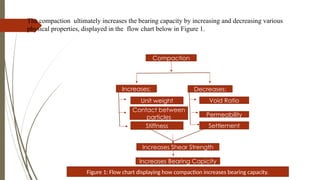
Soil compaction is a process of increasing soil density by reducing air voids, which improves the soil’s strength, stability, and load-bearing capacity. Various compaction tests are conducted to determine the optimum moisture content (OMC) and maximum dry density (MDD) of soil.