This presentation provides an overview of Porifera (sponges). It discusses their classification, features, canal systems, and examples from different classes. The key points are:
- Porifera are multicellular, sessile marine organisms with a diploblastic body plan and canal system for water flow. Their bodies have pores, canals, and choanocyte cells.
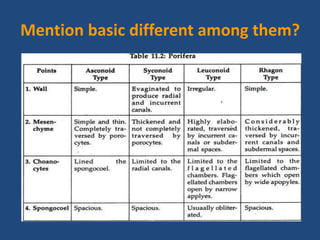
- Phylum Porifera is divided into 3 main classes based on skeleton composition: Calcarea have calcium carbonate spicules; Hexactinellida have silica spicules; and Demospongiae have smaller triaxon and six-rayed spicules.
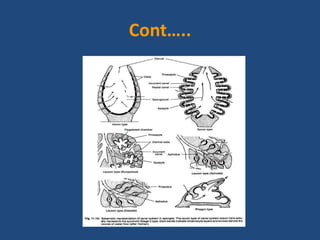
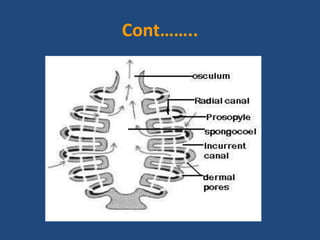
- The syconoid canal system of scypha