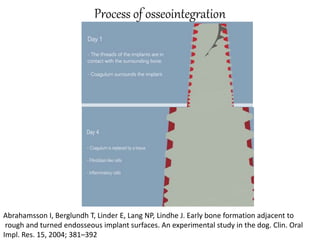
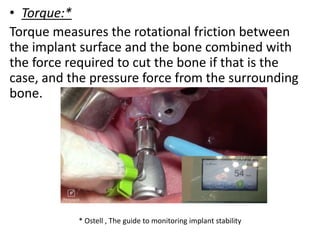
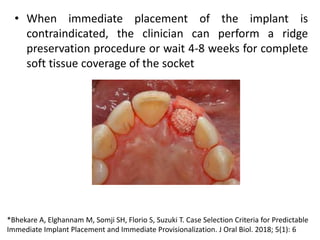
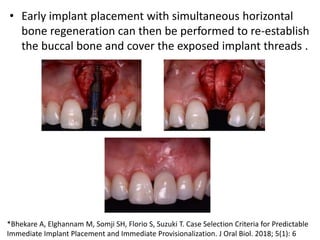
The document discusses various loading protocols for dental implants, including immediate, early, and conventional loading methods, highlighting the importance of primary stability and patient selection for successful outcomes. Several guidelines for immediate loading are provided, including recommendations based on bone quality, implant size, and patient conditions. It also emphasizes the distinctions between implant placement at the time of extraction versus healed sites, stressing the need for careful planning and evaluation of the bone and tissue conditions.