1. The document discusses the process of administration, scoring, and reporting of tests, including planning tests based on learning objectives, preparing blueprints, developing test items, administering tests uniformly, scoring objectively, and evaluating tests and student performance.
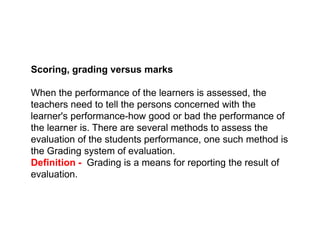
2. It also compares grading systems to marking systems, noting advantages of letter grades over numerical marks in providing summaries, combining scores, and comparing performance.
3. Procedures for assigning letter grades include transforming various assessment scores to percentile ranks, weighting scores, summing totals, and using standards to determine grade cutoffs.