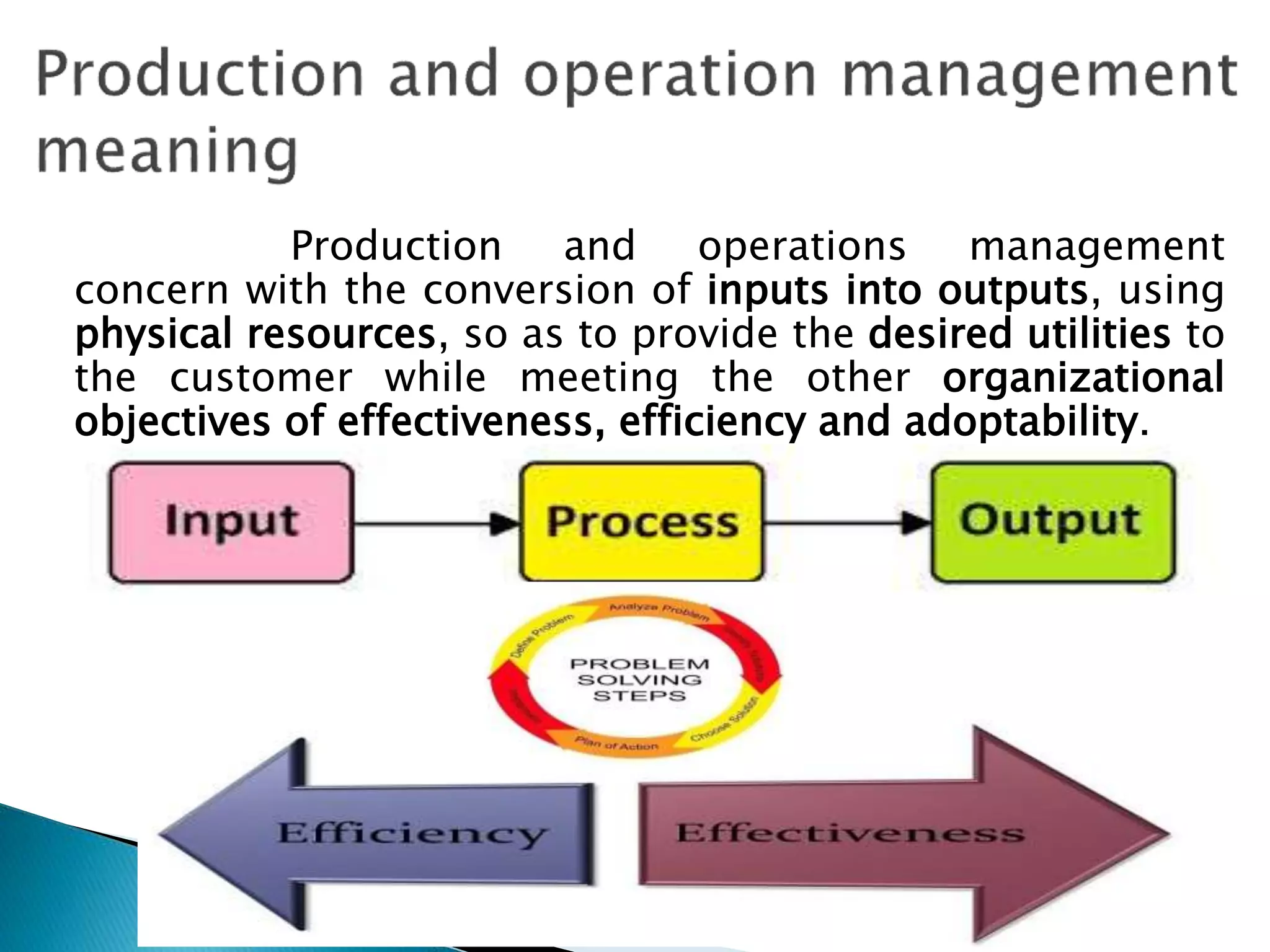
Production and operations management deals with converting inputs into useful outputs through physical transformation processes while meeting organizational objectives like effectiveness, efficiency, and adaptability. There are different types of production systems like job shop production, batch production, and mass production characterized by factors like volume, variety, and process flow. Key areas of production and operations management include location planning, facility layout, inventory management, quality control, and maintenance management. Automation uses mechanical and electronic systems to operate production and has advantages like increased productivity but also disadvantages such as potential job losses and reduced purchasing power.