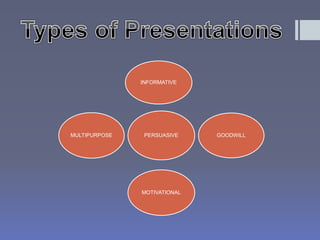
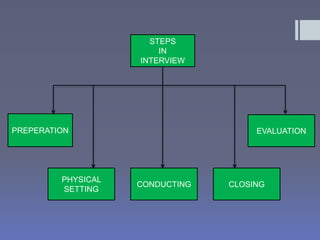
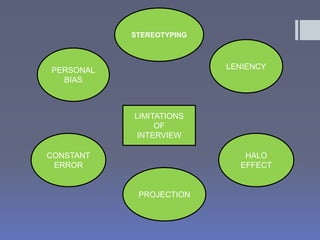
The document discusses various types of presentations including persuasive, goodwill, informative, motivational, and multipurpose presentations. It provides details on each type such as persuasive presentations trying to convince an audience to buy a product or service. The document also discusses important aspects of giving effective presentations such as focusing the presentation, telling compelling stories, giving an entertaining performance, using media to enhance but not distract, and providing a takeaway item. Finally, it touches on causes of boredom like lack of variety and ways to prevent boredom during presentations.