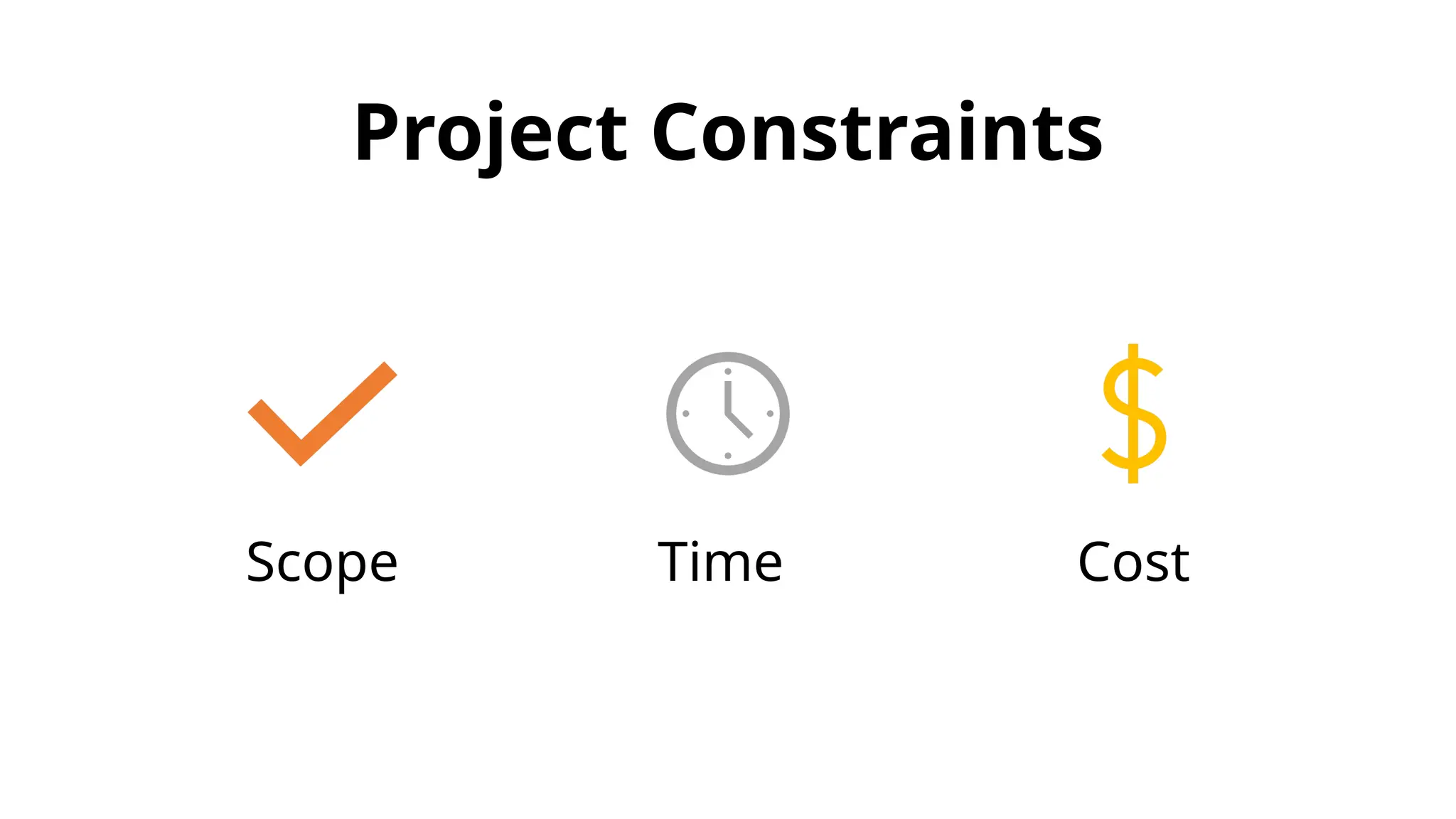
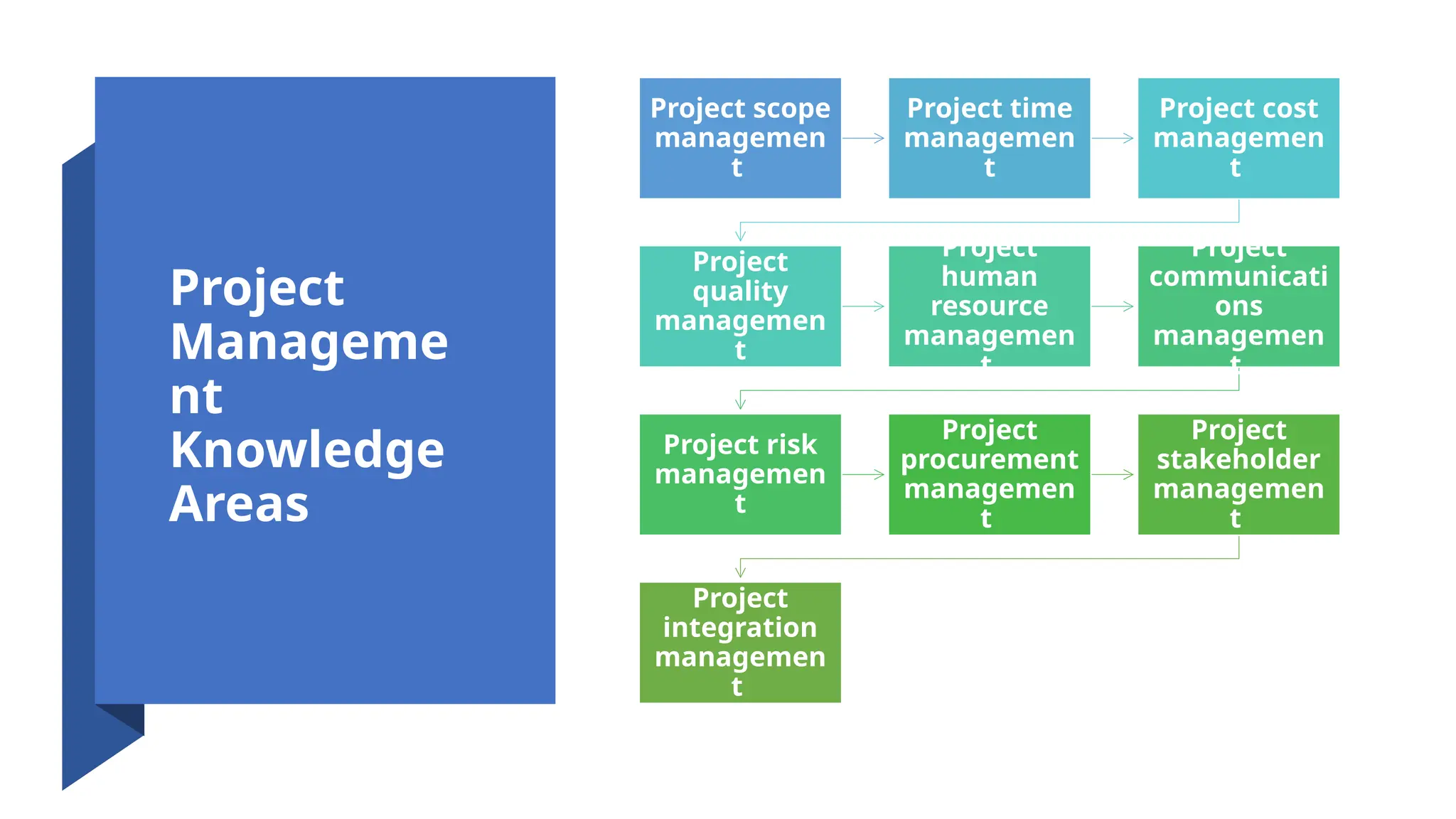
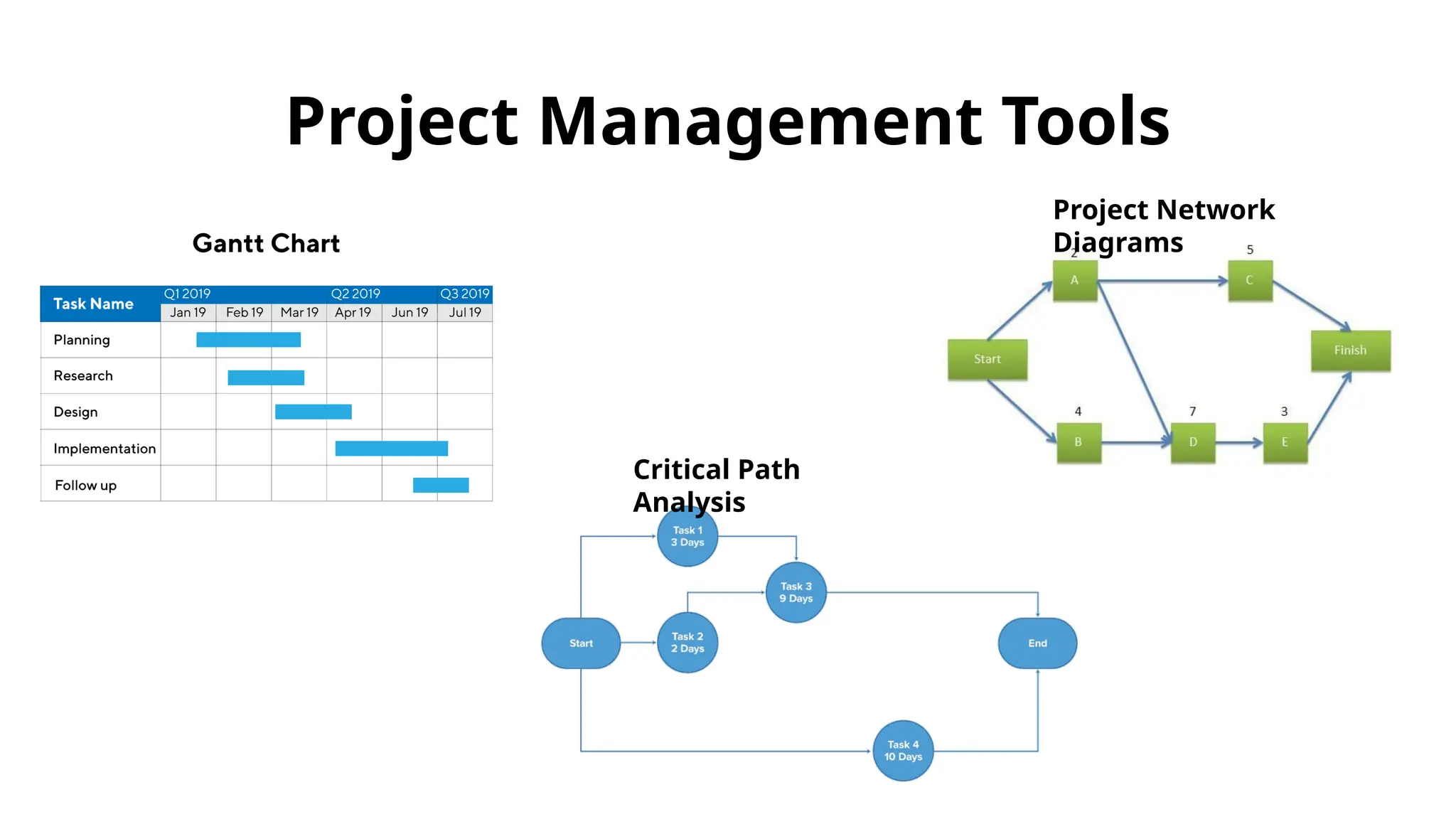
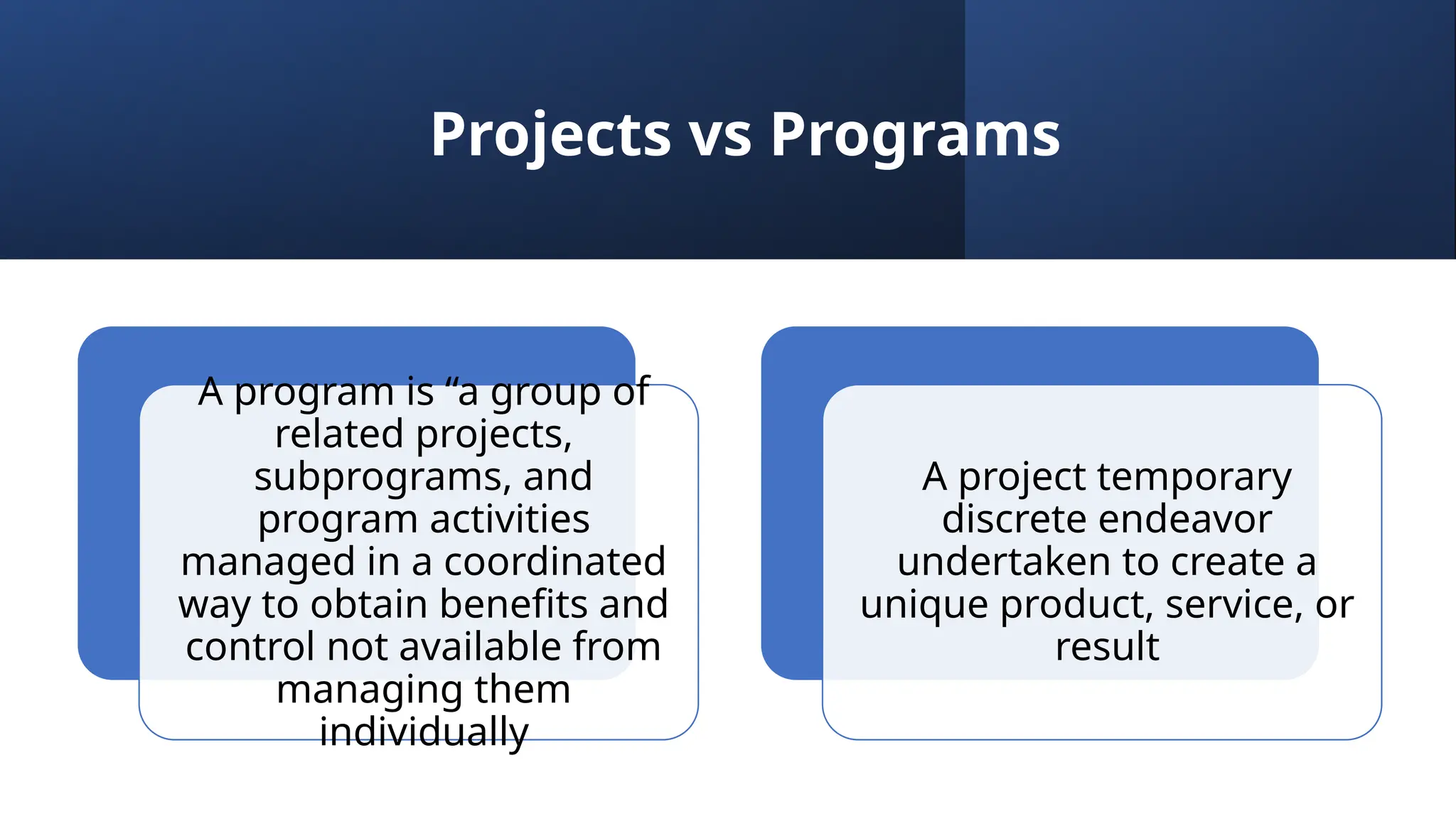
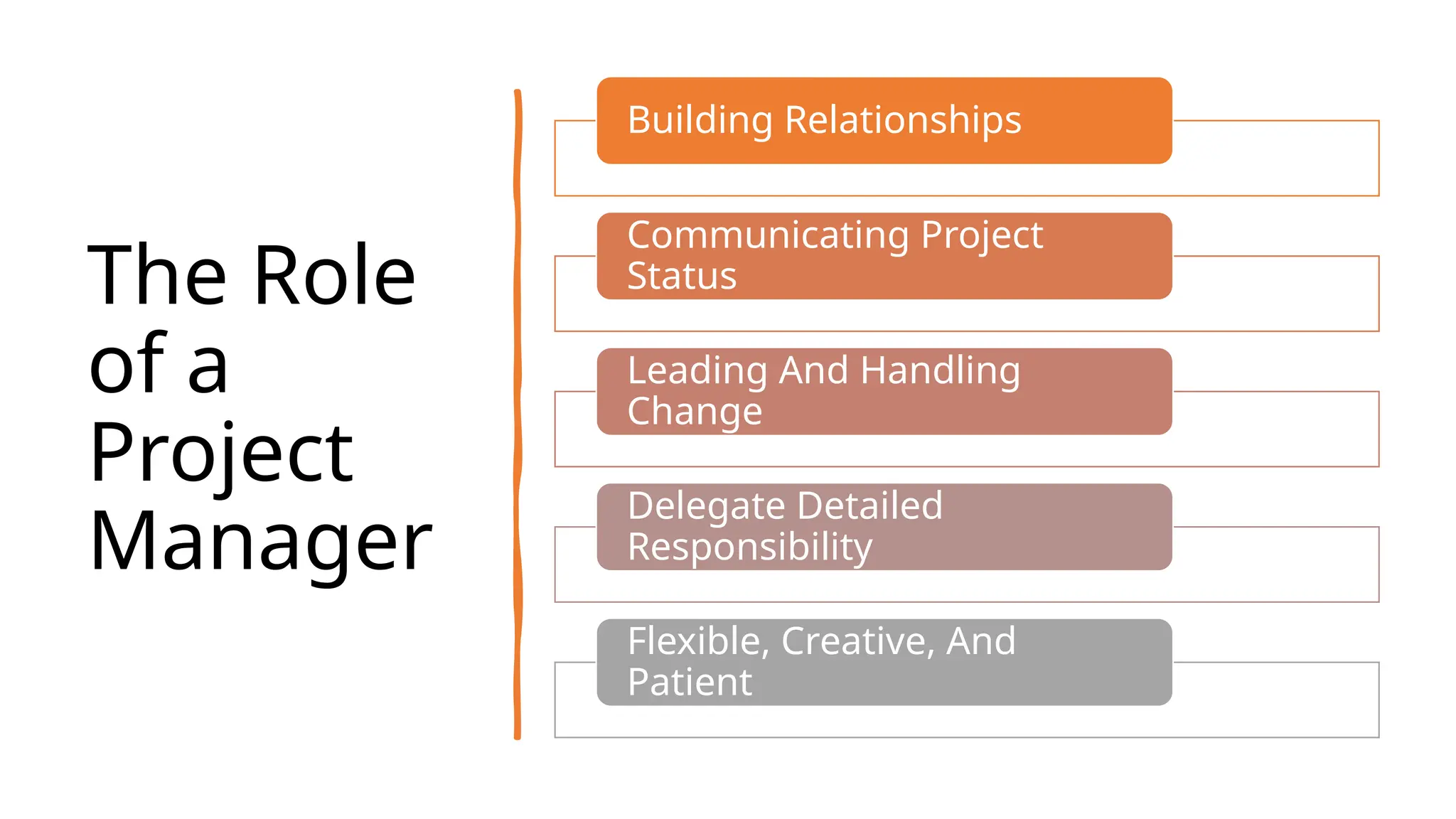
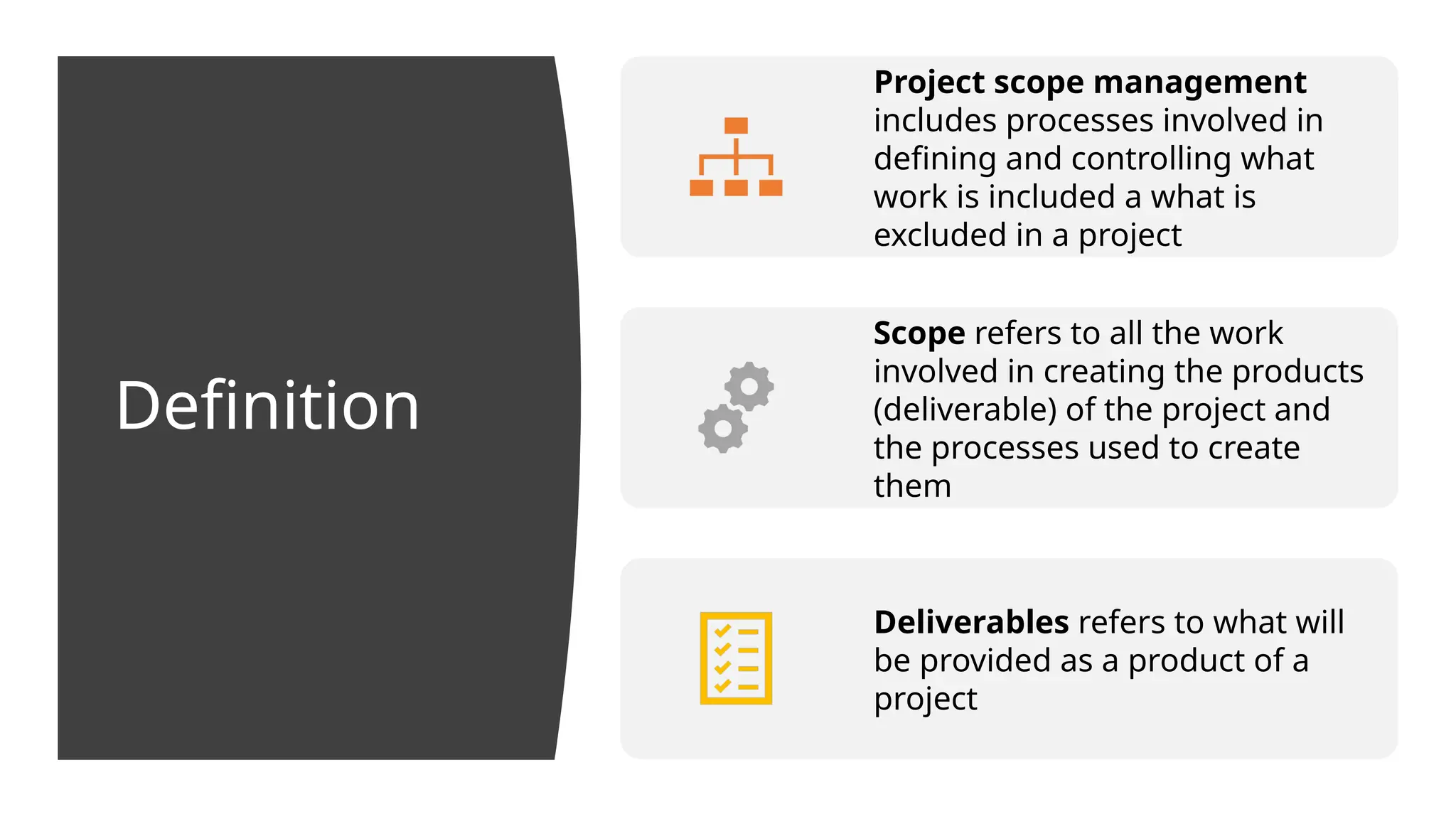
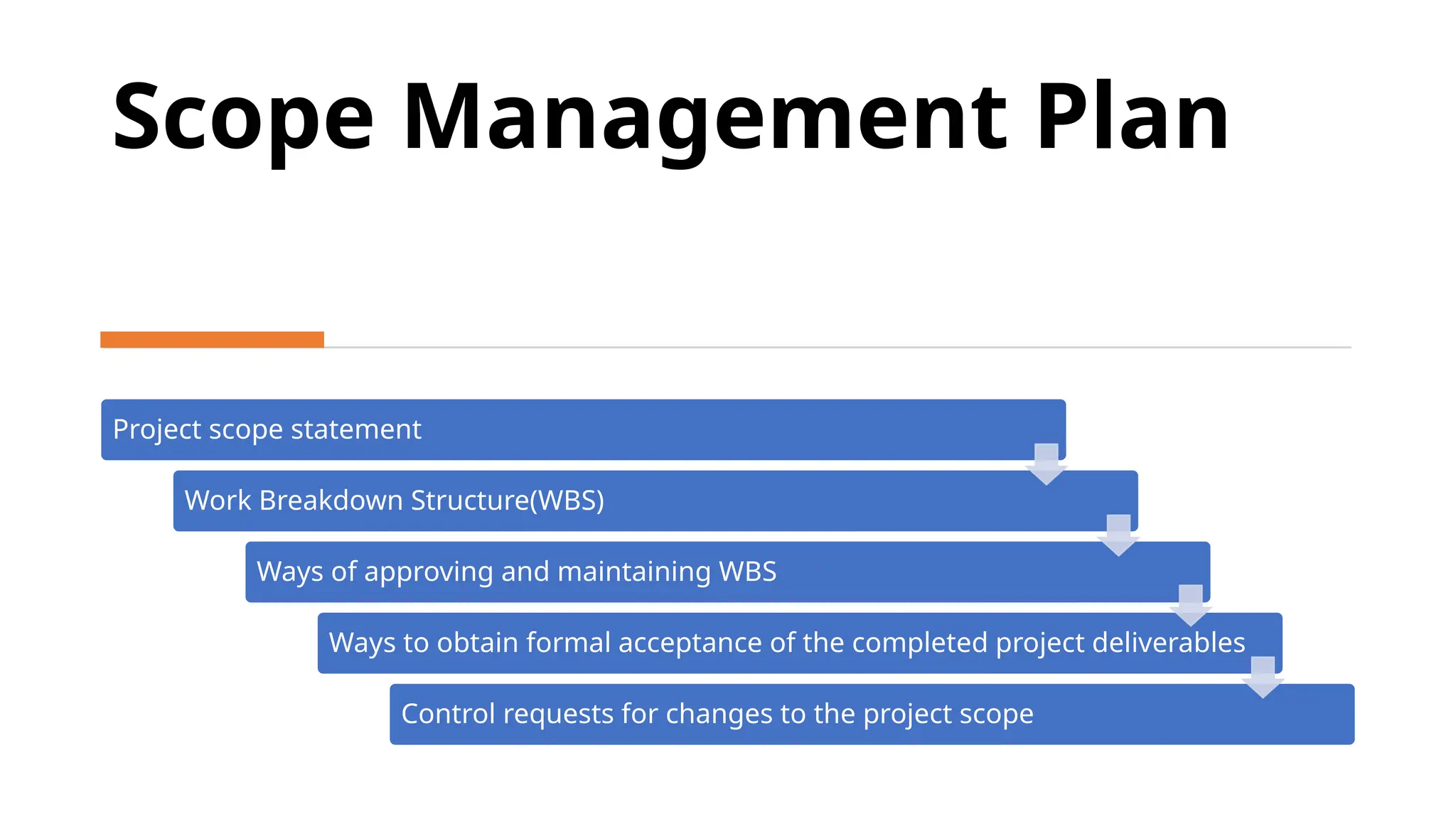
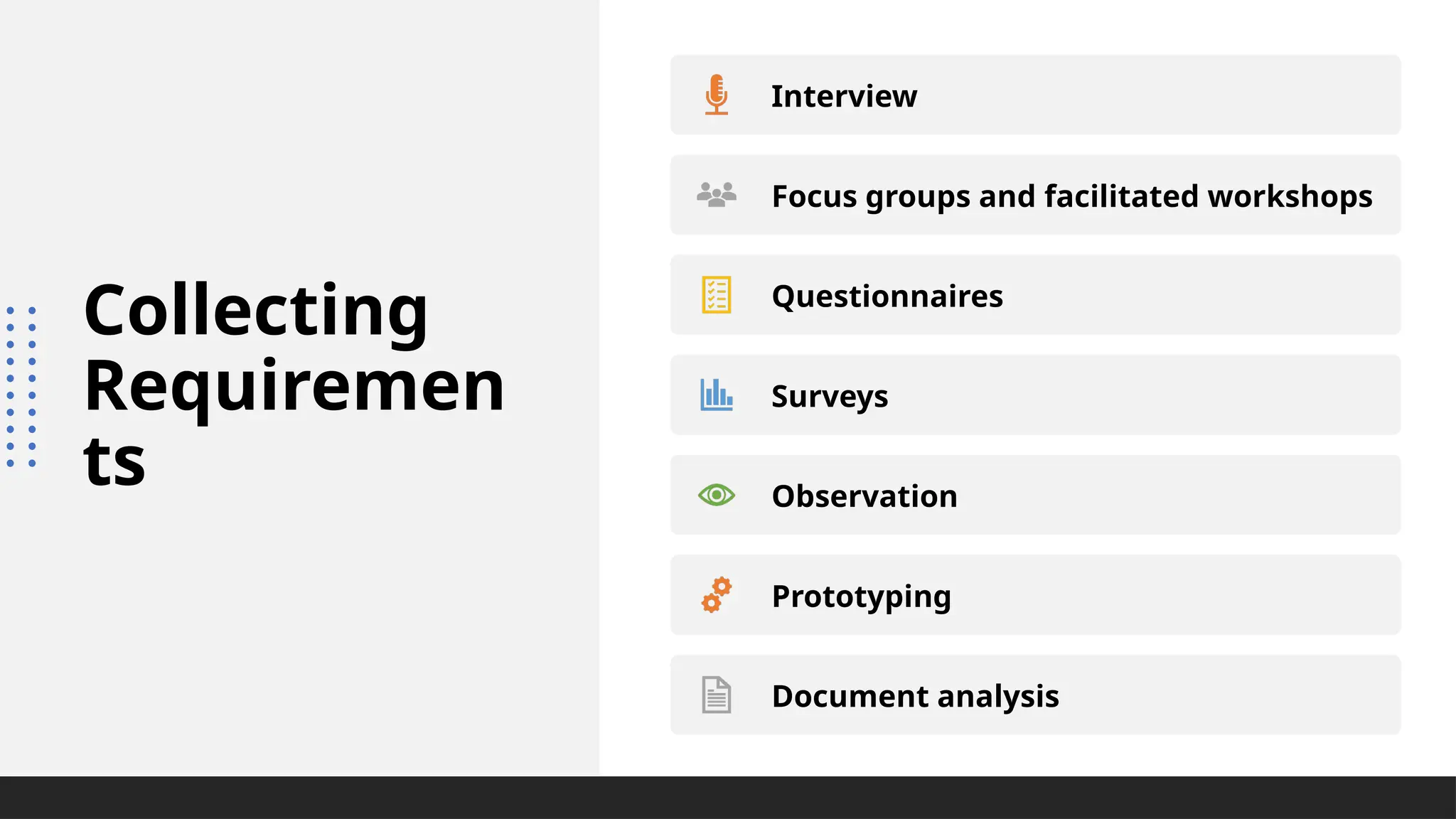
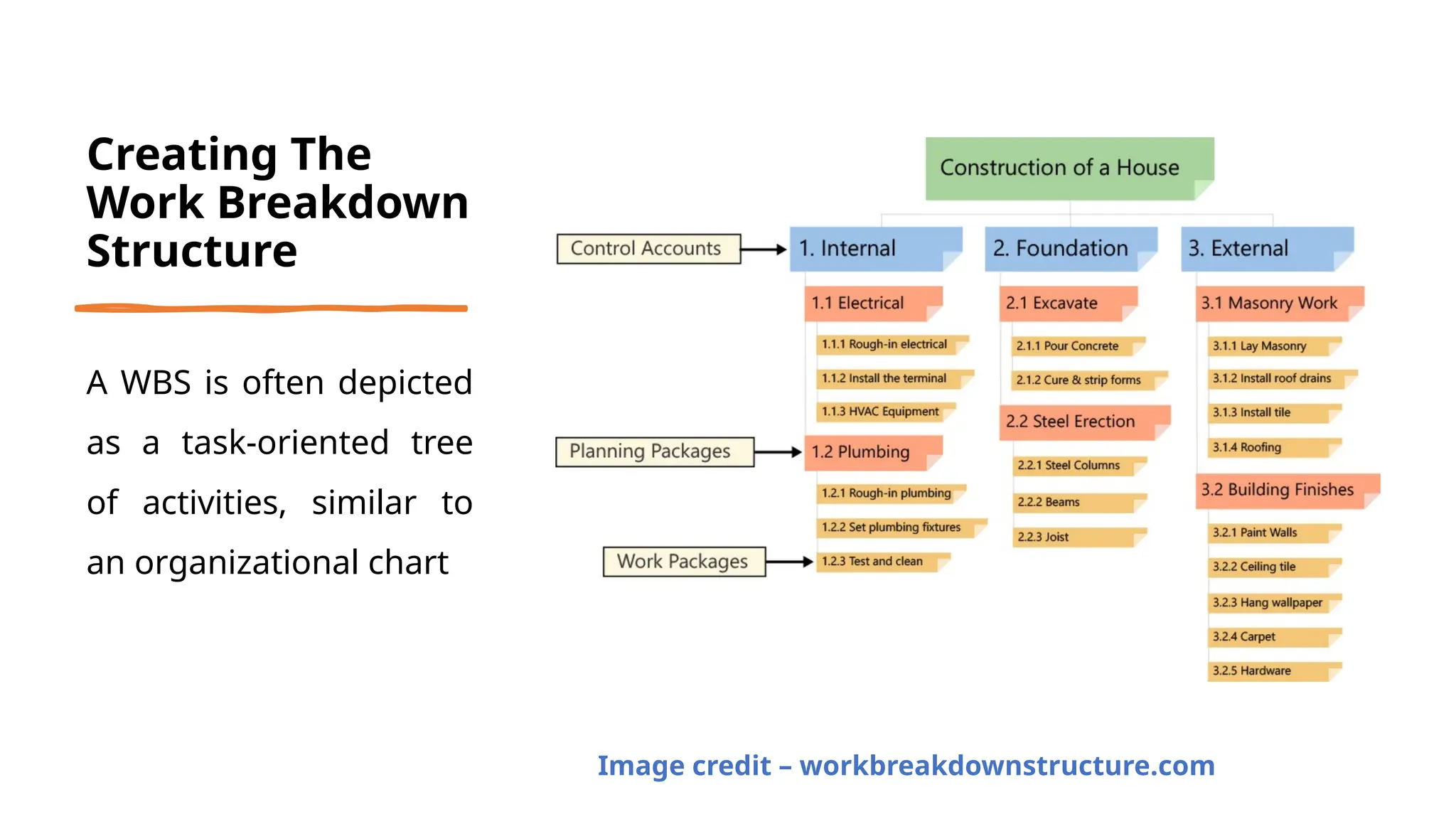
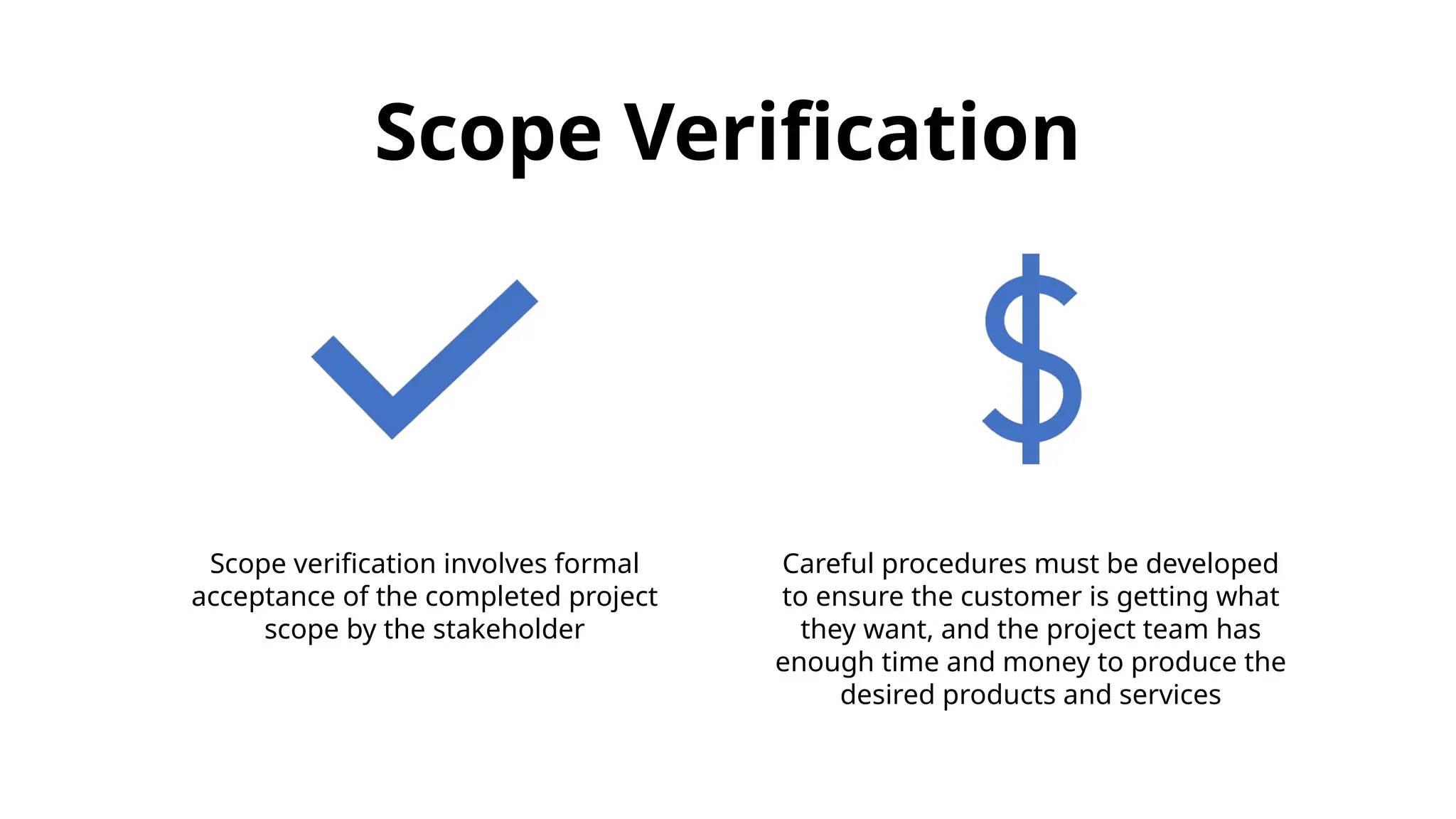
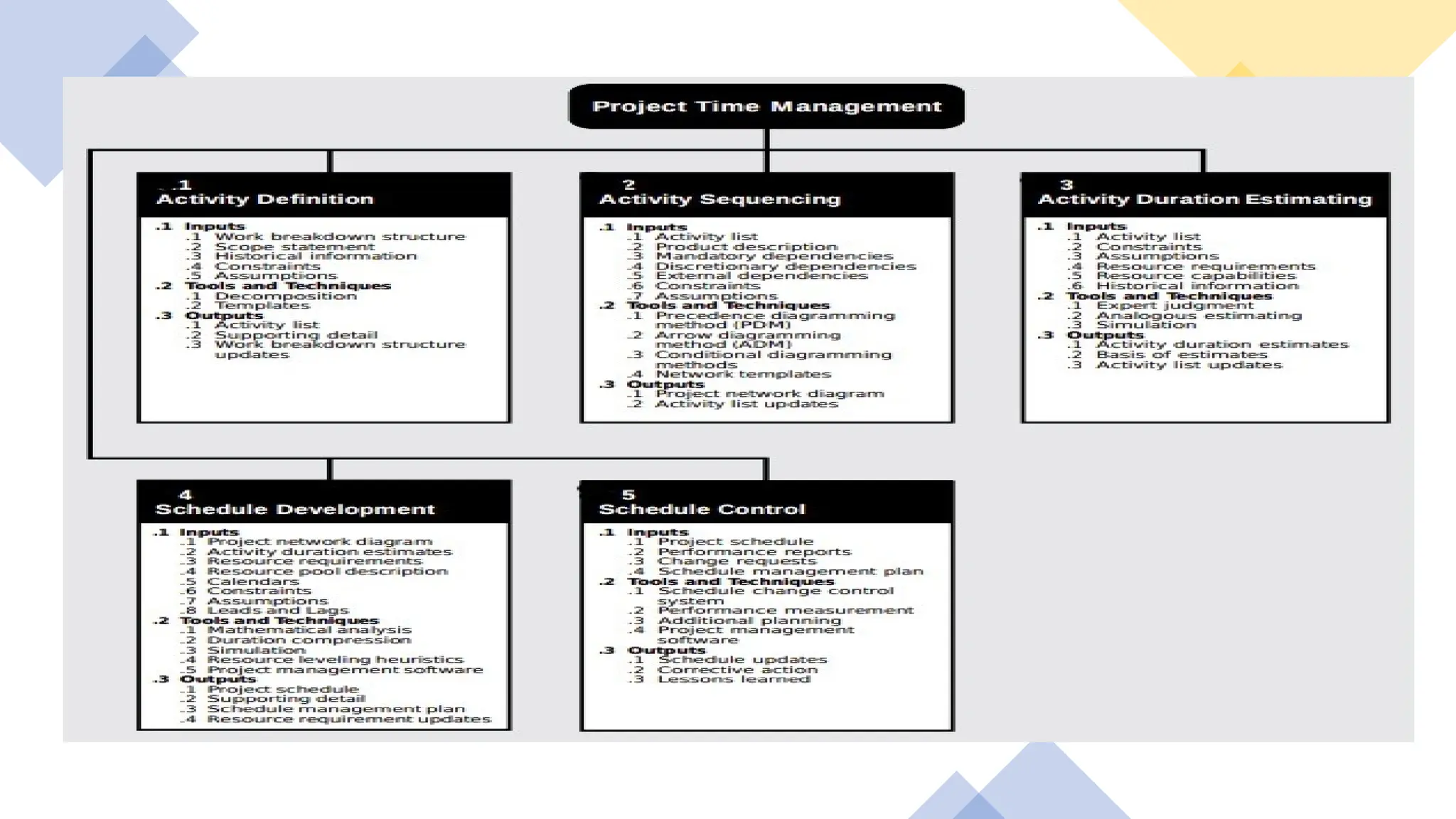
The document outlines the fundamentals of project management, emphasizing its importance in ensuring the successful delivery of projects through effective scope, time, and cost management. It highlights the growing demand for project-related roles and the key attributes and knowledge areas necessary for project managers, alongside comparing projects, programs, and portfolios. Additionally, it discusses the agile project management approach, its principles, and advantages, emphasizing flexibility and continuous improvement.