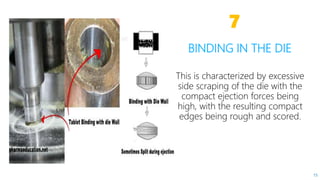
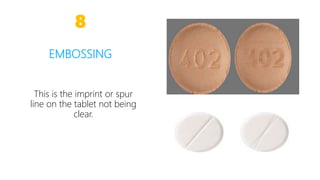
This document summarizes common defects that can occur during tablet manufacturing such as capping, lamination, sticking, picking, mottling, chipping, binding in the die, embossing, low tensile strength, and weight variation. For each defect, the document outlines the causes and how to prevent the defect from occurring. The document provides references for additional information on tablet defects that can be avoided.