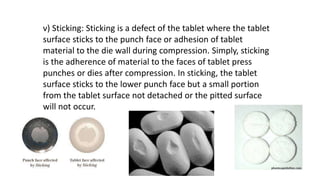
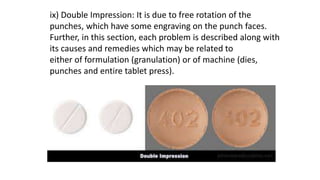
This document discusses common tablet defects including capping, lamination, cracking, chipping, sticking, picking, binding, mottling, double impression, and edging/collaring. For each defect, the causes and remedies are provided. The main causes are related to formulation issues like moisture content, binder/lubricant amount, granule size/properties. The remedies involve modifying the formulation, drying process, compression settings and using proper tooling/punches.