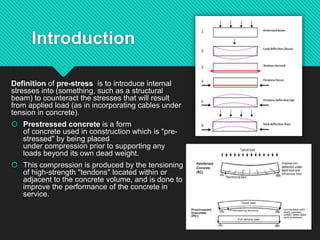
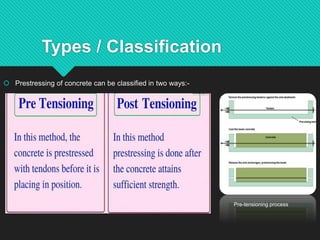
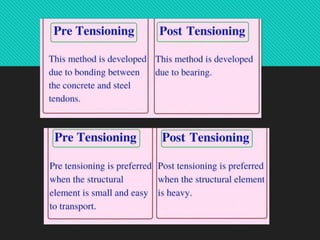
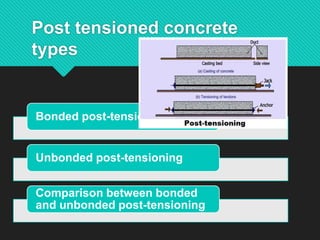
Prestressing is a technique where internal stresses are introduced into a material to counteract loads. In prestressed concrete, high-strength tendons placed under tension are used to put concrete structures into compression before loads are applied. There are two types of prestressing: pre-tensioning, where concrete is cast around tensioned tendons; and post-tensioning, where tendons are tensioned after concrete has set. Bonded post-tensioning permanently bonds tendons to concrete using grout, while unbonded post-tensioning allows tendon movement. Prestressed concrete provides benefits like crack control, durability, and ability to build larger structures. Common applications include bridges, buildings, dams, tanks, and nuclear containment