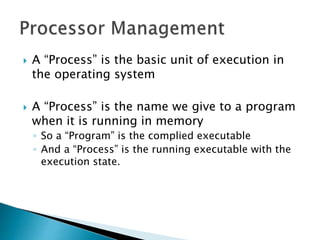
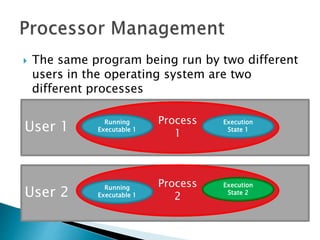
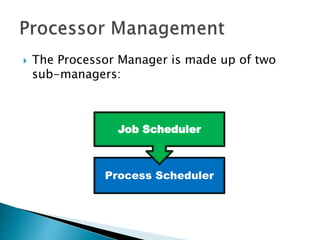
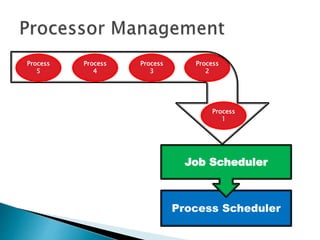
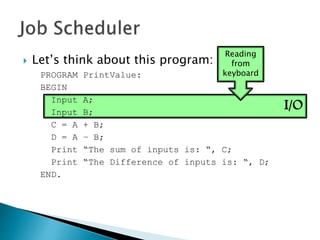
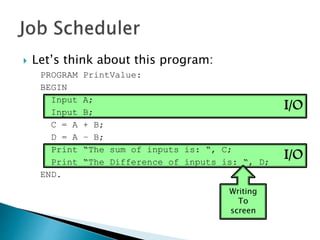
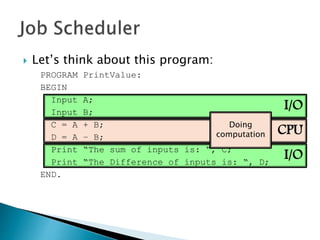
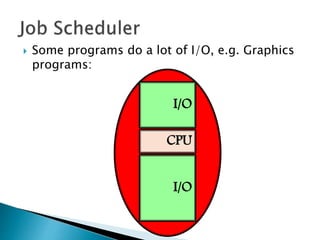
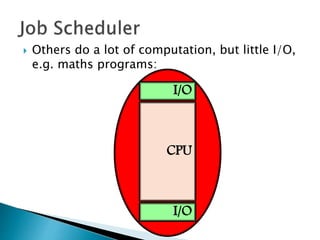
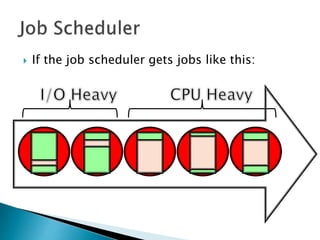
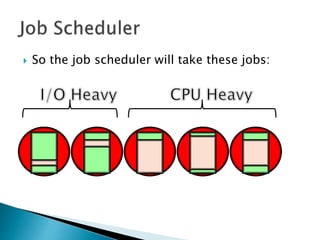
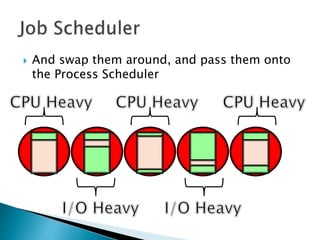
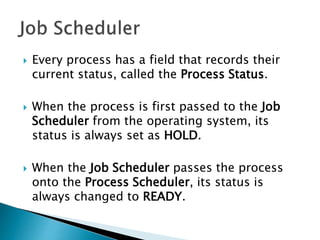
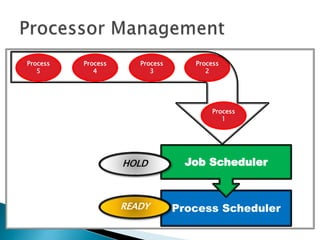
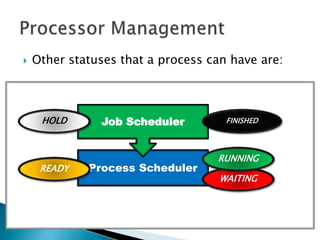
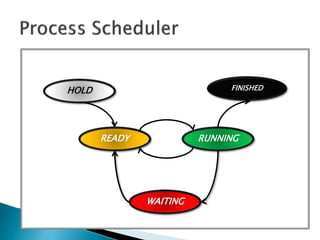
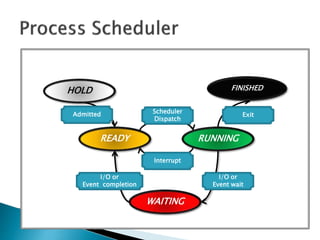
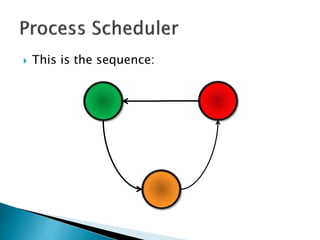
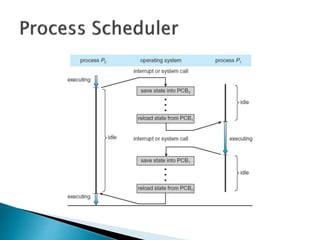
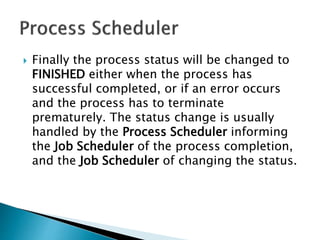
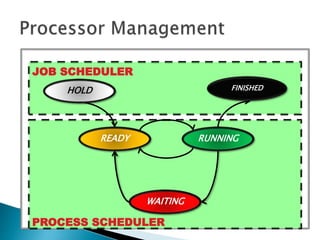
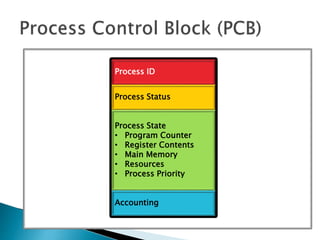
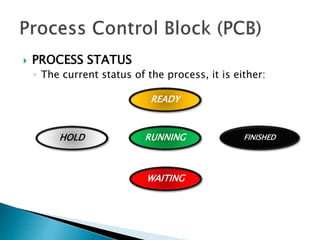
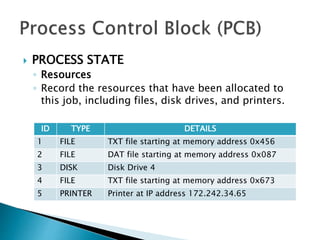
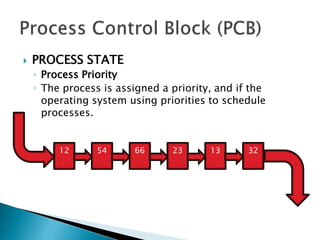
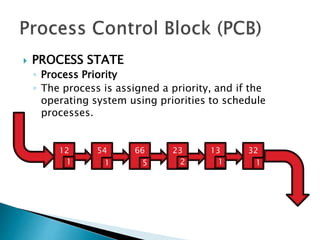
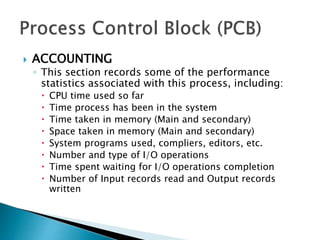
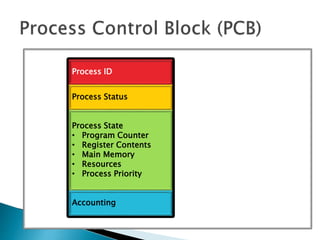
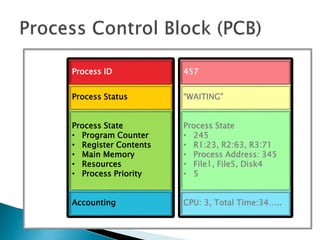
The document discusses how operating systems use processes and scheduling to allow multiple programs to run simultaneously. It explains that a process is the running instance of a program and contains the program counter, registers, memory allocation, and other state information. The operating system uses process scheduling and a process control block (PCB) for each process to track status, allocate CPU time, and handle interrupts and blocking for I/O. It outlines common scheduling algorithms like first-come first-served, shortest job next, priority, and round robin.