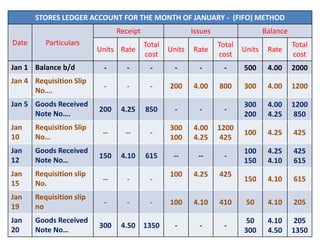
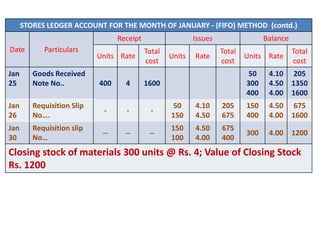
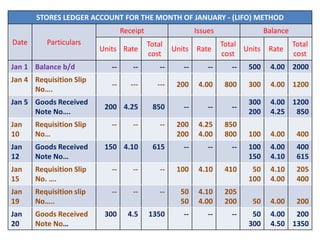
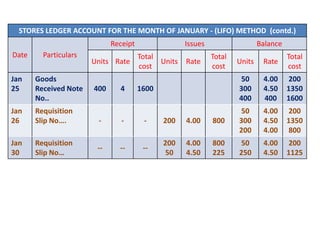
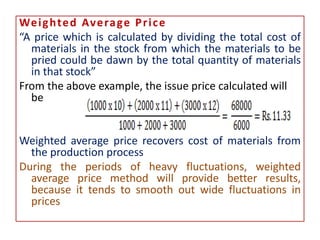
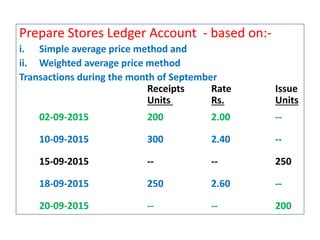
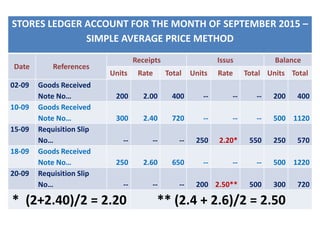
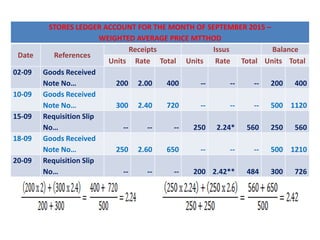
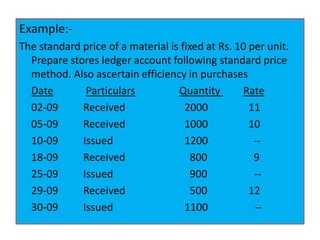
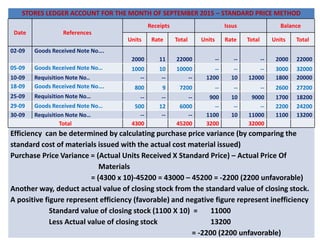
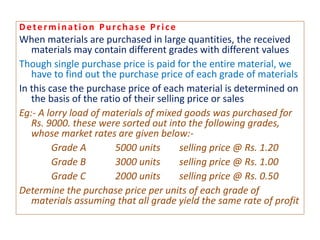
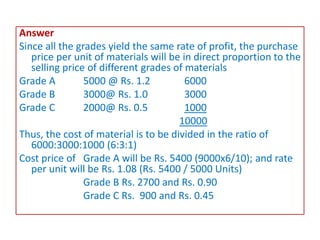
This document discusses various methods for pricing material issues, including first in first out (FIFO), last in first out (LIFO), and average cost methods. FIFO prices issues based on the earliest materials received, while LIFO prices based on the latest materials. Average cost methods calculate a weighted average price based on total cost and quantity to smooth out price fluctuations. The appropriate pricing method depends on factors like price trends and the nature of materials.