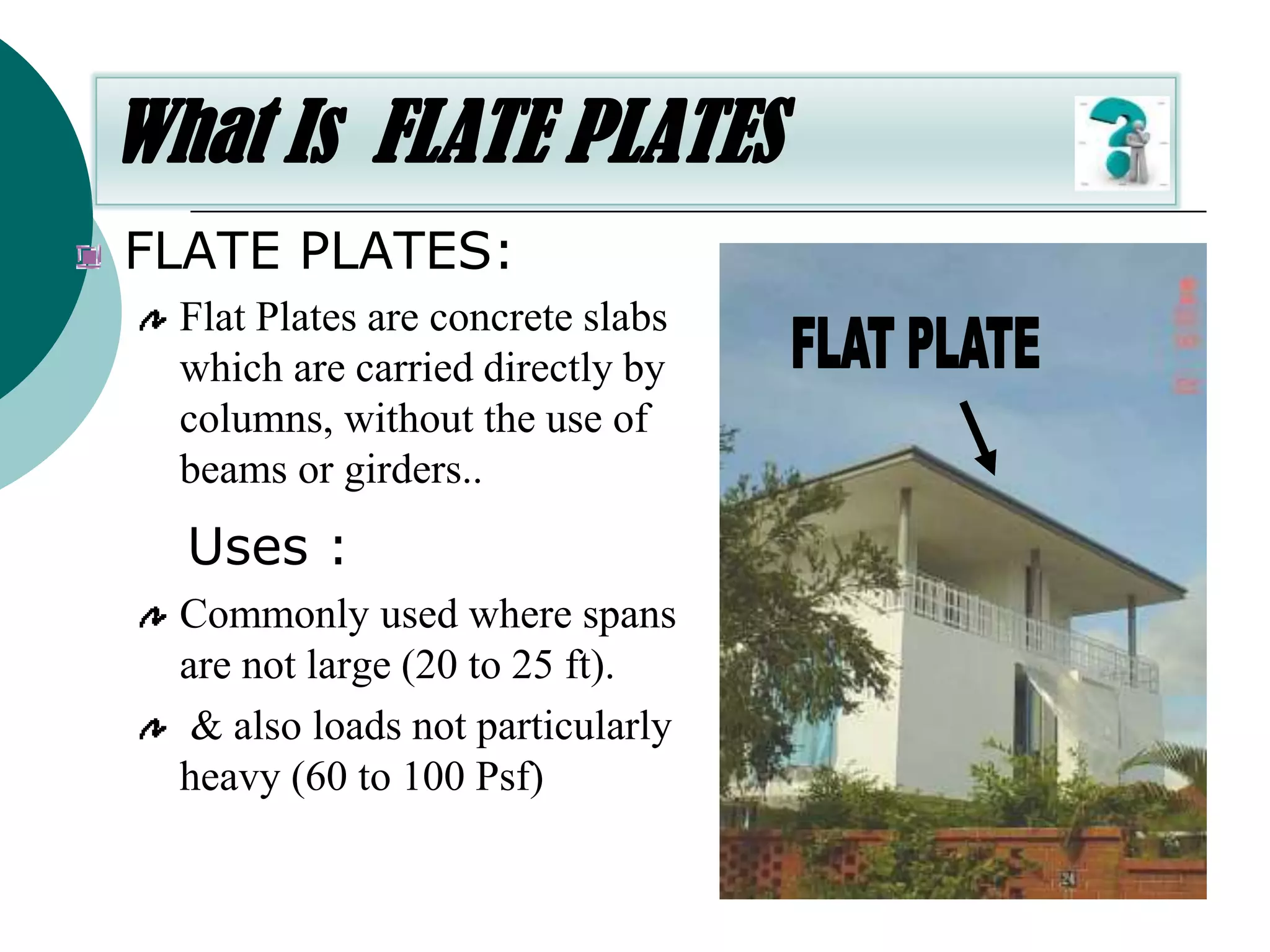
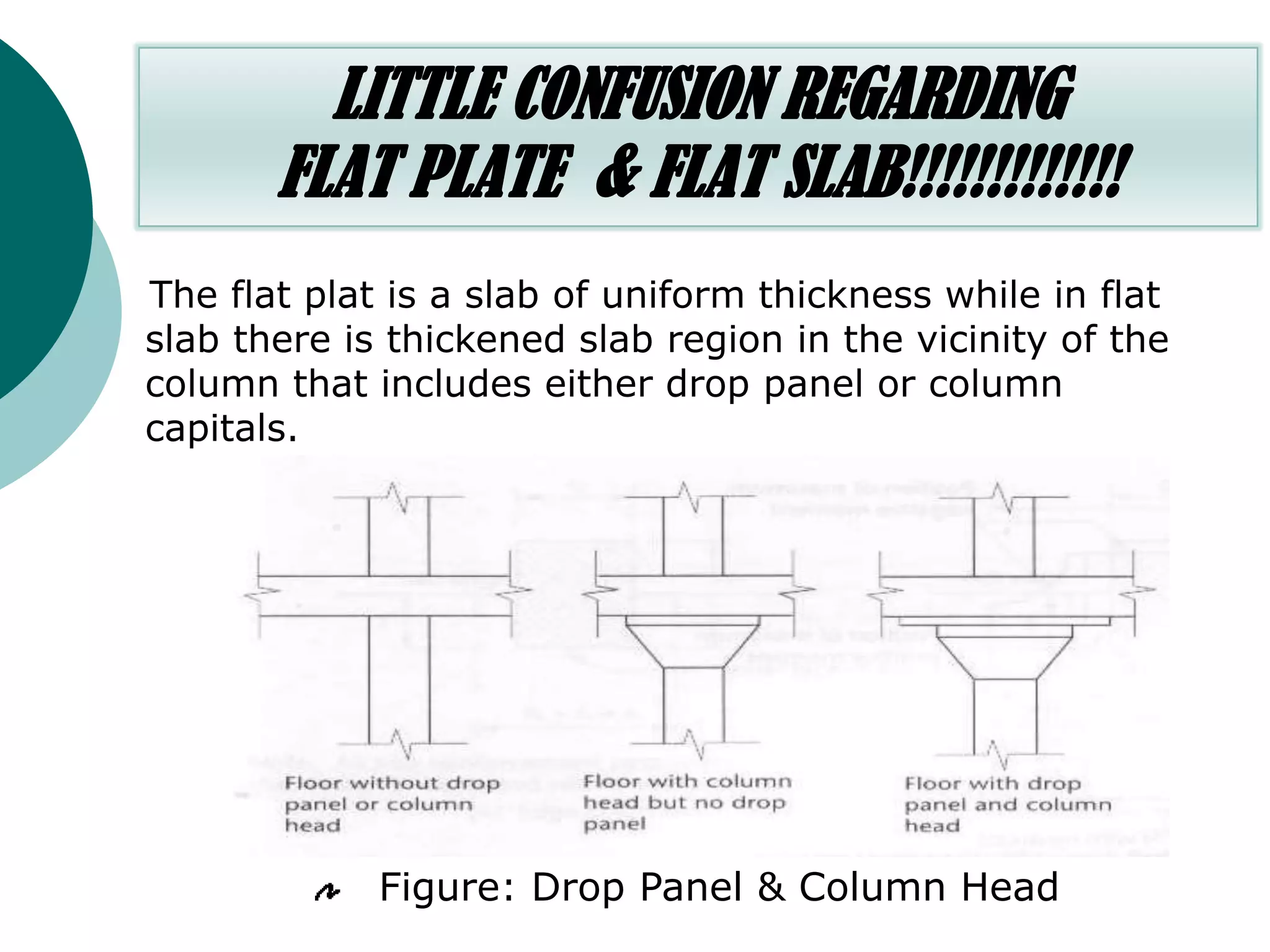
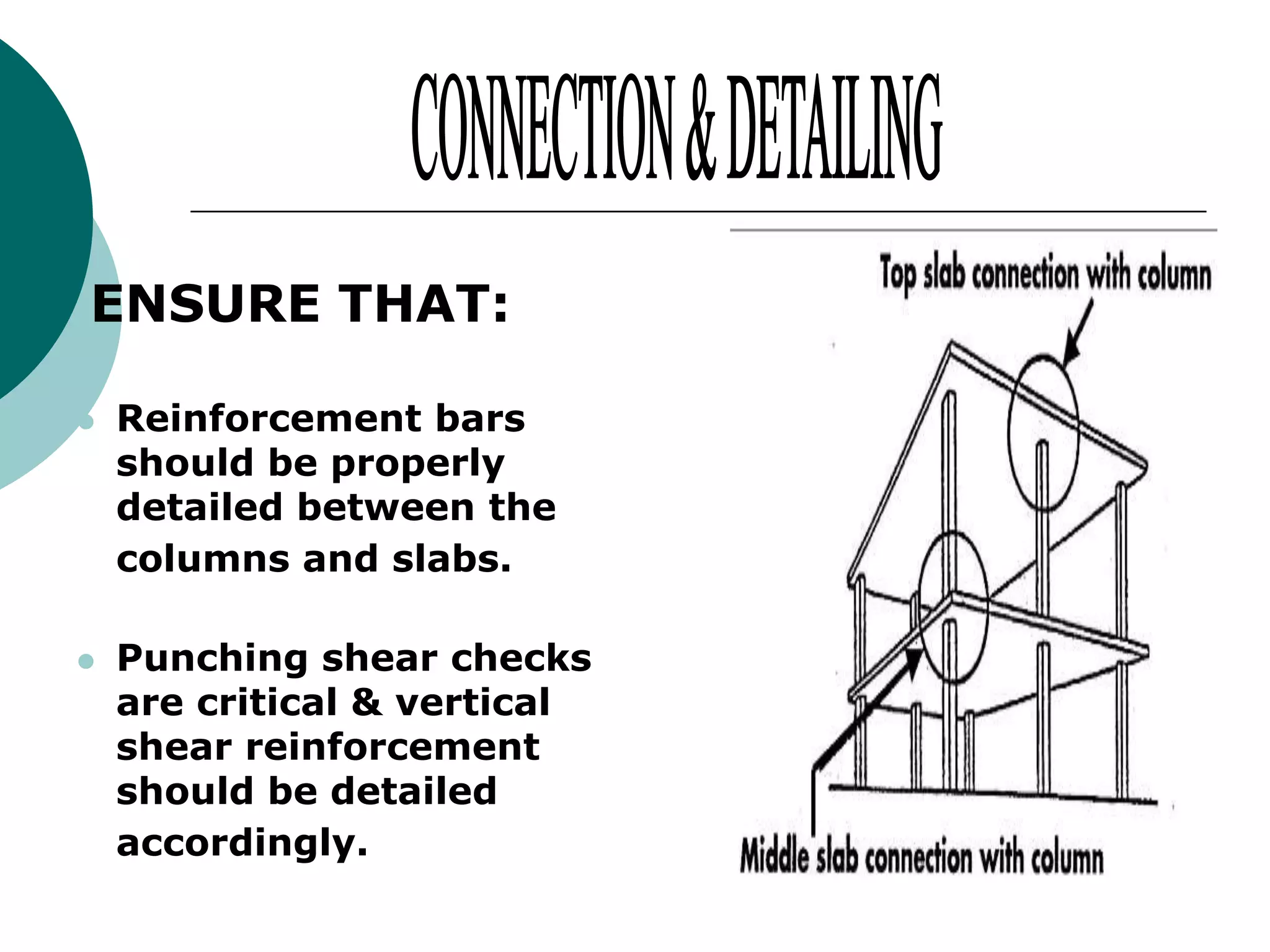
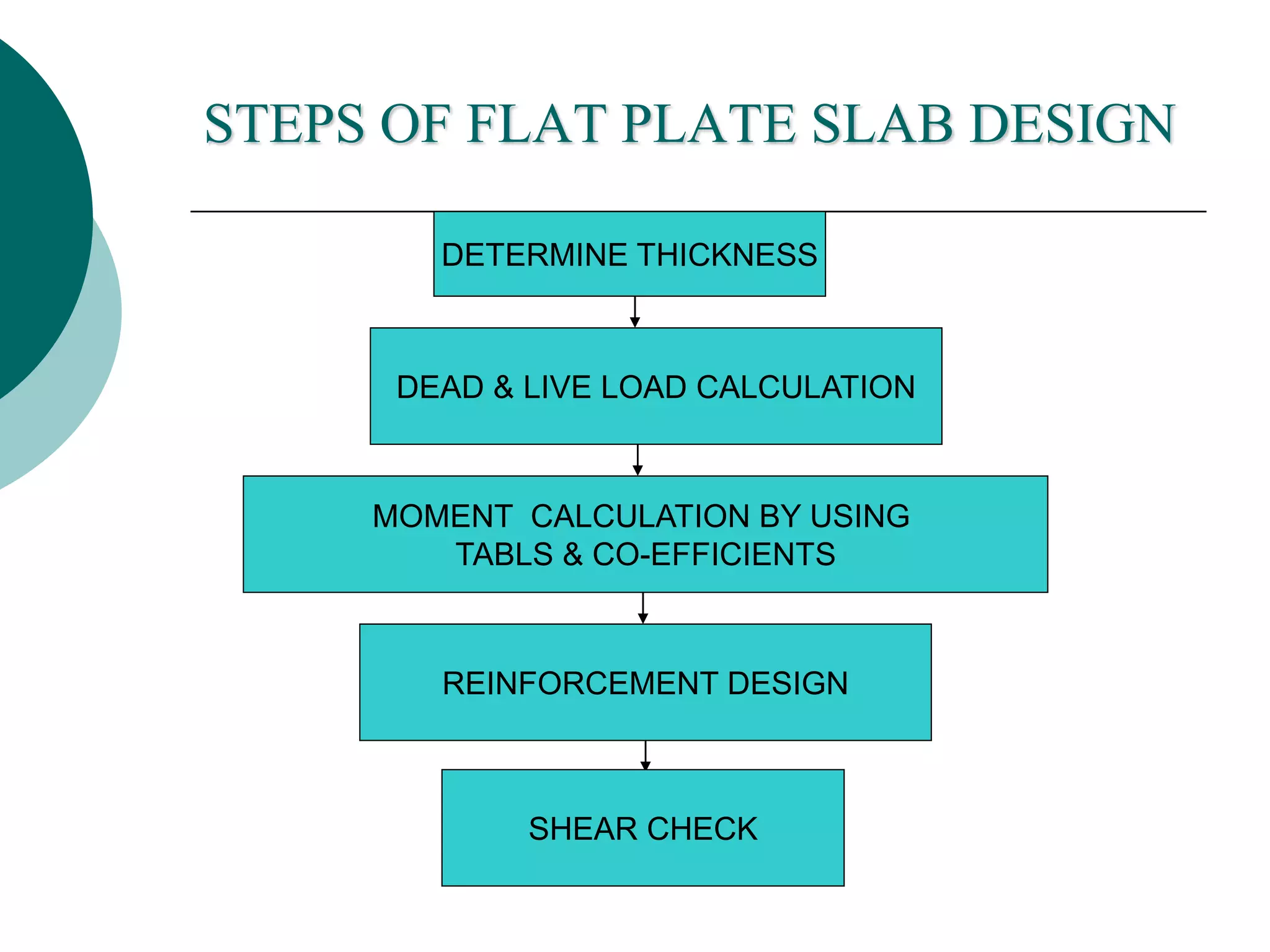
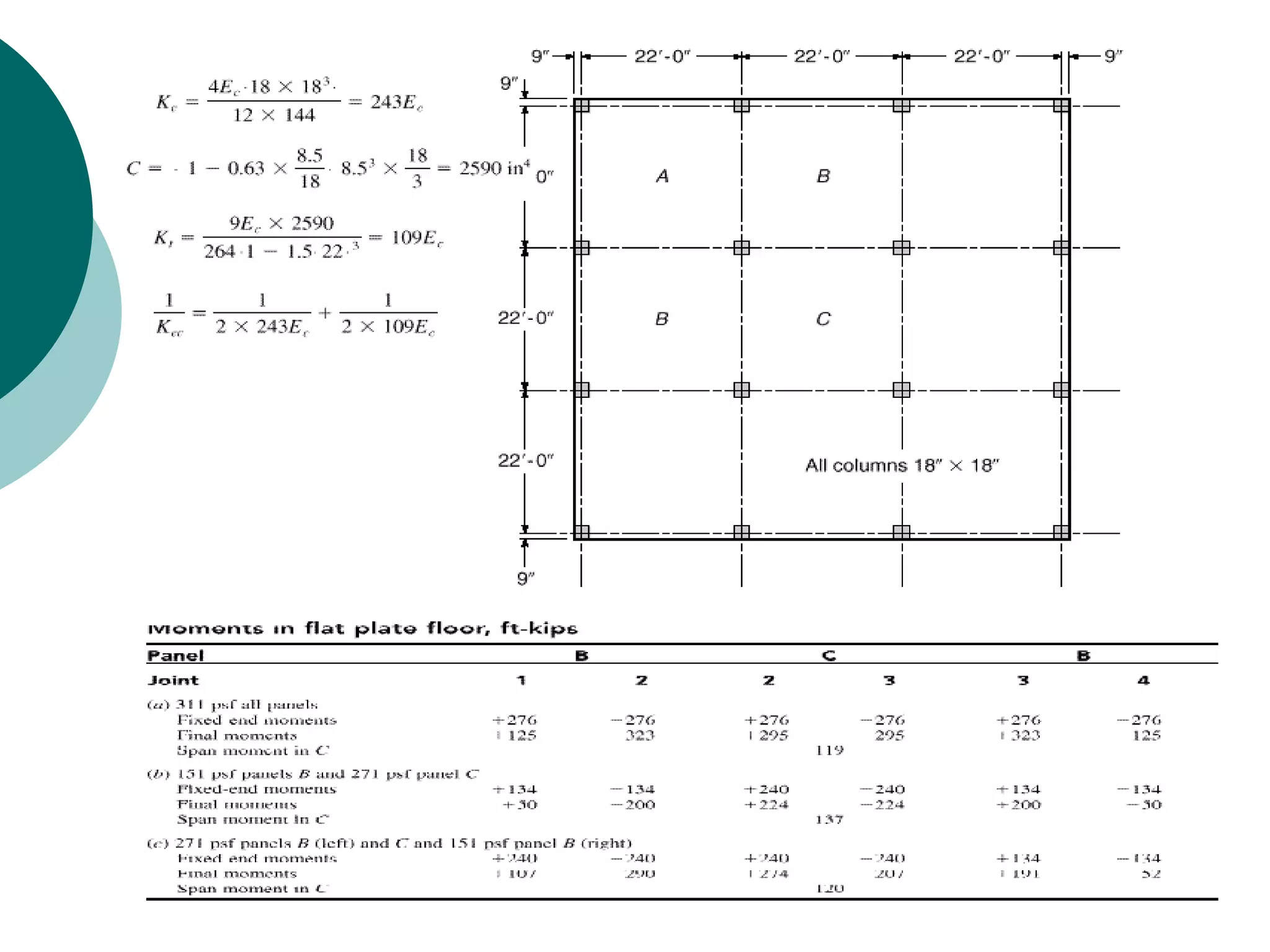
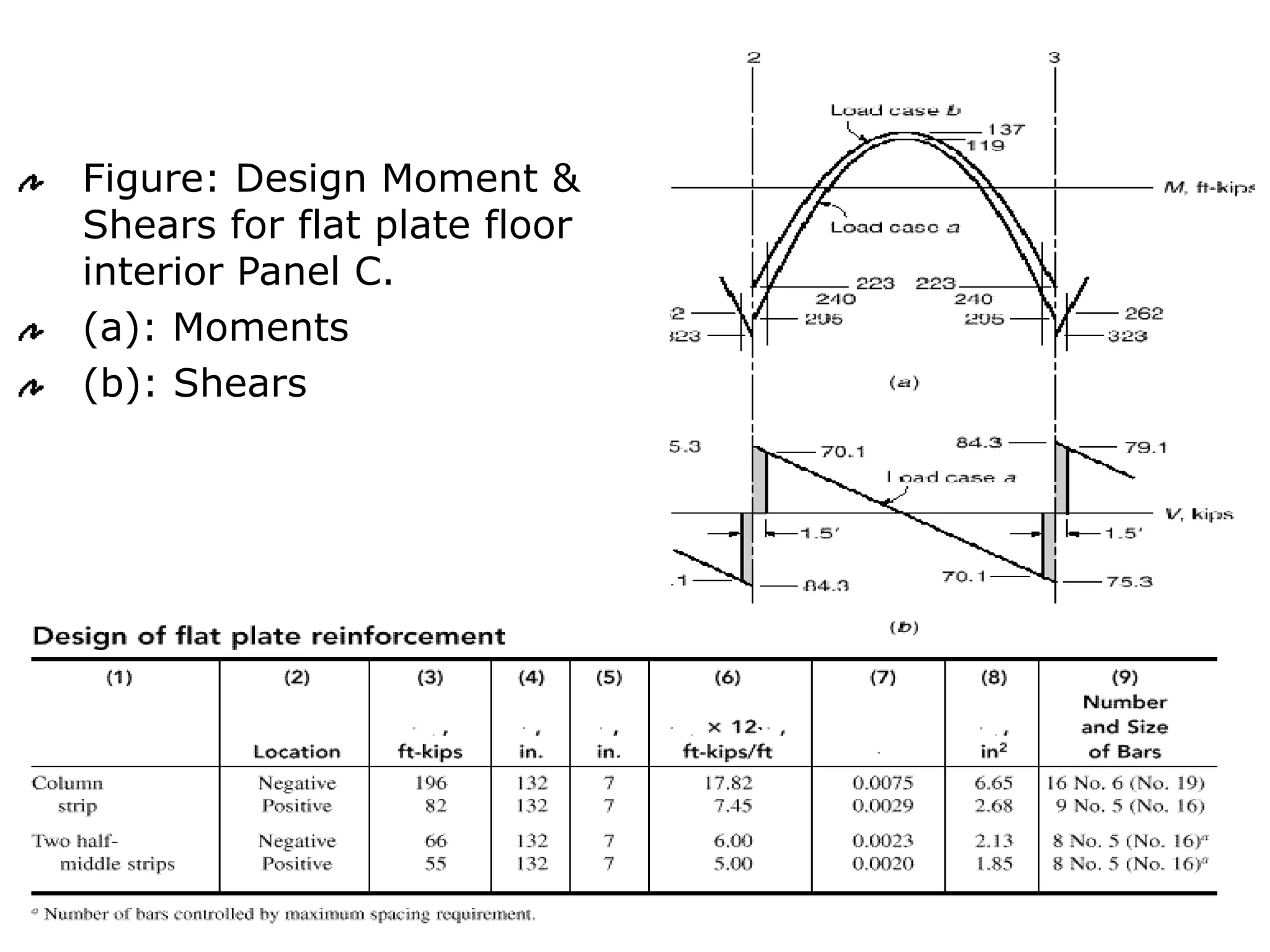
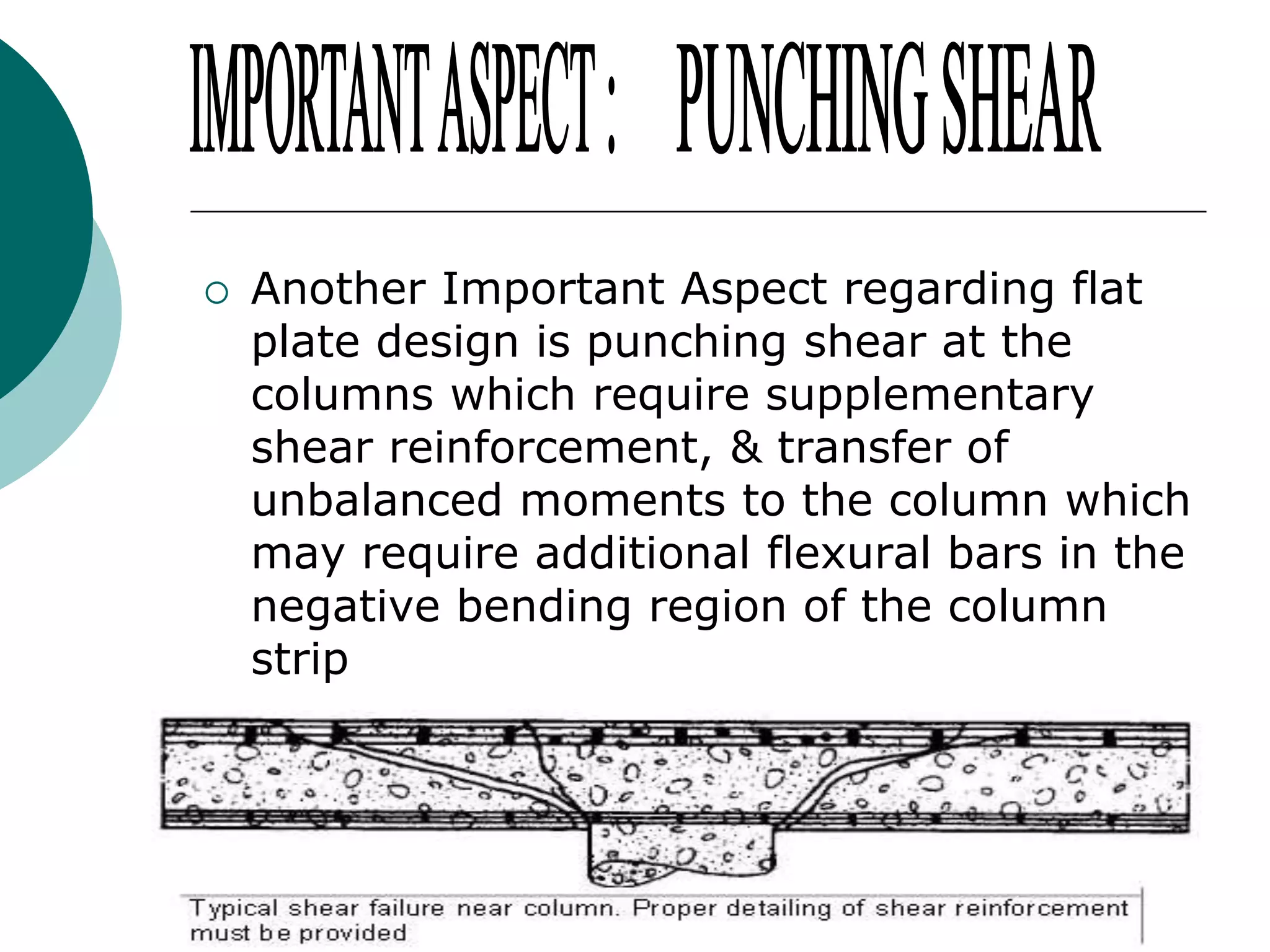
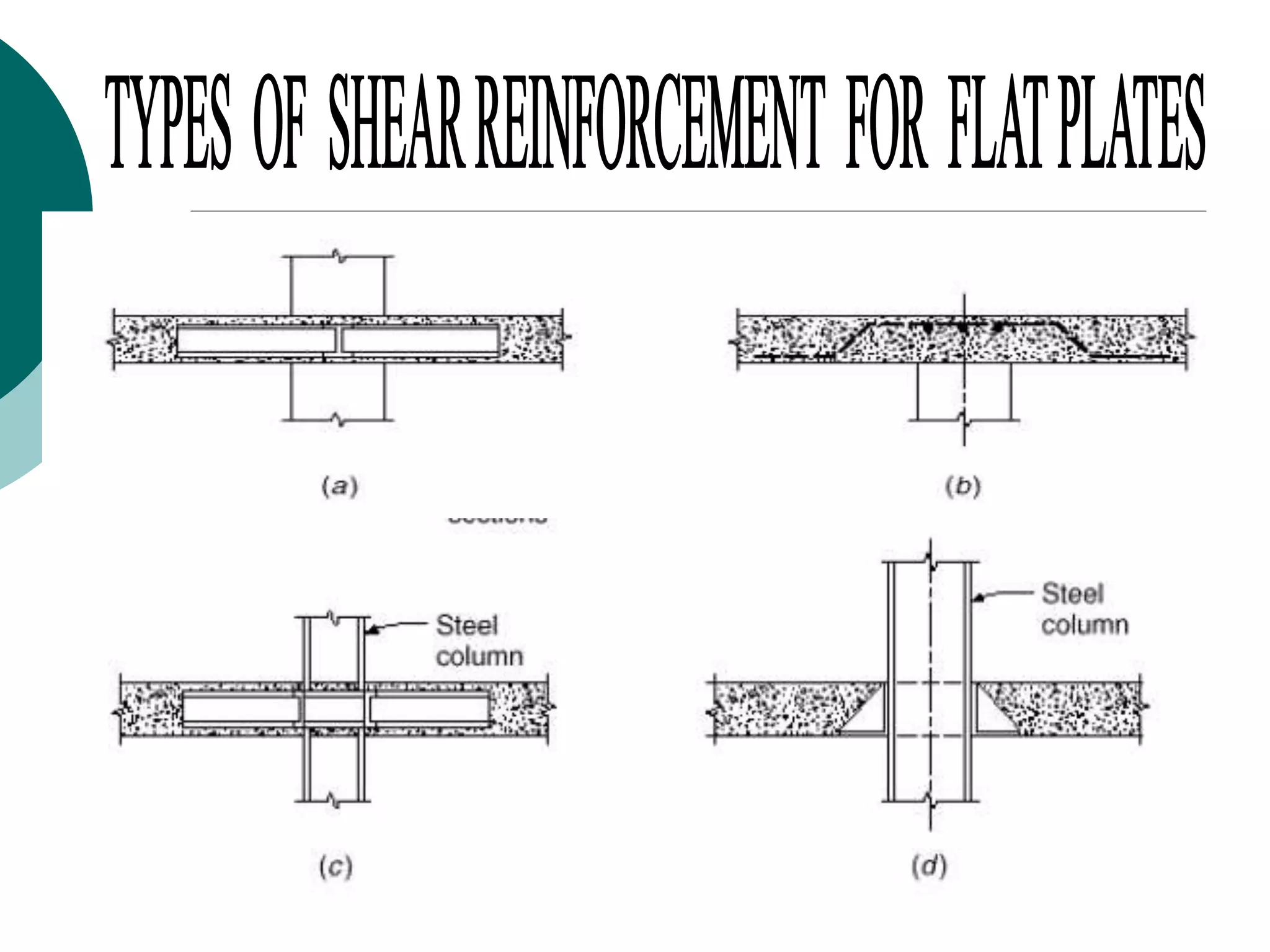
This document discusses the design of flat plate slabs. Flat plates are concrete slabs that are carried directly by columns without beams or girders. They are commonly used for spans up to 25 feet and loads up to 100 pounds per square foot. The load is directly transferred to the columns, making punching shear at the column connections critical. Proper reinforcement detailing is required between the slab and columns. Moment determination and shear design are important steps in the flat plate slab design process. Advantages include simplified formwork and reduced story height, while limitations include increased thickness and weight.