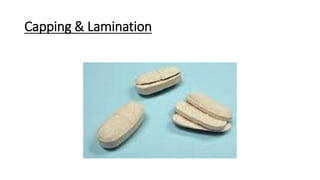
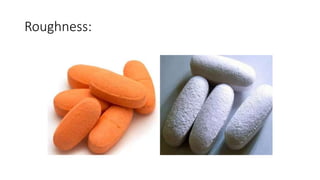
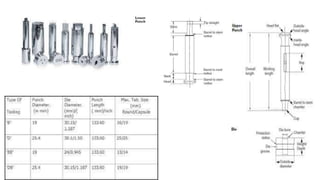
This document summarizes common defects that can occur during tablet processing and coating. It describes defects such as capping, lamination, picking and sticking that can happen during compression from factors like moisture content, tooling issues, and compression speed. Defects in film coating like roughness, orange peel effect, bridging and filling are also outlined along with causes and remedies. Various tablet tooling sizes and types are defined at the end.