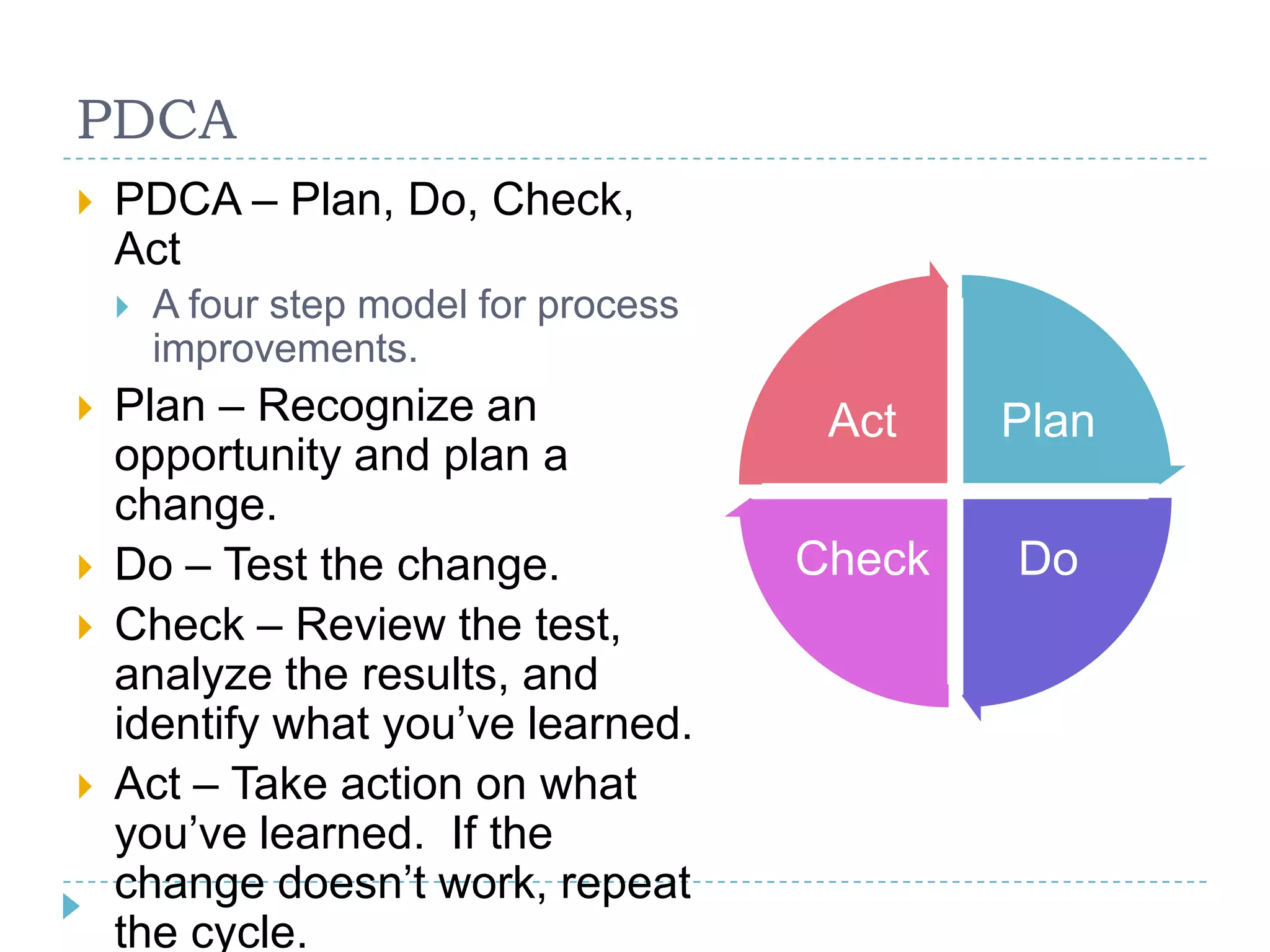
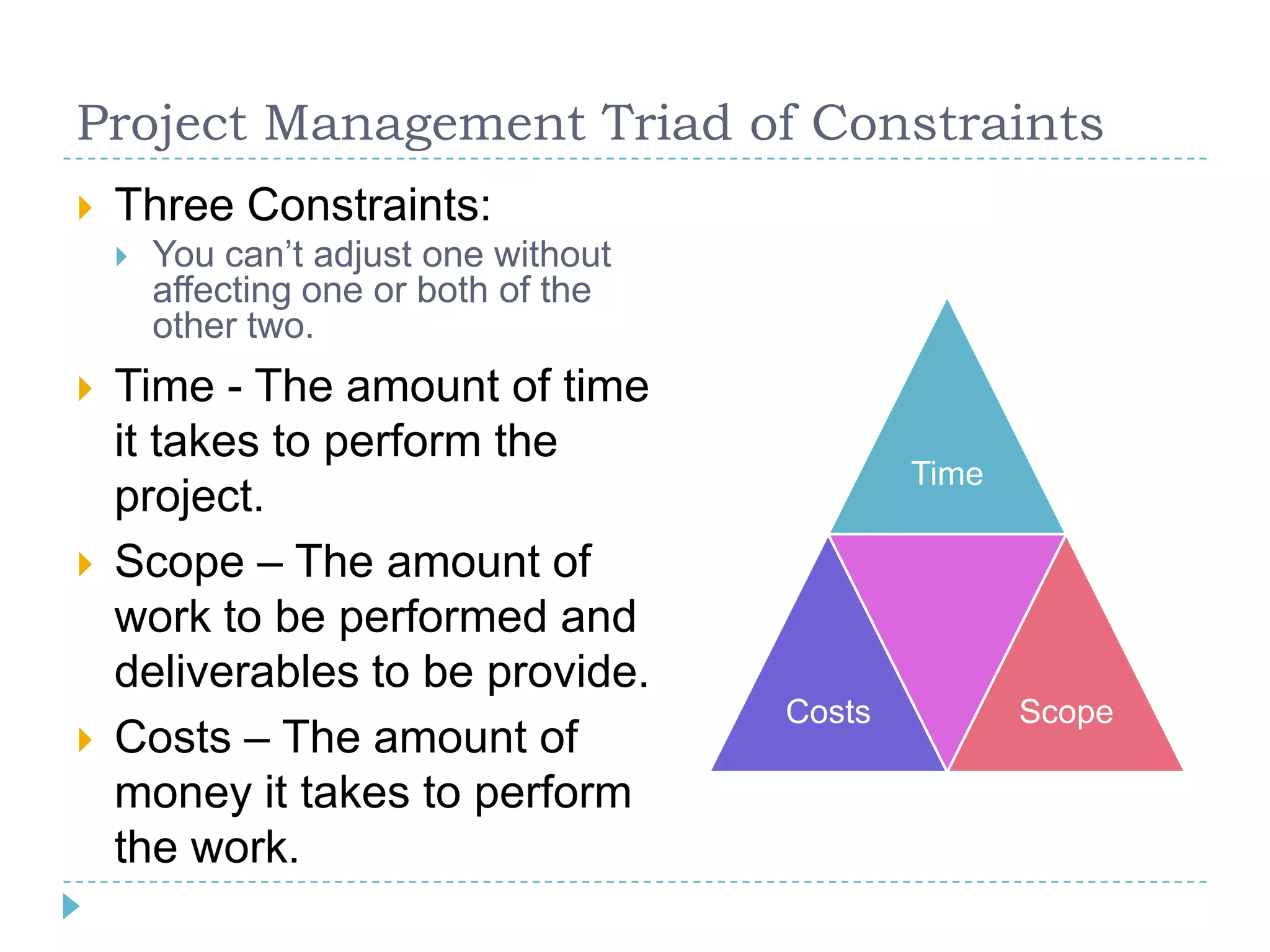
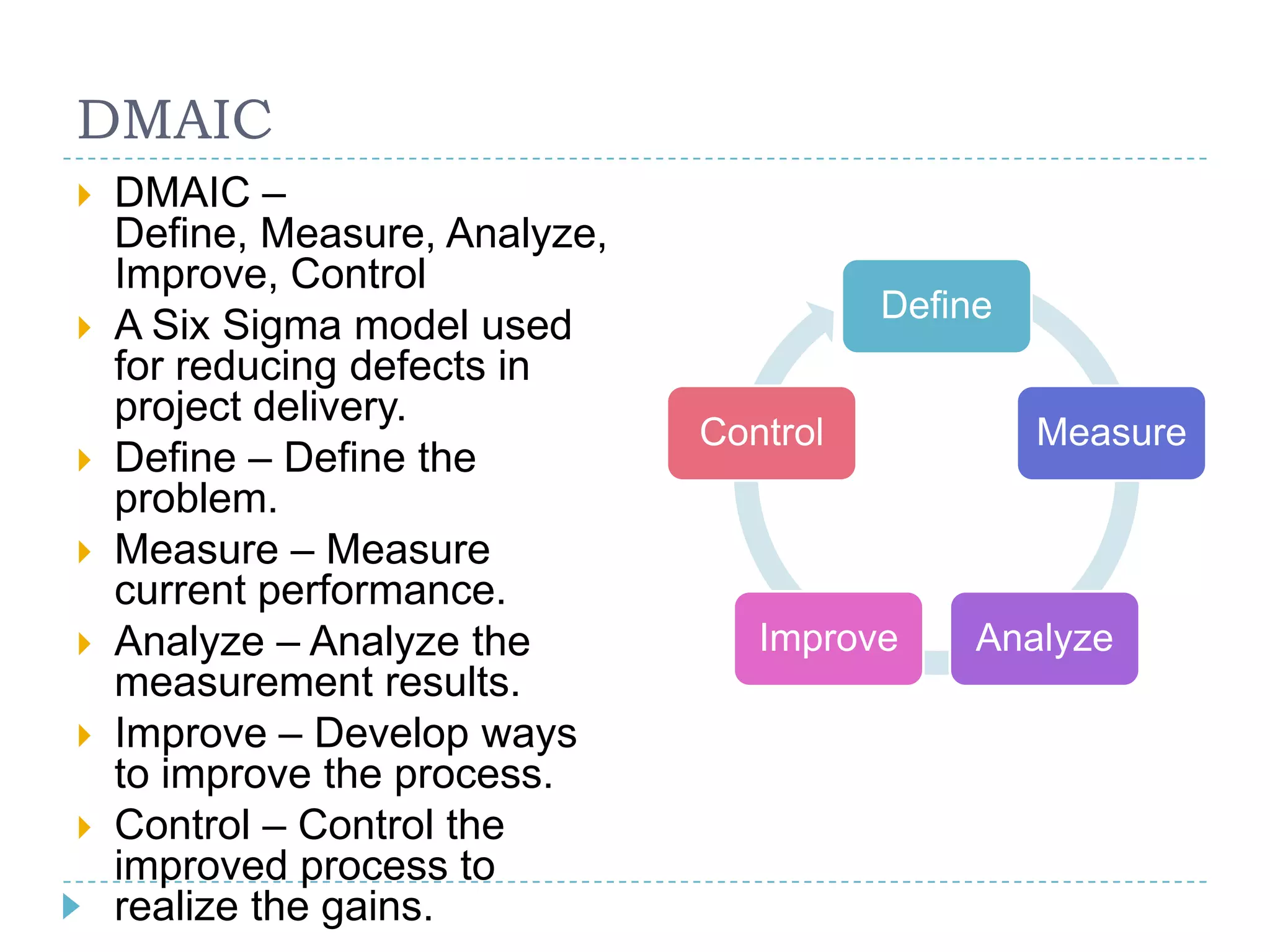
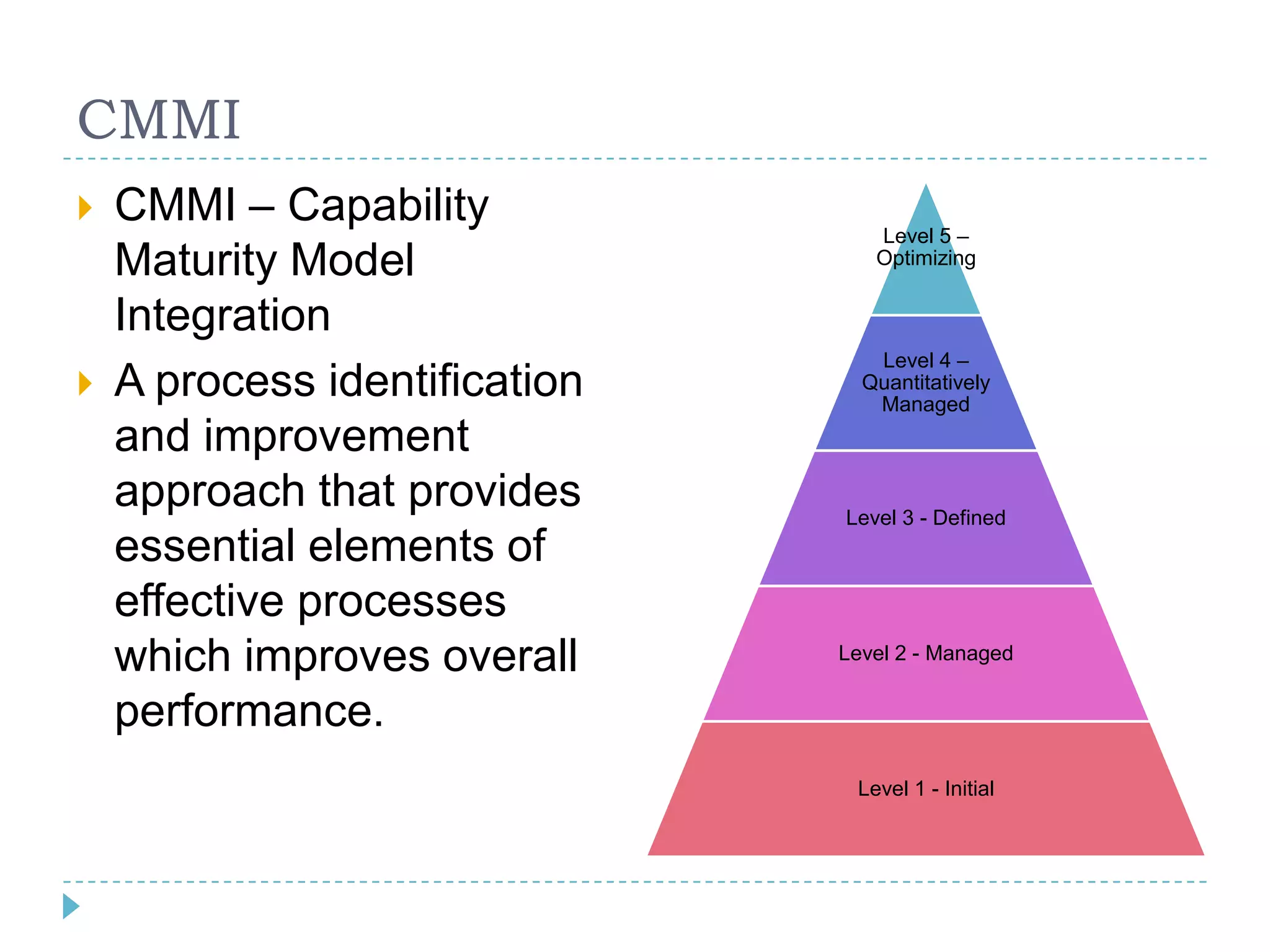
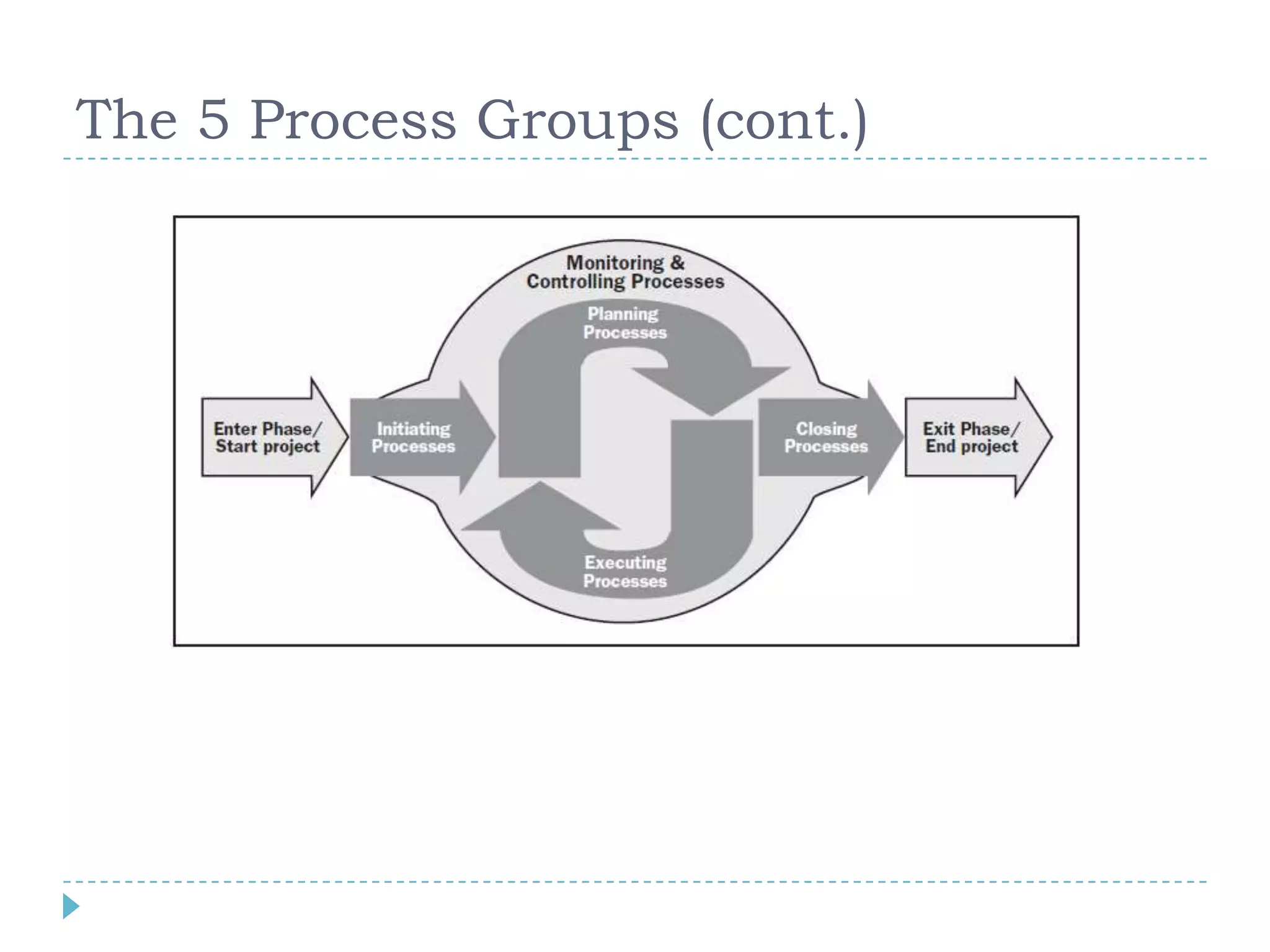
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to project management, outlining its key concepts, definitions, and methodologies, such as the project's temporary nature, the project management triad of constraints (time, scope, and cost), and various process improvement methods like PDCA and DMAIC. It describes the five process groups (initiation, planning, executing, monitoring, and closing) and the nine knowledge areas essential for effective project management. The aim is to enhance understanding and improve project delivery and efficiency by educating on fundamental project management disciplines and processes.