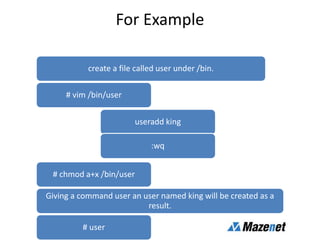
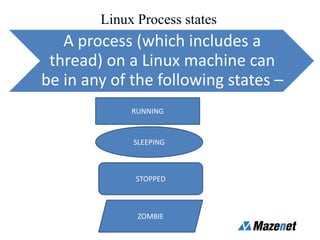
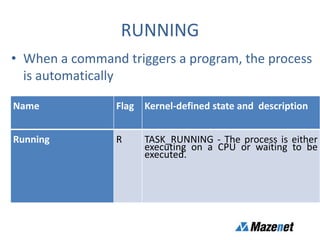
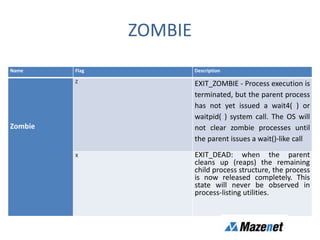
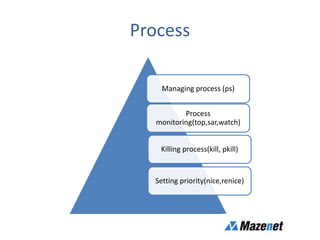
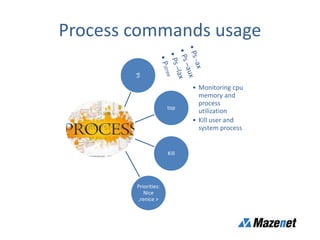
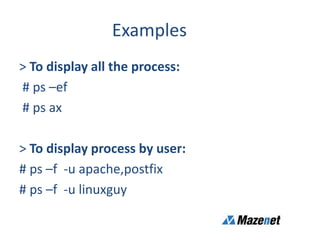
This document discusses processes in Linux. It defines a process as a running instance of a program in memory that is allocated space for variables and instructions. All processes are descended from the systemd process. It describes process states like running, sleeping, stopped, and zombie. It also discusses process monitoring and management tools like top, ps, kill, and setting process priorities with nice and renice. Examples are provided on using ps to view specific processes by user, name, ID, parent ID, and customize the output.