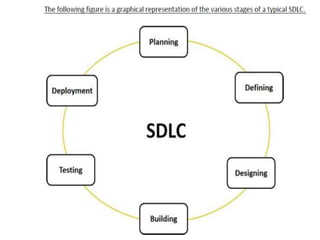
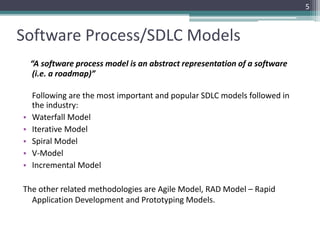
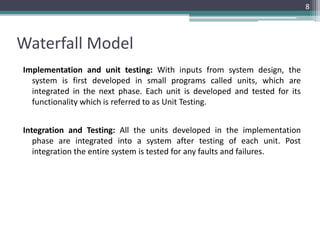
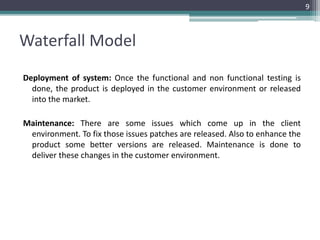
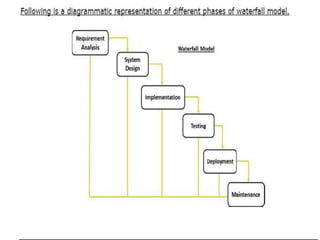
This document provides an introduction to the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process for a software engineering course. It describes the typical stages of the SDLC, including planning, requirements analysis, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. It then focuses on explaining the Waterfall model as one of the most popular SDLC models, outlining its sequential phases and noting that it is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and stable scope.