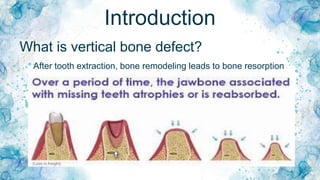
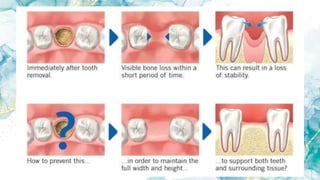
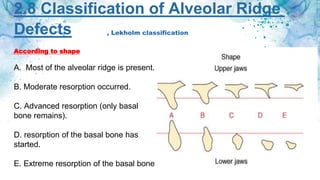
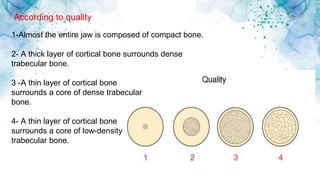
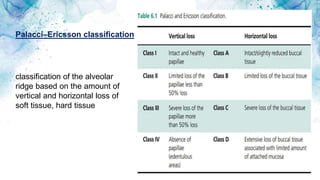
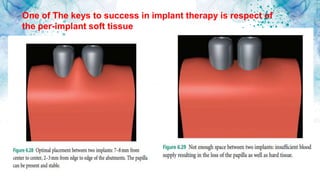
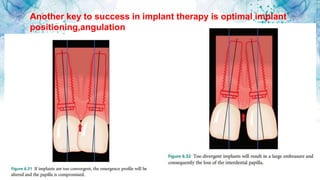
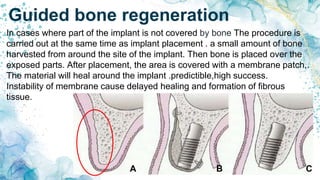
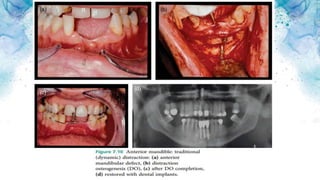
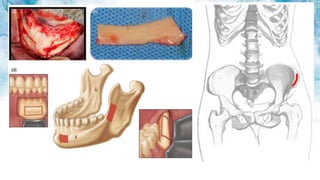
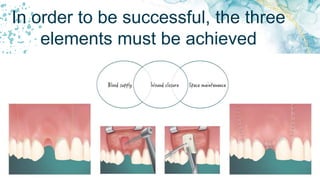
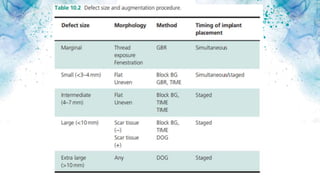
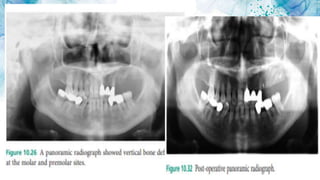
Vertical bone defects occur after tooth extraction as bone remodeling leads to resorption. There are several classifications of alveolar ridge defects based on the amount and location of bone loss. Key factors for implant success include respecting the per-implant soft tissue and optimal implant positioning and angulation. Common techniques for treating vertical bone defects include guided bone regeneration, osteoperiosteal flap ridge-split, distraction osteogenesis, and block grafting. These use bone grafting materials and biomaterials as scaffolds to regenerate bone. Future advances like growth factors, stem cells, and 3D printing may improve outcomes. Sinus lifts can augment the posterior maxilla where resorption has left insufficient bone for dental implants.