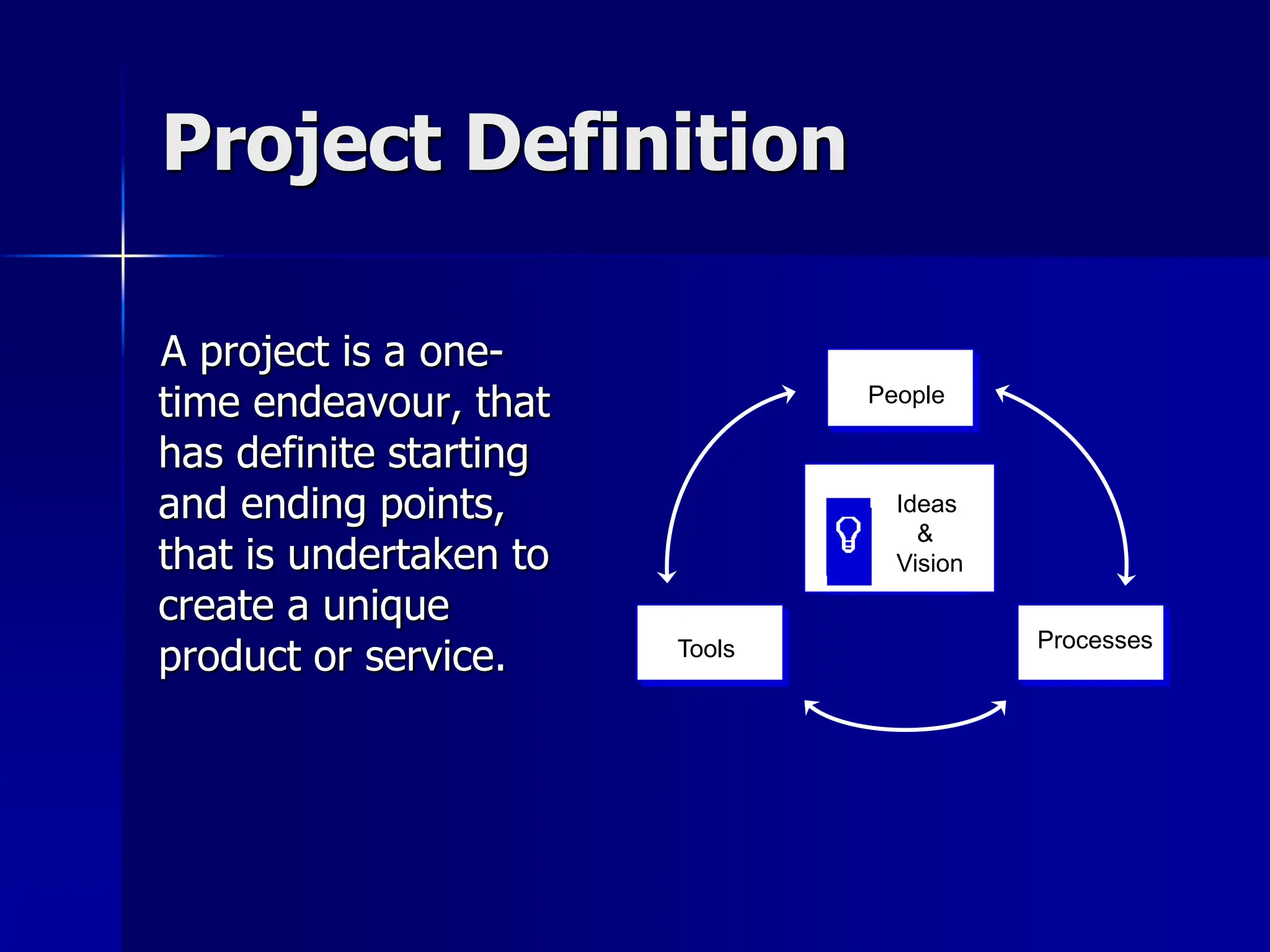
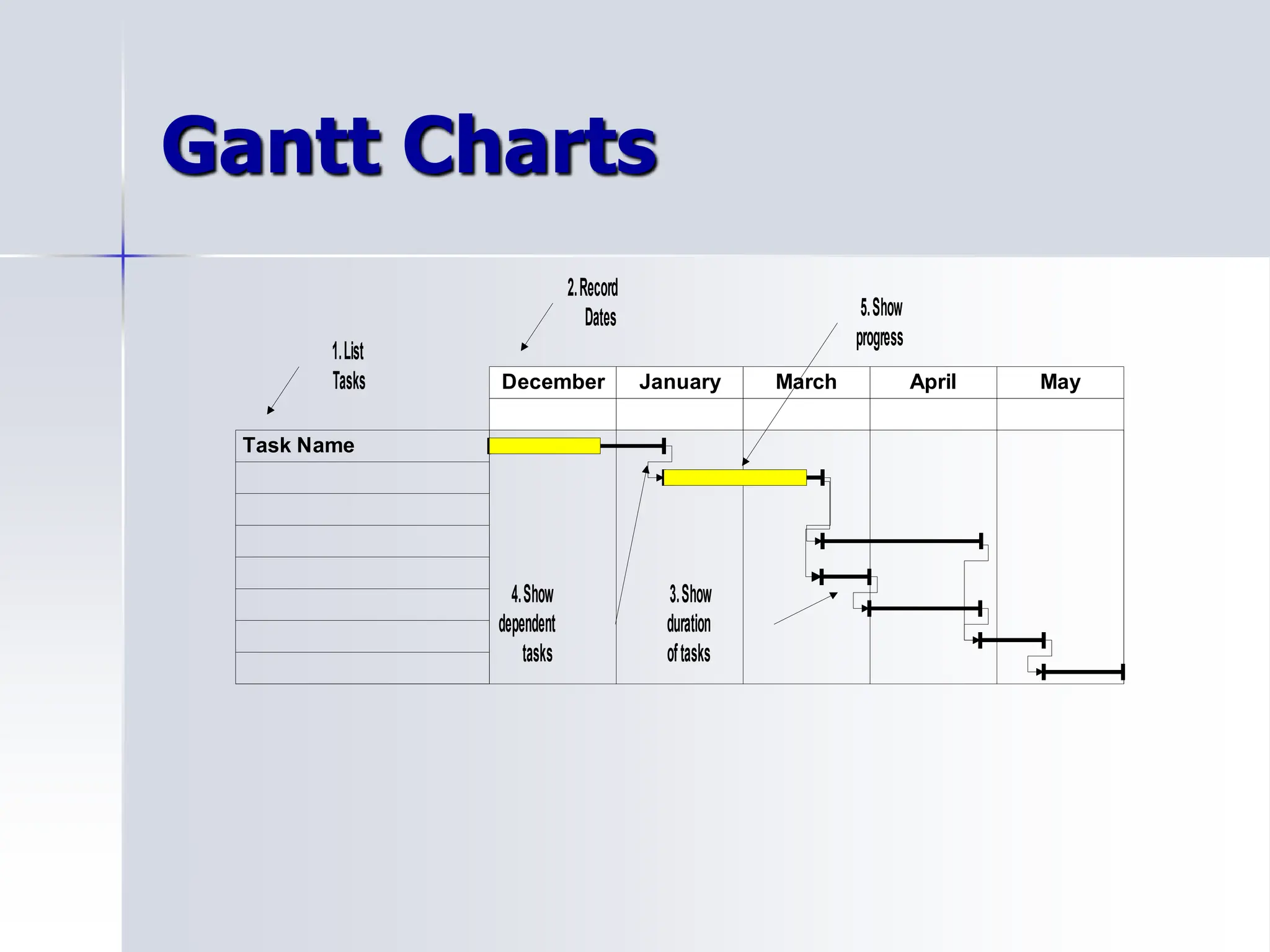
The document outlines an agenda for a project management training session. It includes discussions of common project challenges like communication and planning. It also covers the key aspects of project management including the project cycle of initiating, planning, implementing, managing and closing. The training will focus on practical skills like creating a project charter, work breakdown structure and Gantt chart. Effective communication, monitoring progress and addressing issues will also be discussed.