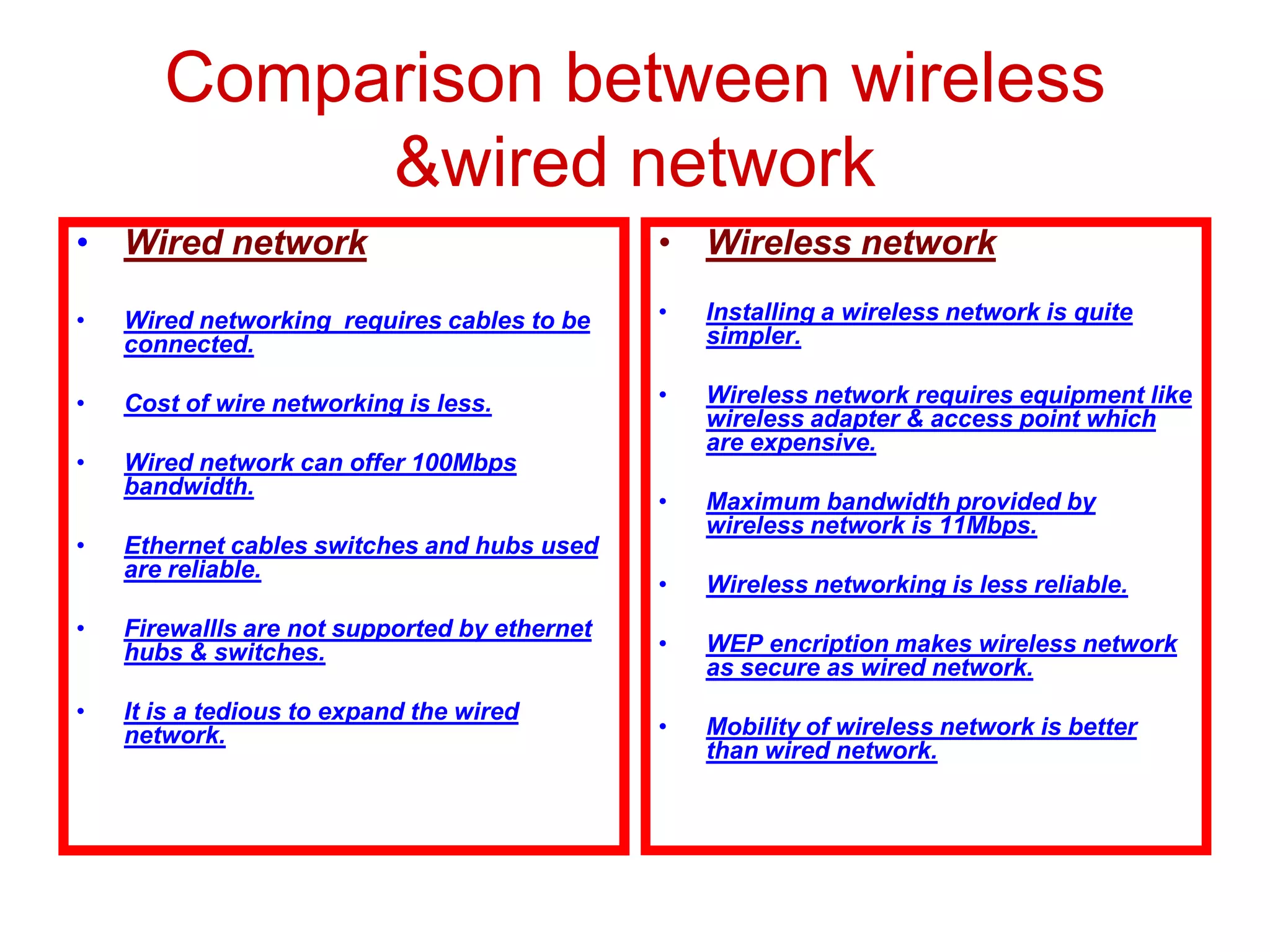
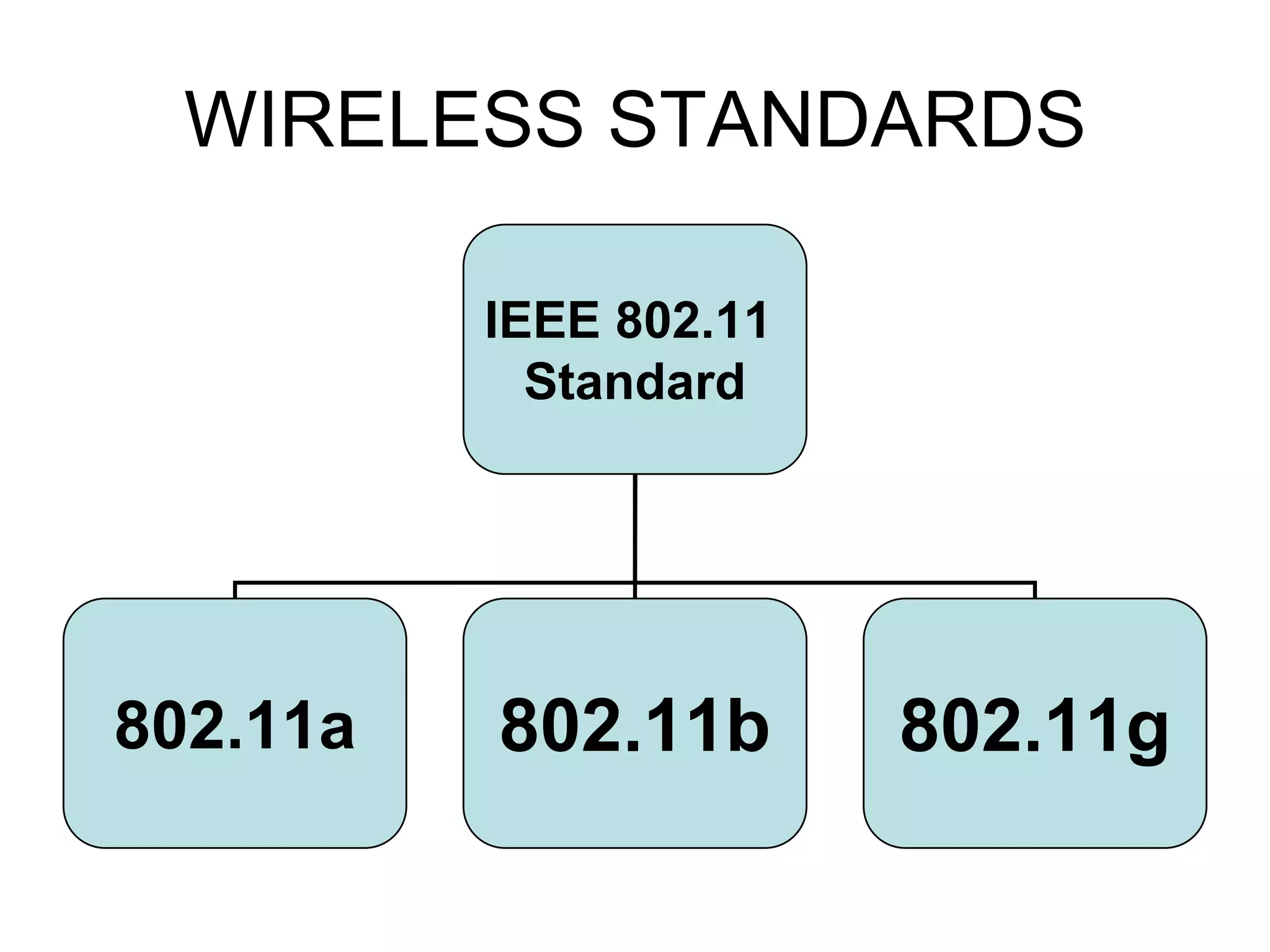
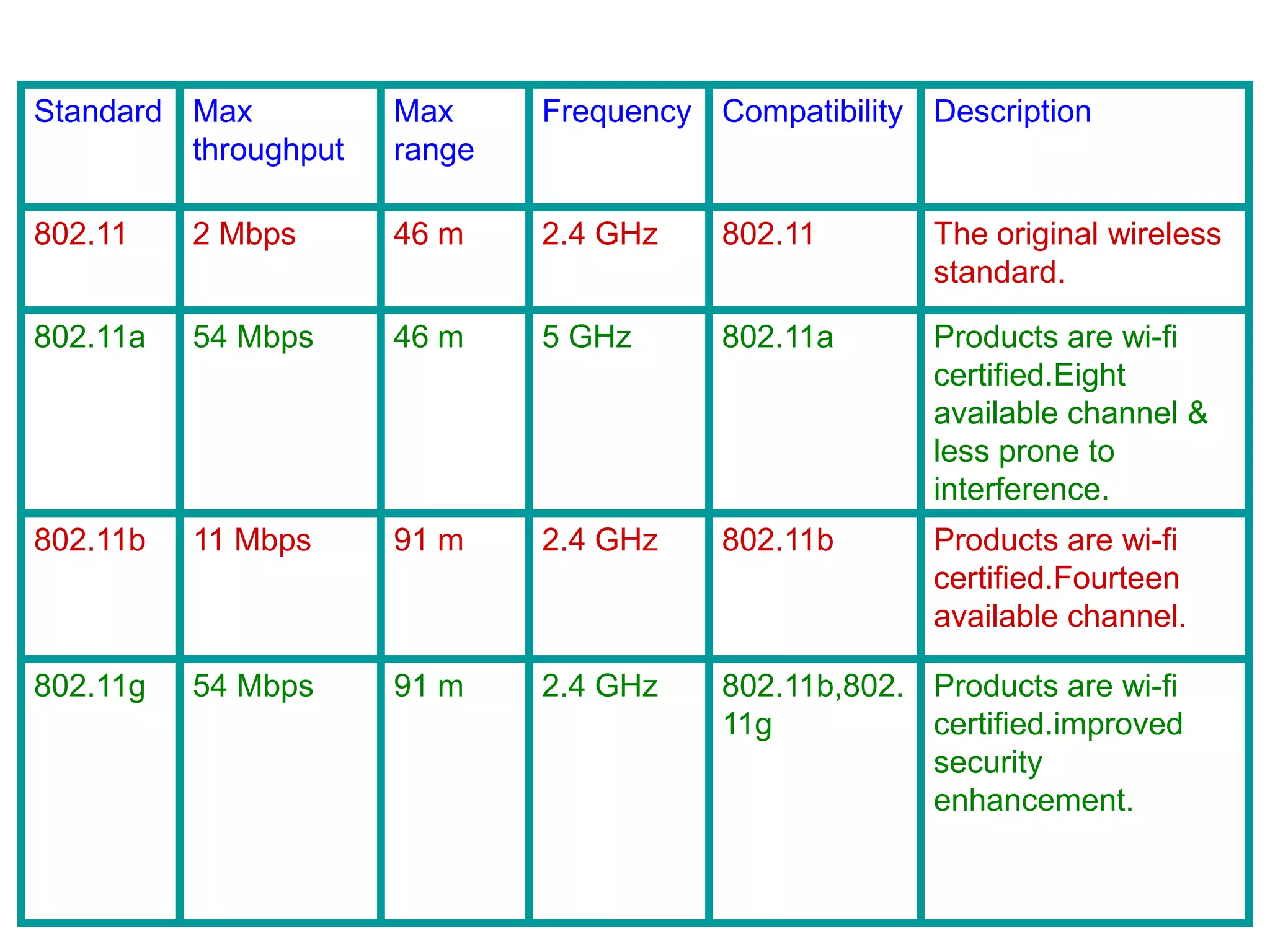
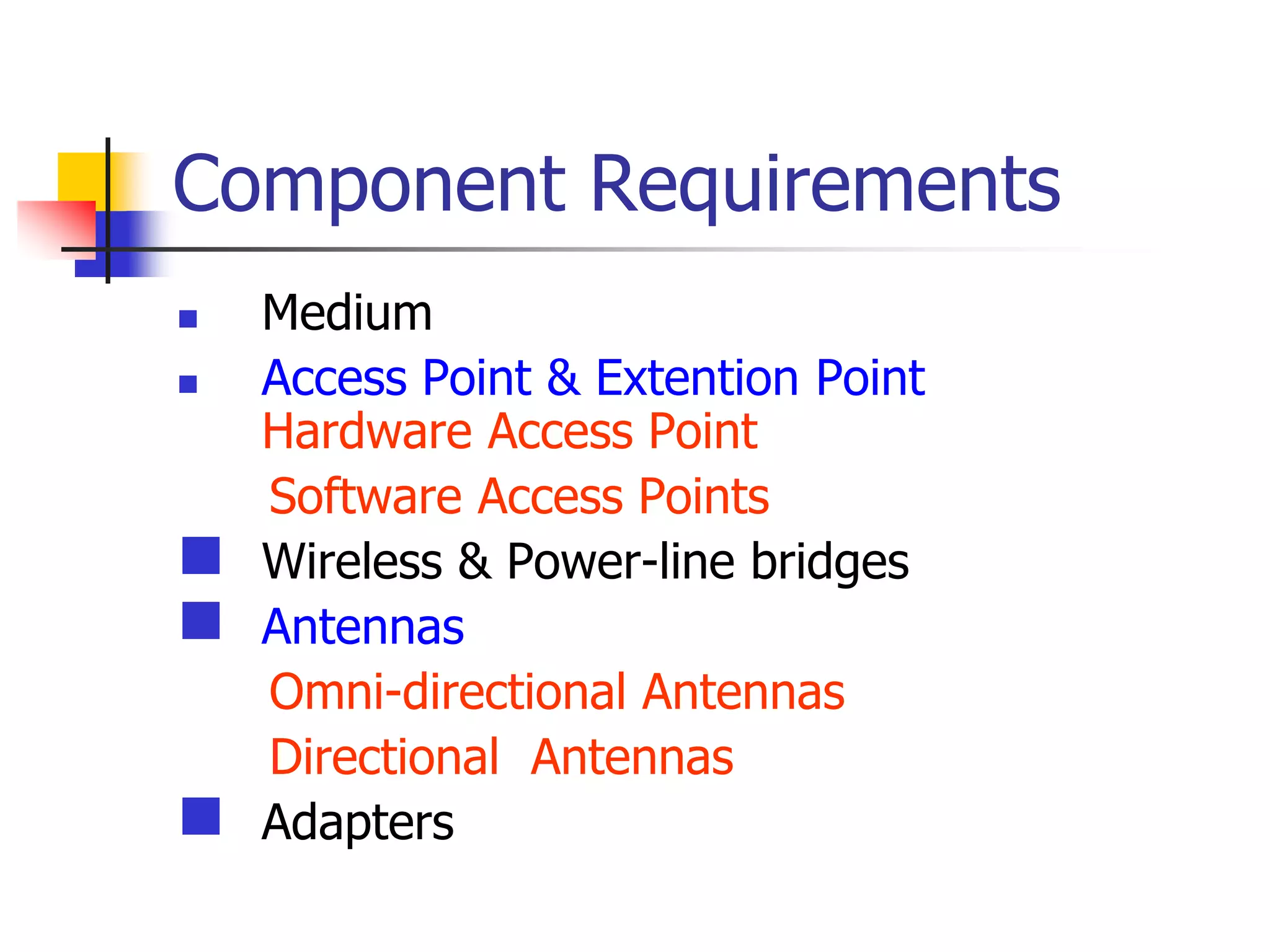
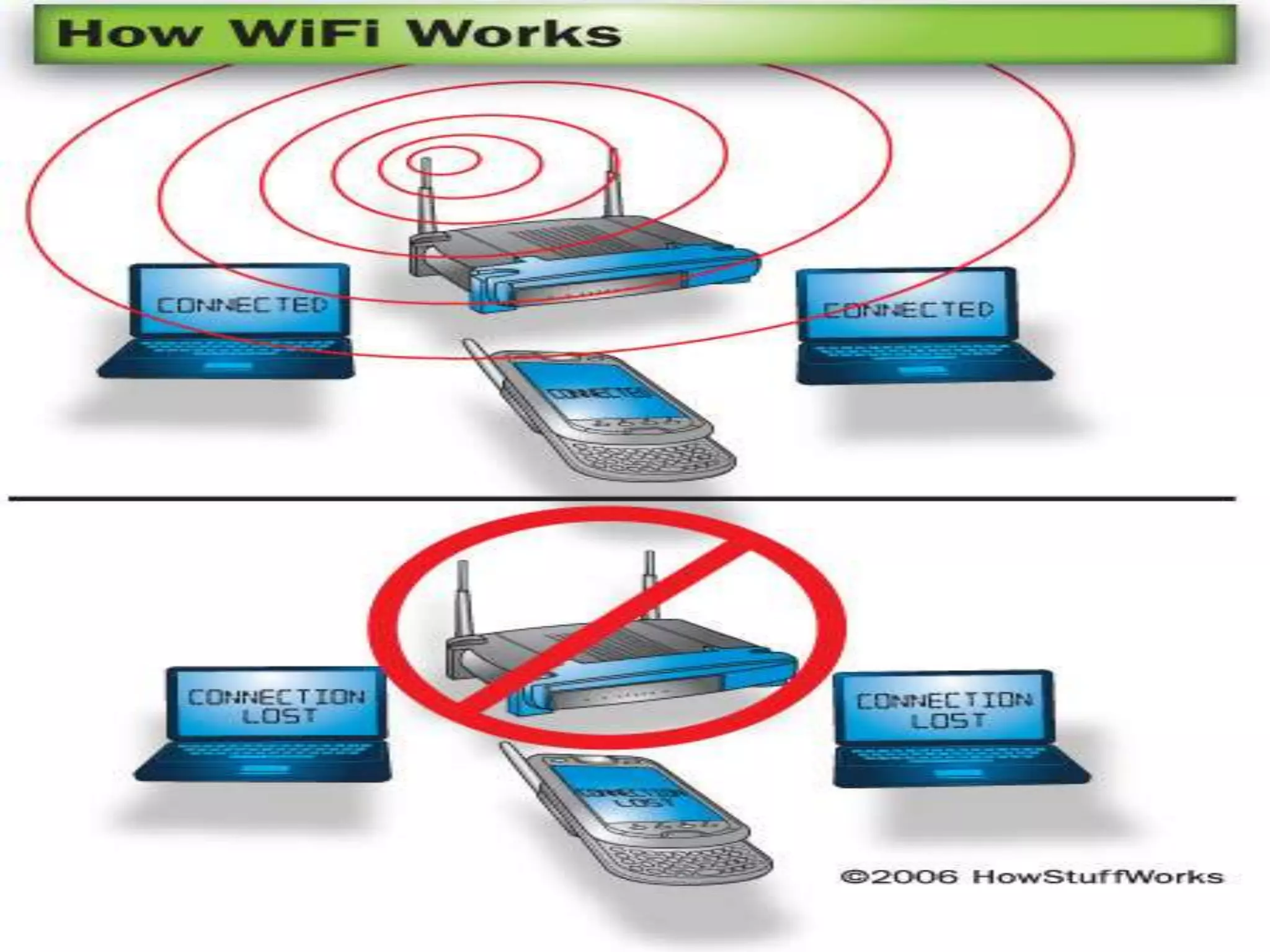
Wi-Fi was invented in 1991 and is based on IEEE 802.11 standards for wireless local area networks. It allows devices to connect to the internet or communicate with each other wirelessly within a particular range. Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit data between devices using antennas. A wireless router receives Wi-Fi signals and decodes them, transmitting the information to the internet via an Ethernet connection. Common Wi-Fi standards include 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g which operate at different speeds and frequencies. Wi-Fi enables wireless internet access on devices like laptops and smartphones within range of an access point or wireless hotspot.