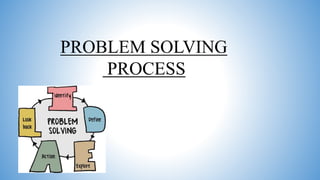
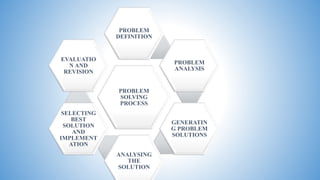
This document provides an overview of problem solving methods and scientific methods. It defines problem solving as a process of overcoming difficulties to attain a goal using sequential steps of observation through action. The scientific method is described as a systematic, empirical, and critical investigation of hypotheses about natural phenomena. Both approaches involve defining the problem, analyzing it, generating and evaluating potential solutions, selecting the best solution, and evaluating/revising it. The key difference is that scientific methods aim to develop generalizable knowledge through controlled experiments, while problem solving focuses on a specific problem.