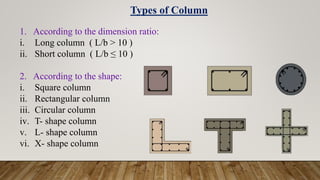
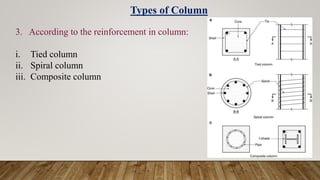
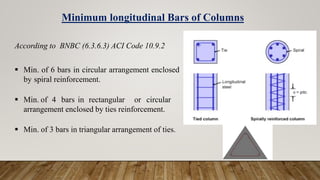
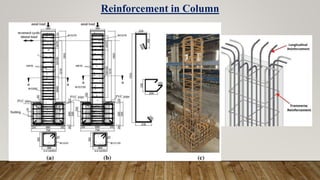
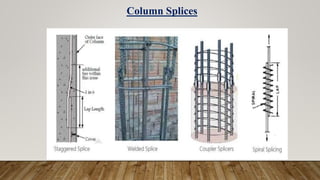
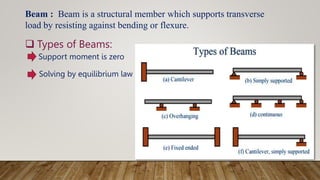
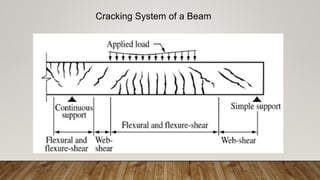
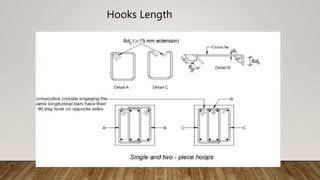
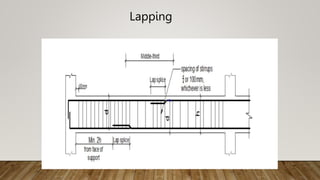
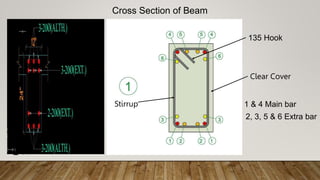
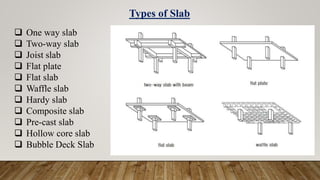
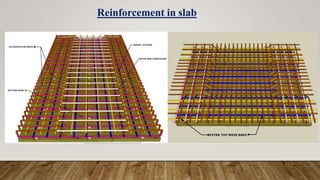
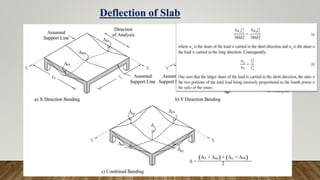
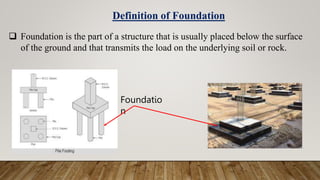
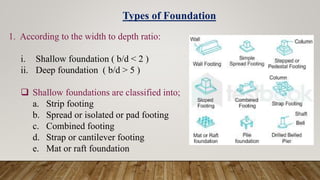
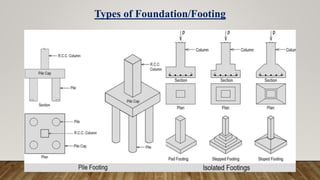
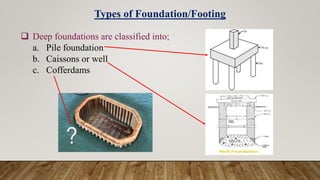
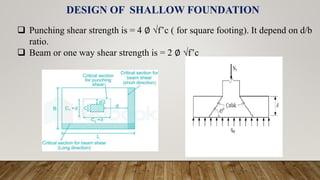
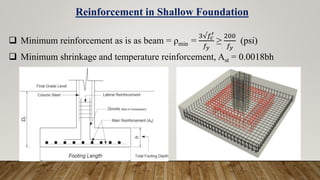
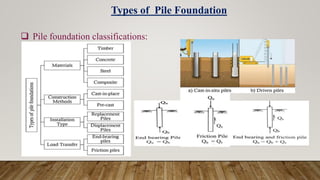
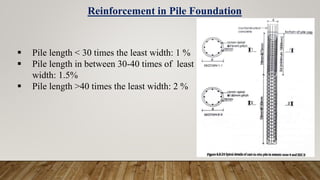
The document is a presentation on building design covering columns, beams, slabs, and foundations, detailing their definitions, types, reinforcement requirements, and design considerations. It emphasizes the structural roles of these elements, outlining specifications for sizing and reinforcement based on different codes. Key aspects include failure modes of columns, types of foundations, and various considerations for ensuring stability and safety in structural design.