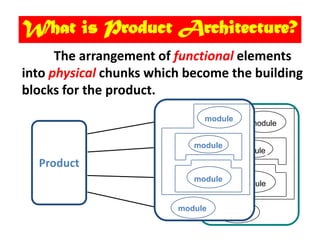
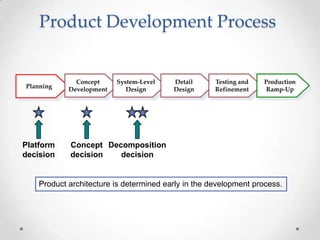
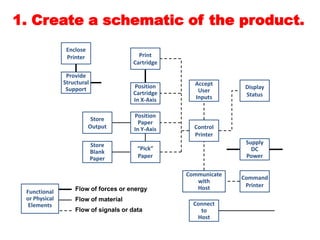
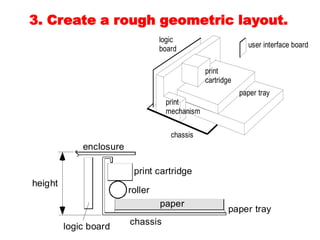
The document discusses product architecture, which is the arrangement of functional elements into physical chunks or modules that make up the core building blocks of a product. It notes that product architecture is determined early in the development process and impacts factors like manufacturing cost, product evolution, and more. The document provides examples of modular versus integral architecture and walks through establishing the architecture for a sample desk jet printer.