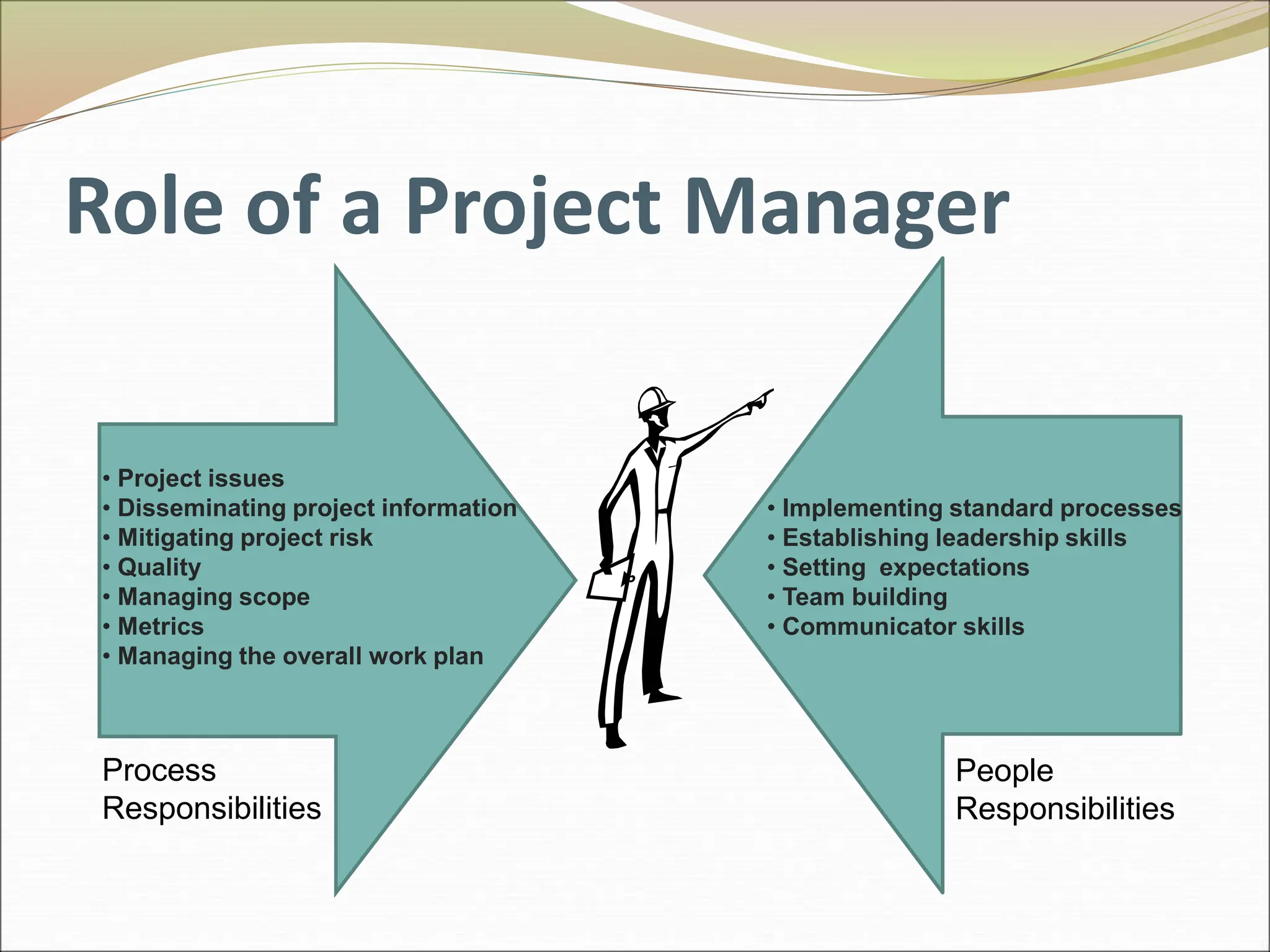
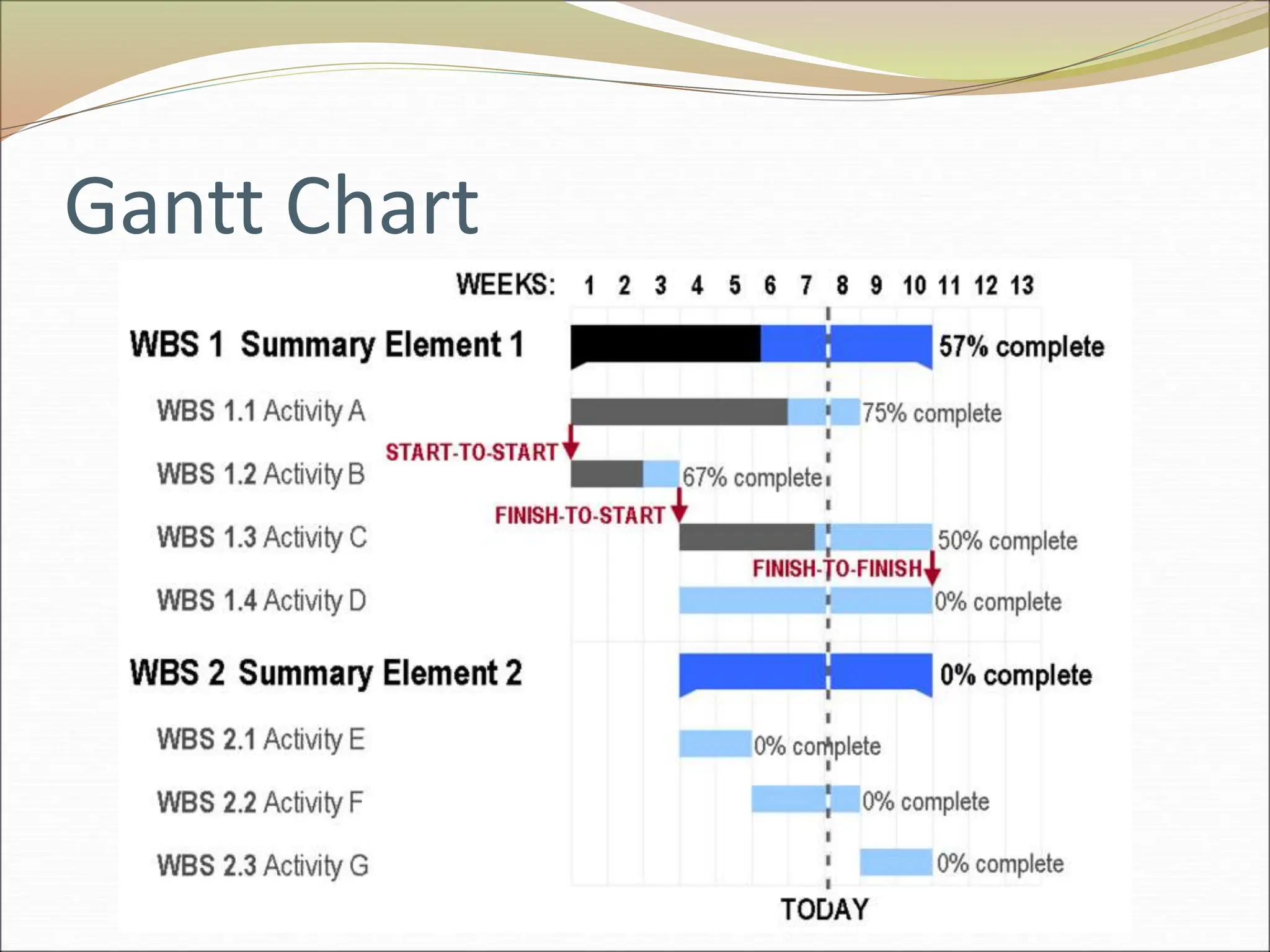
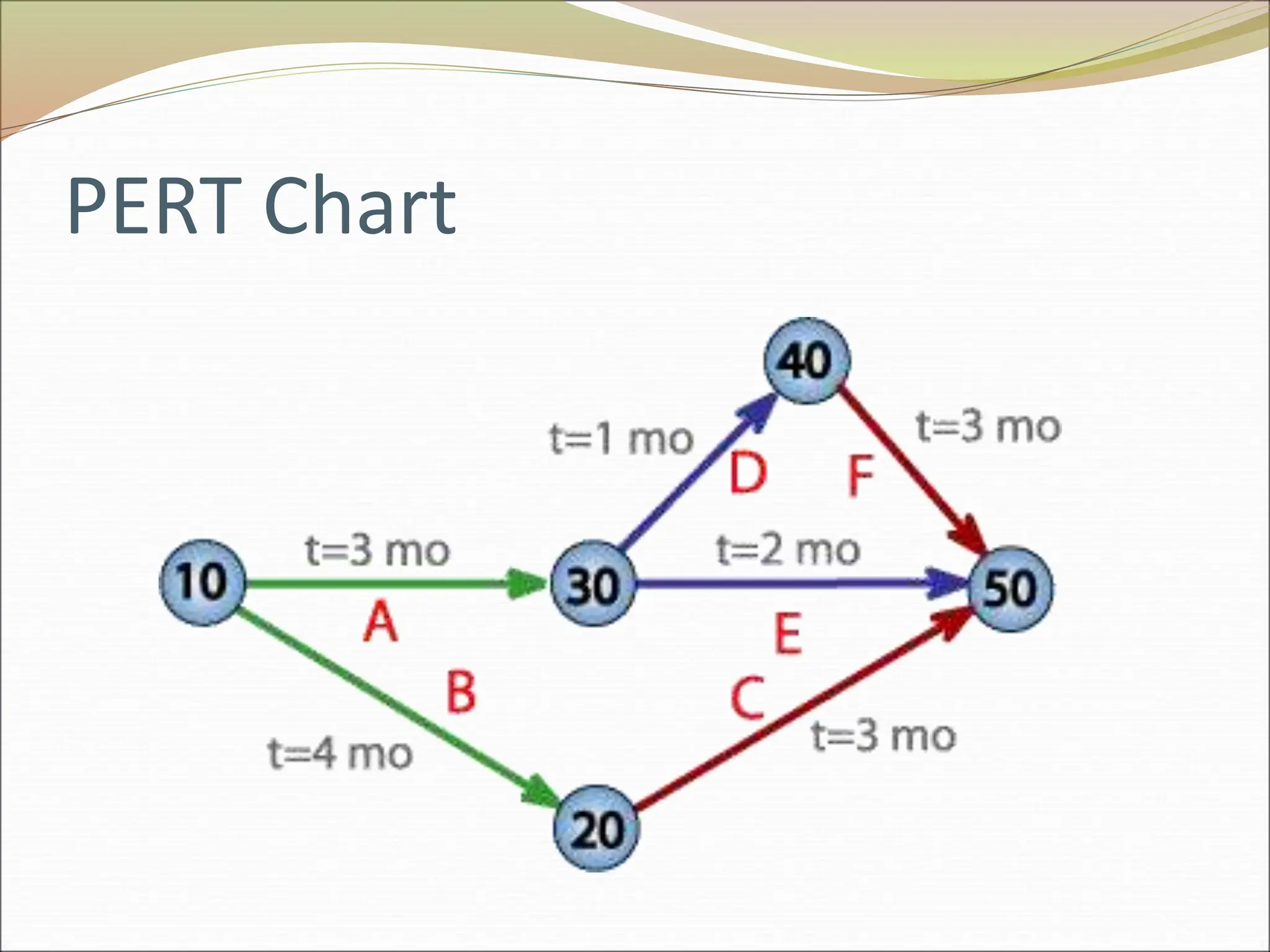
The document provides an introduction to key concepts in project management including defining a project, characteristics of projects, factors that lead to project success or failure, and what project management entails. It describes the triple constraint of quality, scope, and time/cost that project managers must balance. It also outlines several key areas that project managers are responsible for including scope management, issue management, cost management, quality management, communications management, risk management, and change control management. Finally, it discusses the typical project life cycle and some common project management tools like Gantt charts and PERT charts.