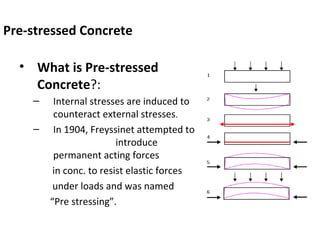
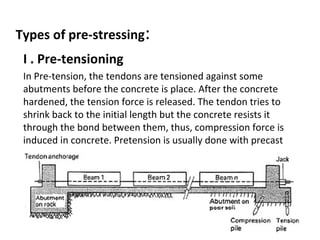
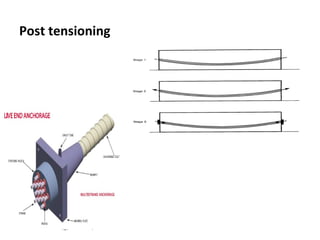
The presentation discusses prestressed concrete, a method where internal stresses are introduced to counteract external forces, improving structural integrity. It outlines the principles of prestressing, including pre-tensioning and post-tensioning methods, alongside their advantages such as reduced material needs and enhanced load resistance. Prestressed concrete is applied in various structures, including bridges and nuclear plants, and is recognized for its cost-effectiveness and strength.