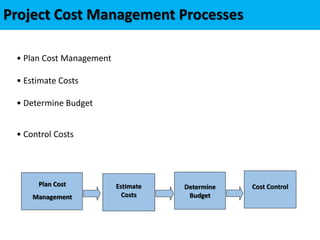
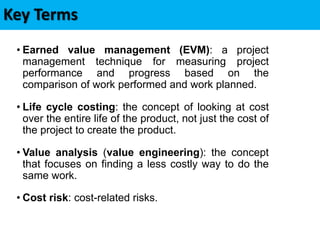
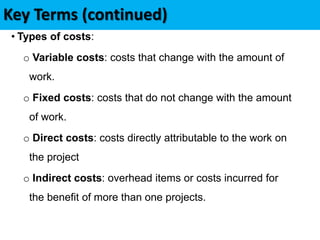
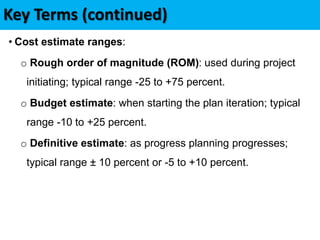
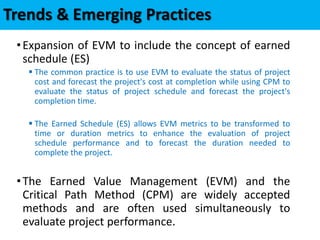
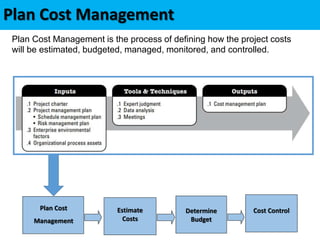
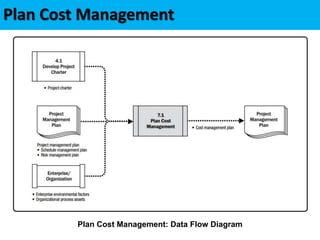
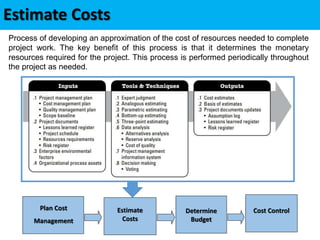
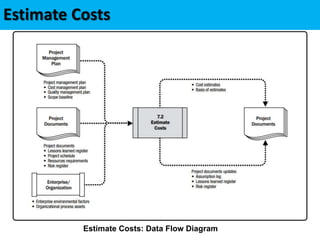
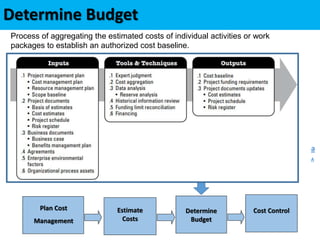
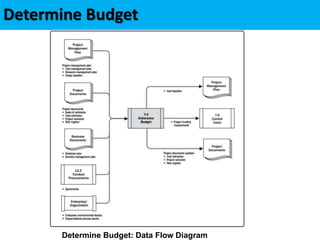
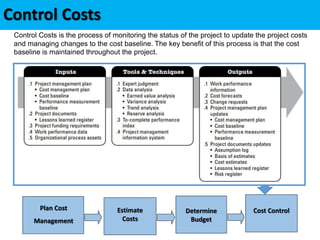
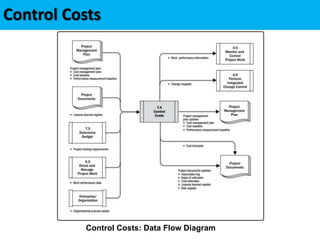
This document discusses project cost management. It defines key concepts like earned value management, life cycle costing, and value analysis. It outlines the four main processes for project cost management: plan cost management, estimate costs, determine budget, and control costs. It also discusses trends like expanding earned value management to include earned schedule and tailoring considerations for areas like knowledge management, estimating and budgeting, and governance.