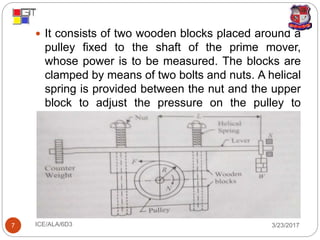
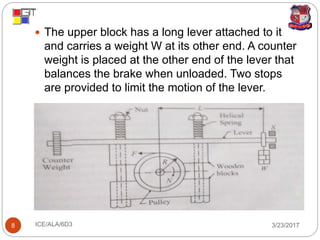
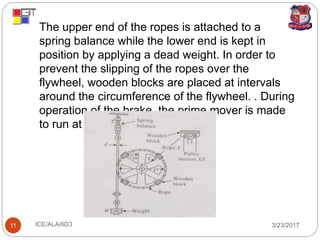
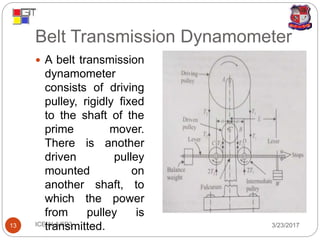
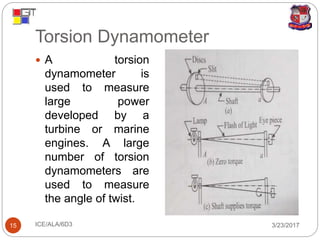
The document discusses different types of dynamometers used to measure the output power of engines. It describes absorption dynamometers like the Prony brake and rope brake dynamometers, which absorb the entire power produced through frictional resistance. It also outlines transmission dynamometers like the belt transmission and torsion dynamometers, which transmit power through the dynamometer to another machine where it can be measured. The Prony brake uses wooden blocks and weights on a lever to apply a braking force, while the rope brake winds rope around a drum connected to the engine.