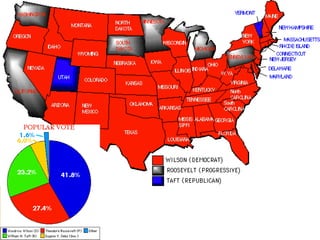
President Theodore Roosevelt implemented a "Square Deal" policy with three main goals: controlling corporations through antitrust laws, protecting consumers, and conserving natural resources. His administration filed numerous antitrust lawsuits, passed laws regulating the food and drug industries and empowering regulatory agencies, and set aside hundreds of millions of acres of federal land for conservation. Overall, Roosevelt took an active approach to expanding the federal government's role in regulating businesses and protecting citizens.