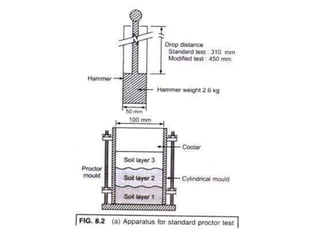
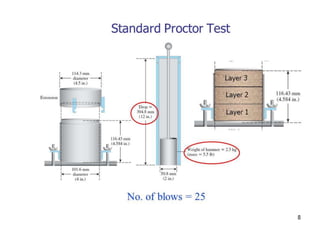
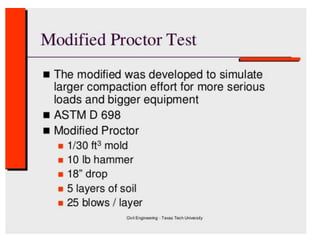
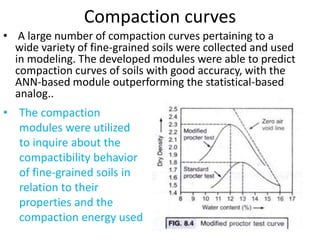
The Proctor compaction test is used to determine the optimal moisture content and maximum dry density of soils. It involves compacting soil samples in a mold using a standardized compactive effort at different moisture contents. The dry density is measured for each sample to create a compaction curve showing the relationship between dry density and moisture content. The peak of the curve indicates the optimum moisture content and maximum dry density, which represent the conditions when the soil is most dense and has the highest load-bearing capacity. The test is important for determining how to properly compact soils in the field.