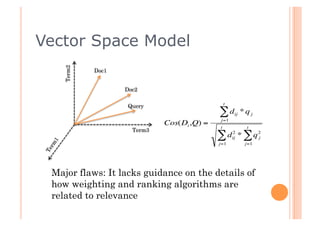
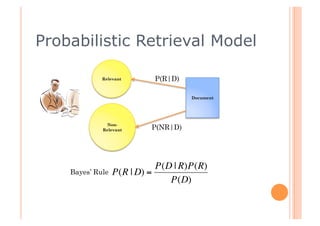
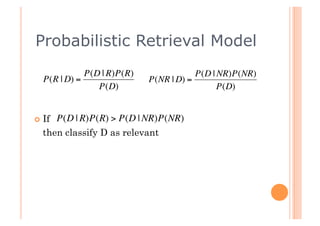
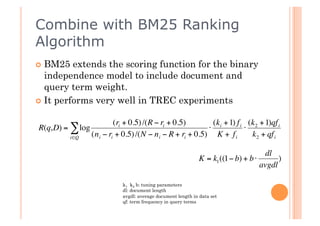
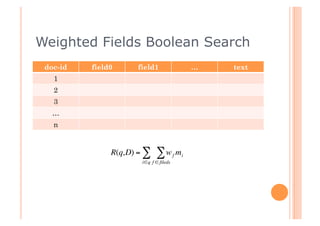
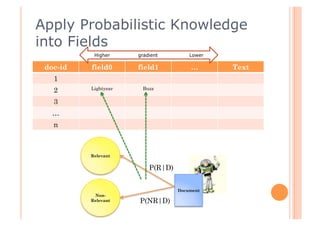
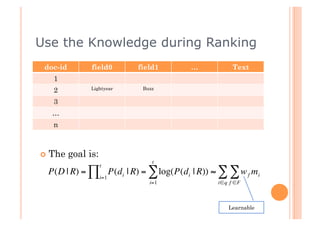
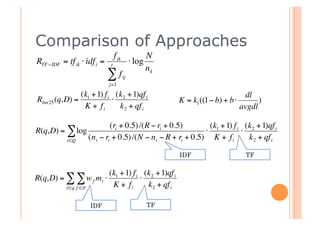
This document discusses incorporating probabilistic retrieval knowledge into TFIDF-based search engines. It provides an overview of different retrieval models such as Boolean, vector space, probabilistic, and language models. It then describes using a probabilistic model that estimates the probability of a document being relevant or non-relevant given its terms. This model can be combined with the BM25 ranking algorithm. The document proposes applying probabilistic knowledge to different document fields during ranking to improve relevance.