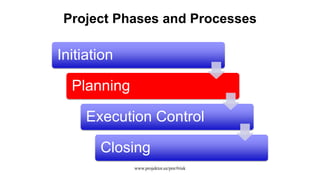
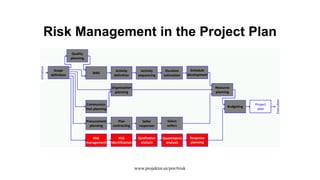
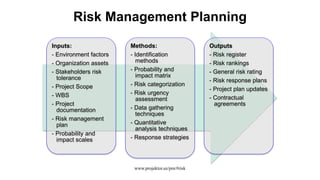
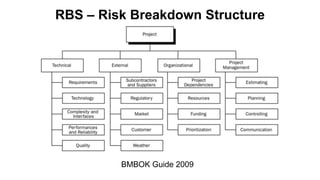
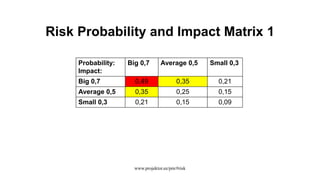
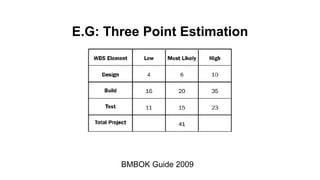
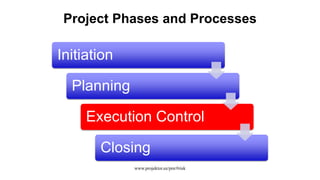
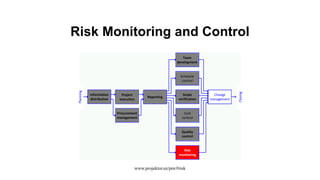
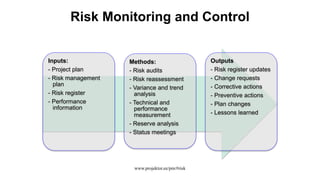
The document discusses risk management for projects. It defines risk as an uncertain event that can positively or negatively impact project duration, cost, scope, or quality. The purposes of risk management are to identify, analyze, and respond to risks in order to increase the likelihood of positive events and decrease the likelihood of negative events. The key components of risk management are planning, identification, analysis, response planning, and monitoring and control. Risk management should be incorporated into the overall project plan.