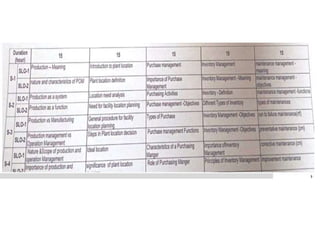
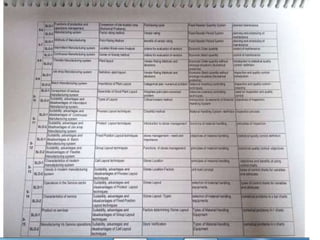
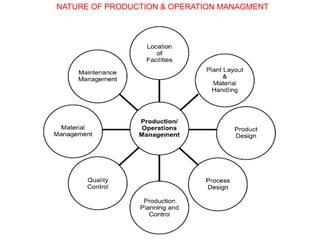
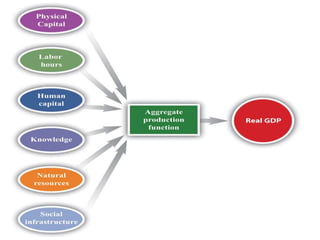
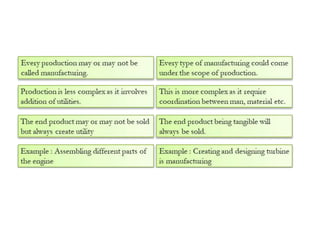
Production management involves planning and regulating operations to transform materials into finished products, focusing on key elements like products, plant, process, programs, and people. It encompasses both strategic and operational activities, utilizing tools like production planning and control (PPC) to optimize resource utilization. Various manufacturing systems, including job shop, batch, mass, and flexible manufacturing, reflect different approaches to production, while productivity is evaluated as the ratio of output to input, influenced by several factors.