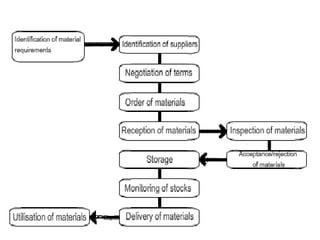
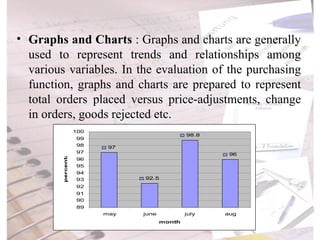
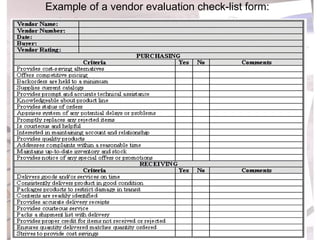
The document discusses evaluation of purchase management performance. It outlines various quantitative and qualitative metrics that can be used, including price advantage, inventory levels, and relations with suppliers. Internal and external agencies can evaluate performance. Methods include forms, flowcharts, checklists and key performance ratios. A purchase audit examines the organization, policies, procedures, evaluation and reporting of the purchase department.