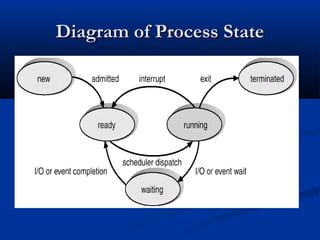
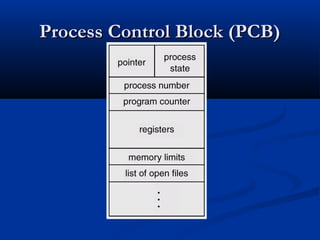
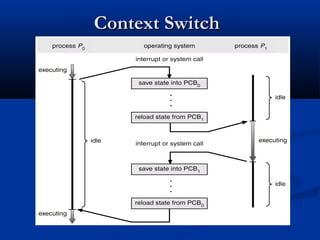
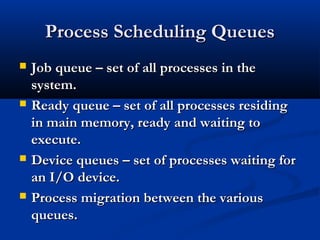
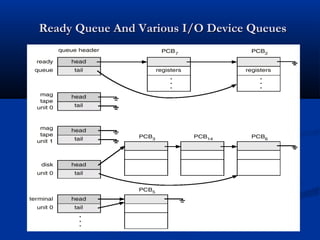
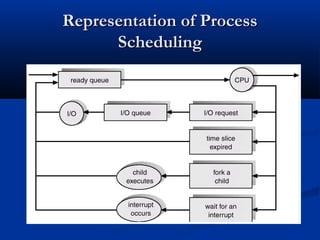
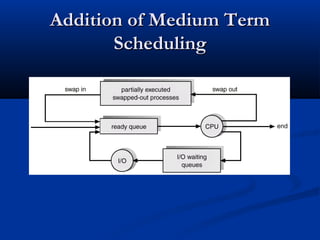
This document discusses process management in operating systems. It defines a process as a program in execution. Processes can be either CPU-bound or I/O-bound. The operating system manages processes through functions like creation, scheduling, and context switching. Processes exist in various states like running, ready, waiting, and terminated. The CPU utilizes scheduling algorithms like first come first served and round robin to allocate processes to the CPU. Processes communicate through interprocess communication mechanisms like message passing and shared memory.