Embed presentation
Downloaded 98 times



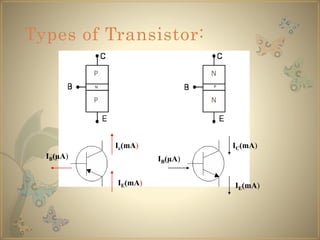
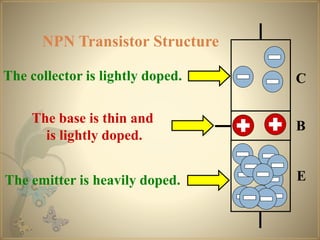
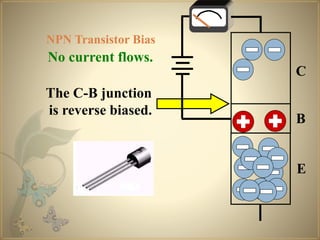
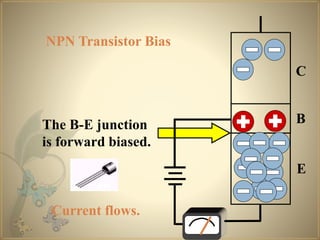
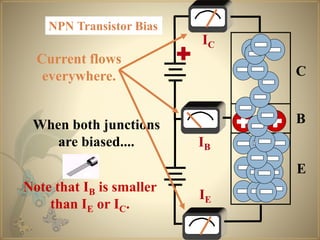
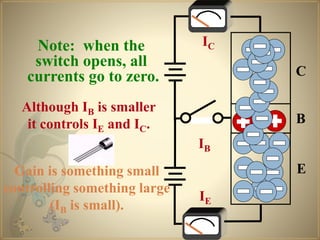
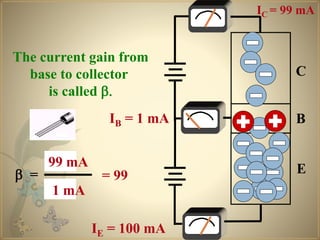
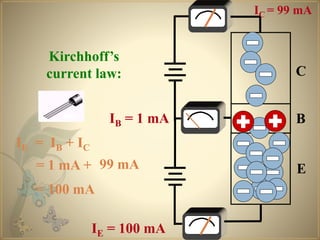
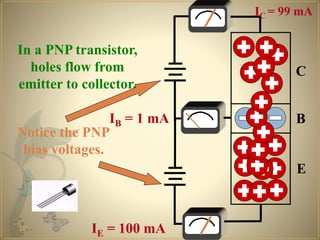

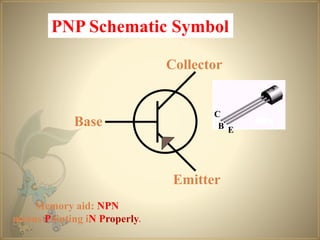

Transistors are semiconductor devices that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. The transistor was invented in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley at Bell Labs. There are two main types of transistors: NPN and PNP. In an NPN transistor, electrons flow from the emitter to the collector, while in a PNP transistor, holes flow from the emitter to the collector. The base terminal controls the flow of current through the collector and emitter.













