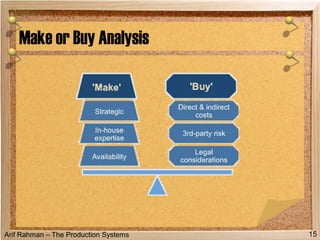
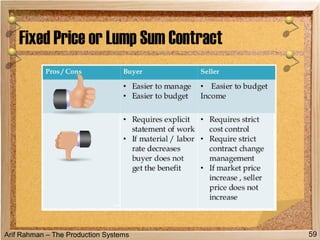
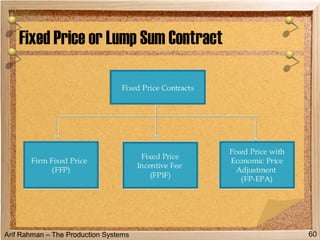
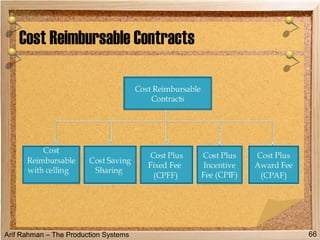
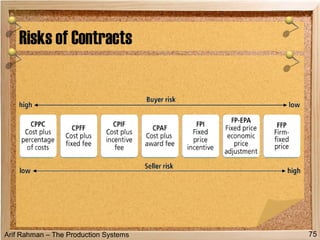
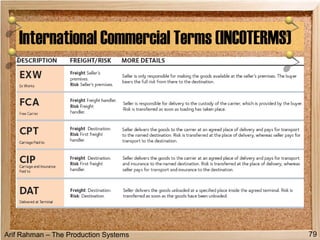
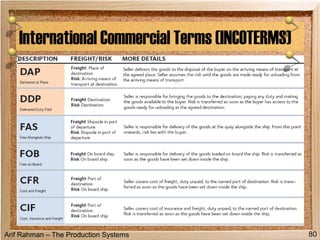
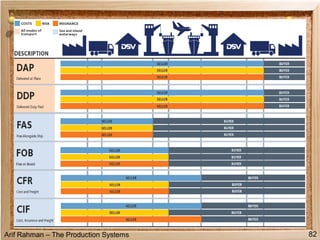
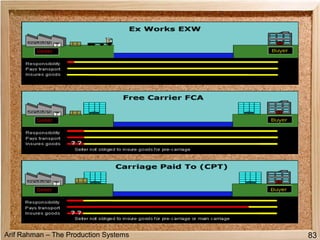
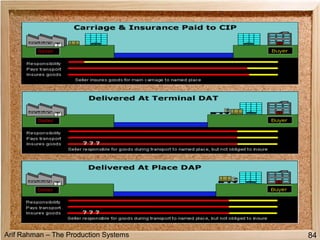
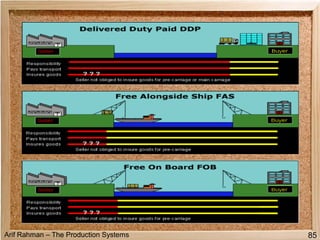
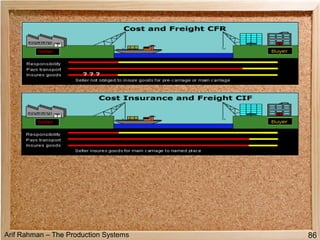
The document discusses material procurement and inventory management. It covers topics like demand management, different purchasing systems (petty cash, blanket order, rate contract, tender, subcontracting, stockless, e-procurement), procurement procedures, supplier relationship management, and factors for determining the number of suppliers (single vs multiple source policies). Effective logistics management aims to control material flows to meet customer needs through activities like procurement and inventory management.