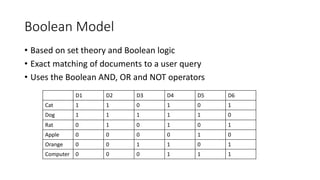
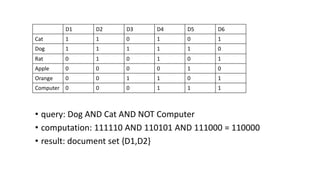
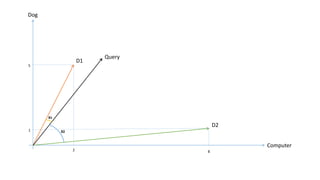
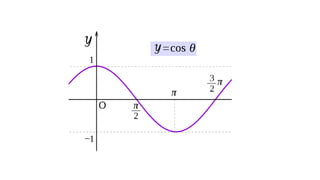
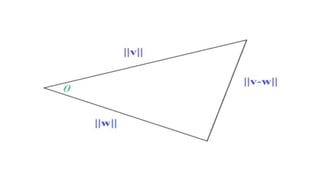
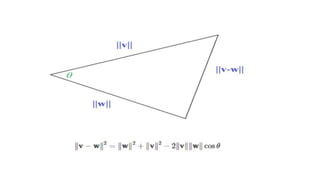
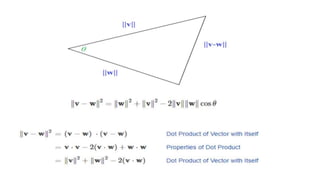
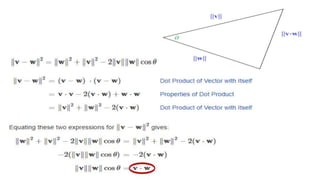
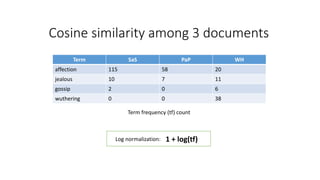
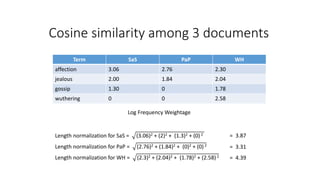
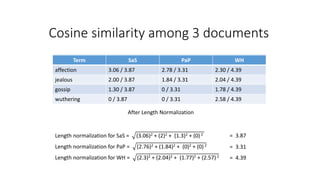
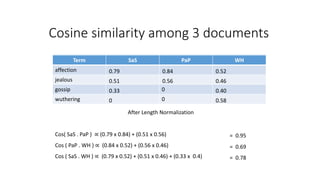
The document compares the Boolean model and the vector space model for information retrieval. The Boolean model emphasizes exact matching using Boolean operators but lacks ranking and synonymy considerations, while the vector space model represents documents and queries as vectors, allowing for similarity computation through cosine similarity. Both models have advantages and disadvantages in terms of implementation, scalability, and processing speed.