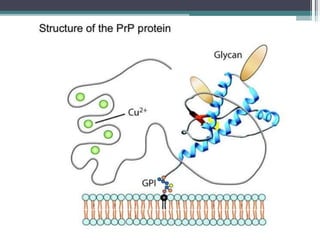
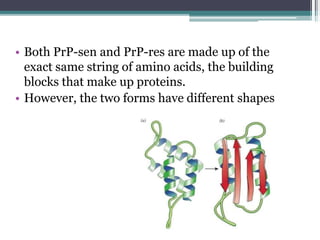
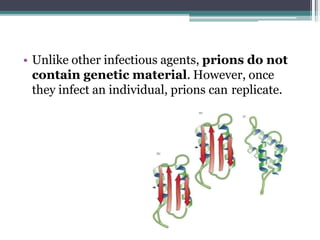
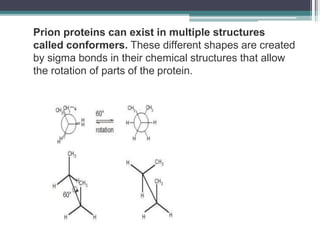
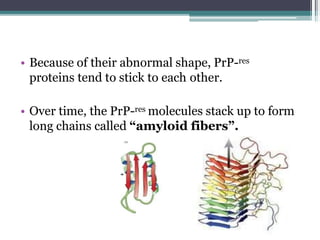
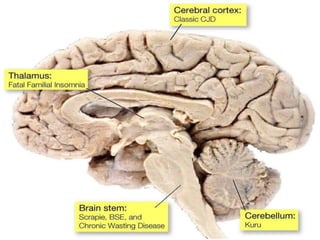
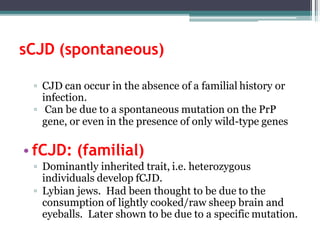
Prions are abnormal infectious protein particles that cause neurodegenerative diseases. They can occur through infection, genetic mutation, or spontaneously. Prions are unique in that they can replicate without nucleic acids by converting normal prion proteins (PrP-sen) into an abnormal form (PrP-res). Accumulation of PrP-res causes neuronal death and symptoms like dementia. Common prion diseases include Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans and mad cow/scrapie in animals. There is no cure for prion diseases and most result in death within a year of symptoms appearing.