The document discusses the binomial distribution, which models the number of successes in a fixed number of Bernoulli trials. Some key points:
1) A binomial experiment consists of n independent trials with two possible outcomes (success/failure) and a fixed probability p of success on each trial.
2) The binomial random variable X represents the number of successes in n trials.
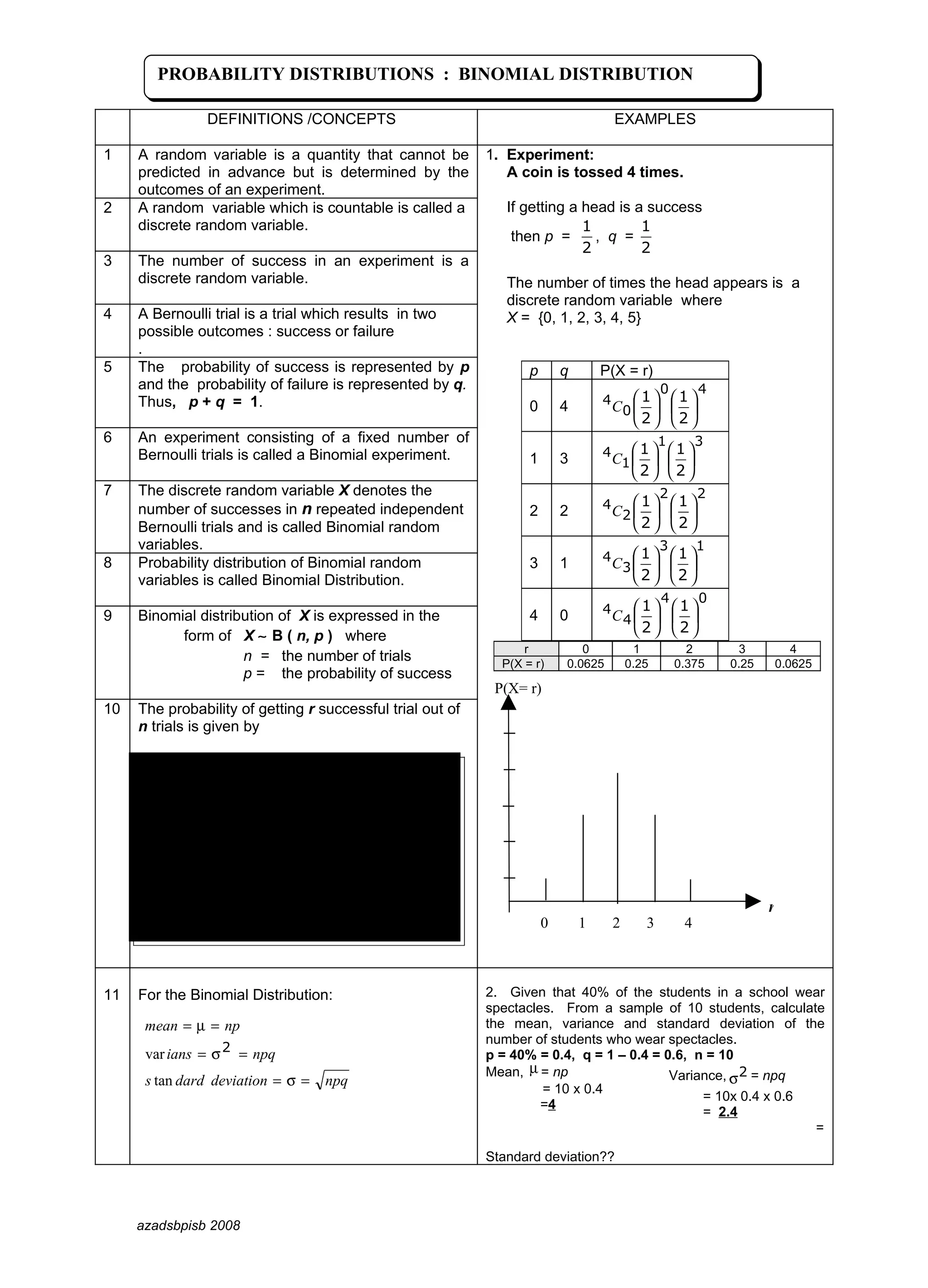
3) The probability of getting exactly r successes in n trials is given by the binomial probability mass function P(X=r) = nCr * pr * q(n-r), where q = 1 - p.
4) For a binomial distribution, the mean is μ = np, the variance is σ2 = np